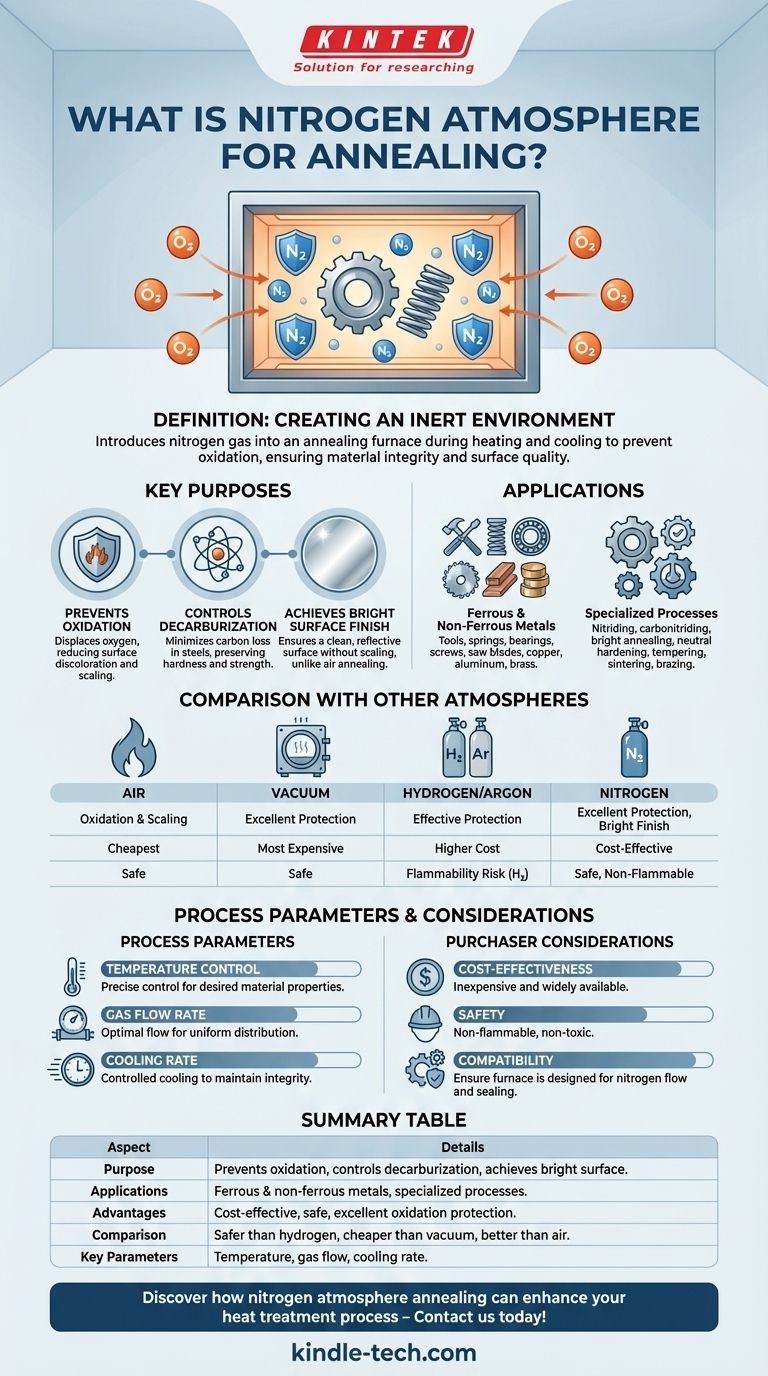
Nitrogen atmosphere for annealing refers to the use of nitrogen gas within an annealing furnace to create an inert environment during the heating and cooling process. This method is primarily employed to prevent oxidation of the material being treated, as oxygen in the air can cause undesirable surface reactions. Nitrogen annealing is particularly beneficial for achieving a bright surface finish, controlling decarburization, and ensuring the material's integrity during heat treatment. It is widely used for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including tools, springs, bearings, and components like screws and saw blades. The process is also applicable in specialized treatments such as nitriding, carbonitriding, and bright annealing.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Nitrogen Atmosphere for Annealing:
- Nitrogen annealing involves introducing nitrogen gas into an annealing furnace to create an inert atmosphere.
- This atmosphere prevents oxidation, which is critical for maintaining the material's surface quality and mechanical properties.
-
Purpose of Nitrogen Atmosphere:
- Preventing Oxidation: Nitrogen is an inert gas that displaces oxygen, reducing the risk of surface oxidation and discoloration.
- Controlling Decarburization: In steel and other carbon-containing materials, nitrogen helps minimize the loss of carbon from the surface, preserving hardness and strength.
- Achieving Bright Surface Finish: Unlike annealing in air, which can lead to scaling and discoloration, nitrogen annealing ensures a clean, bright finish.
-
Applications of Nitrogen Annealing:
- Ferrous Metals: Commonly used for tools, springs, industrial needles, bearings, chainplates, and saw blades.
- Non-Ferrous Metals: Suitable for materials like copper, aluminum, and brass, where oxidation control is critical.
- Specialized Processes: Used in nitriding, carbonitriding, bright annealing, neutral hardening, tempering, sintering, and brazing.
-
Advantages Over Other Atmospheres:
- Compared to air or combustion-based atmospheres, nitrogen provides a cleaner and more controlled environment.
- It is more cost-effective and safer than using hydrogen or argon in some cases, while still offering excellent oxidation protection.
-
Comparison with Other Annealing Atmospheres:
- Vacuum Annealing: Provides excellent oxidation protection but is more expensive and complex.
- Hydrogen/Argon Atmospheres: Effective for specific applications but may pose safety risks (e.g., hydrogen flammability) or higher costs.
- Air Annealing: Cheaper but results in oxidation and scaling, making it unsuitable for applications requiring a bright finish.
-
Considerations for Equipment and Consumable Purchasers:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Nitrogen is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a practical choice for many applications.
- Safety: Nitrogen is non-flammable and non-toxic, reducing safety concerns compared to hydrogen or other reactive gases.
- Compatibility: Ensure the annealing furnace is designed to handle nitrogen atmospheres and has proper gas flow and sealing mechanisms.
-
Process Parameters:
- Temperature Control: The annealing temperature must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired material properties.
- Gas Flow Rate: Optimal nitrogen flow rates ensure uniform atmosphere distribution and effective oxidation prevention.
- Cooling Rate: Controlled cooling in a nitrogen atmosphere helps maintain material integrity and surface finish.
By understanding these key points, equipment and consumable purchasers can make informed decisions about using nitrogen atmospheres for annealing, ensuring optimal results for their specific applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents oxidation, controls decarburization, achieves bright surface finish |
| Applications | Ferrous and non-ferrous metals, specialized processes like nitriding |
| Advantages | Cost-effective, safe, and provides excellent oxidation protection |
| Comparison to Others | More controlled than air, safer than hydrogen, cheaper than vacuum |
| Key Parameters | Temperature control, gas flow rate, cooling rate |
Discover how nitrogen atmosphere annealing can enhance your heat treatment process—contact us today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a controlled atmosphere system? Mastering Air Composition for Industrial & Lab Processes
- Why is atmosphere control essential during the pyrolysis of silicone composites? Ensure High-Density Ceramic Integrity
- What is controlled atmosphere in heat treatment? Master Surface Chemistry for Superior Metal Parts
- What is a controlled atmosphere lab furnace? Master Material Protection and Transformation
- Why is a controlled atmosphere furnace with a quartz tube used for W-SiC thin films? Optimize Phase Transformation
- Why is nitrogen gas used in annealing process? Prevent Oxidation and Achieve Superior Metal Properties
- Why is nitrogen used in heat treatment? For Dual Control: Protection & Surface Hardening
- What is the role of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace in the growth of alpha-Al2O3 and alpha-Fe2O3 oxide films?



















