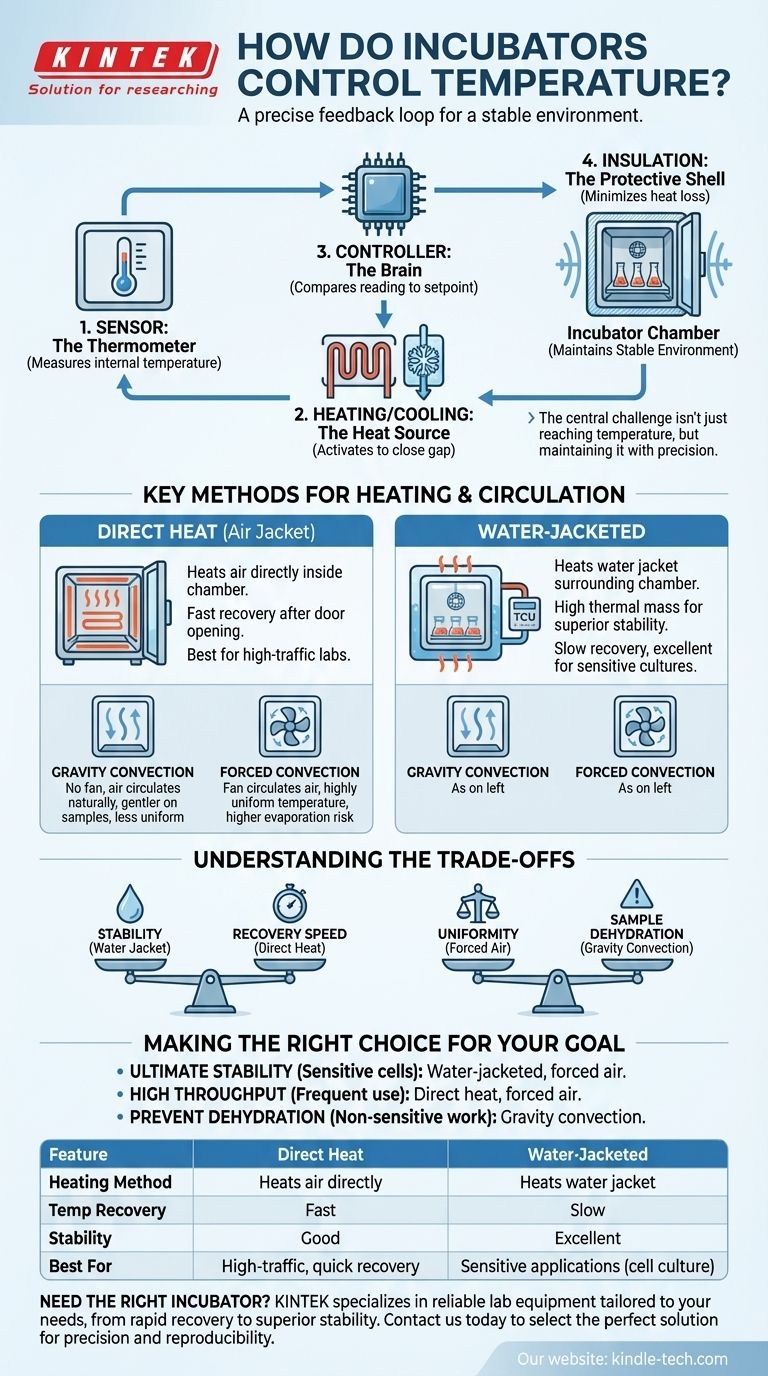
At its core, an incubator controls temperature using a simple but effective feedback loop. A sensor constantly measures the internal temperature, a controller compares this reading to your desired setpoint, and a heating or cooling element is activated or deactivated to close any gap, ensuring a stable environment.
The central challenge in incubation isn't just reaching a temperature, but maintaining it with precision. The method of heating—either through direct air or a water jacket—and the method of air circulation are the key technical choices that dictate an incubator's stability, uniformity, and responsiveness.

The Core Components of Temperature Control
To understand the system, you must first understand its four essential parts. These components work in concert to create a controlled thermal environment.
The Sensor: The Thermometer
The system's "eyes" are a temperature sensor, typically a thermistor or thermocouple, placed inside the chamber. Its sole job is to provide a constant, real-time measurement of the internal temperature.
The Heating Element: The Heat Source
This is the "muscle" of the system. In most modern incubators, this is a resistive heating element or coil that warms the air or a surrounding water jacket when an electric current is passed through it.
The Controller: The Brain
The microprocessor-based controller is the most critical component. It receives the temperature reading from the sensor, compares it to the temperature you have set, and makes the decision to turn the heating element on or off.
The Insulation: The Protective Shell
High-quality insulation in the incubator's walls and door is crucial. It minimizes heat loss to the surrounding room, which reduces the amount of work the heating system has to do and makes the internal temperature far less susceptible to external fluctuations.
Key Methods for Heating and Circulation
While the components are similar, the strategy for delivering and distributing heat defines an incubator's performance. The two primary methods are direct heat and water-jacketed systems.
Direct Heat (Air Jacket) Incubators
In this design, heating elements directly warm the air inside the chamber. To ensure even heating, a fan is often used to circulate the air, a method known as forced convection or mechanical convection.
These systems heat up and recover temperature very quickly after a door opening, making them ideal for labs with high traffic.
Water-Jacketed Incubators
This design, similar to the commercial systems used in extraction, features a separate compartment or "jacket" of water that surrounds the inner chamber. A temperature control unit (TCU) heats this water, which then radiates heat evenly into the incubation chamber.
Because water has a high thermal mass, it holds heat exceptionally well. This provides superior temperature stability and protects samples from short power outages, but it also means the incubator takes much longer to heat up initially and recover from door openings.
Gravity vs. Forced Air Convection
In simpler or older models, there is no fan. These gravity convection incubators rely on the natural principle that hot air rises and cool air sinks to circulate air. This is a gentler process that reduces sample dehydration but can result in less temperature uniformity.
Forced air convection, which uses a fan, creates a highly uniform temperature throughout the chamber but can increase the evaporation and drying of some samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an incubator involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for your specific application.
Temperature Stability vs. Recovery Speed
A water jacket offers unparalleled stability, making it the gold standard for sensitive applications like cell culture. However, its slow recovery after a door opening can be a drawback.
A direct heat system provides excellent recovery speed, which is a major advantage in busy environments, but its internal temperature can be more volatile.
Uniformity vs. Sample Dehydration
Forced air convection provides the best temperature uniformity, ensuring all samples experience the same conditions. The trade-off is a higher rate of evaporation from open plates or media.
Gravity convection is gentler and minimizes drying, but it can create temperature gradients within the chamber, with the top being warmer than the bottom.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is ultimate temperature stability for sensitive cells: A water-jacketed incubator, often with forced air convection, provides the most secure and stable environment.
- If your primary focus is high throughput with frequent door openings: A direct heat, forced-air convection incubator offers the fastest temperature recovery to keep your workflow moving.
- If your primary focus is on preventing sample dehydration and your work is not sensitive to minor temperature variations: A gravity convection incubator is a gentle and effective solution.
Understanding how an incubator achieves its goal empowers you to select the precise tool needed to ensure your work is reliable and repeatable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct Heat (Air Jacket) | Water-Jacketed |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Heats air directly | Heats water jacket surrounding chamber |
| Temperature Recovery | Fast | Slow |
| Stability | Good | Excellent |
| Best For | High-traffic labs, quick recovery | Sensitive applications (e.g., cell culture) |
Need the right incubator for your lab's unique demands? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment tailored to your specific needs—whether you require the rapid recovery of a direct-heat system or the superior stability of a water-jacketed incubator for sensitive cell cultures. Let our experts help you select the perfect solution to ensure precision and reproducibility in your work. Contact us today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the inert gases in a heat treatment furnace? Choose the Right Shield for Your Metal
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2



















