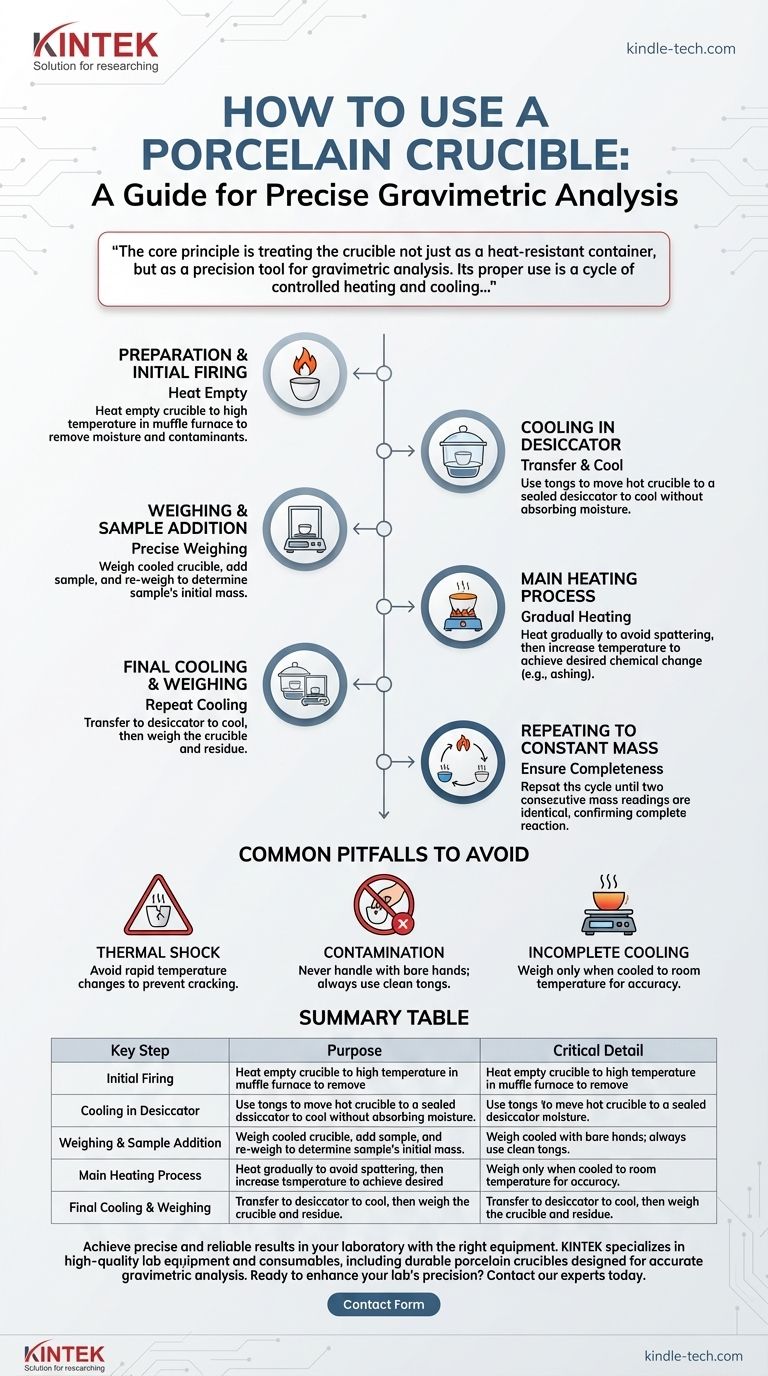
To properly use a porcelain crucible, you must first heat it while empty to a high temperature to remove any moisture and volatile impurities. After cooling it in a desiccator, you weigh it precisely, add your sample, and then heat it strongly to initiate the desired chemical change, such as ashing. The crucible is then cooled again in a desiccator and re-weighed, often repeating the process until a constant mass is achieved.
The core principle is treating the crucible not just as a heat-resistant container, but as a precision tool for gravimetric analysis. Its proper use is a cycle of controlled heating and cooling designed to ensure that any measured change in mass is due solely to the transformation of your sample, not to contaminants or absorbed moisture.
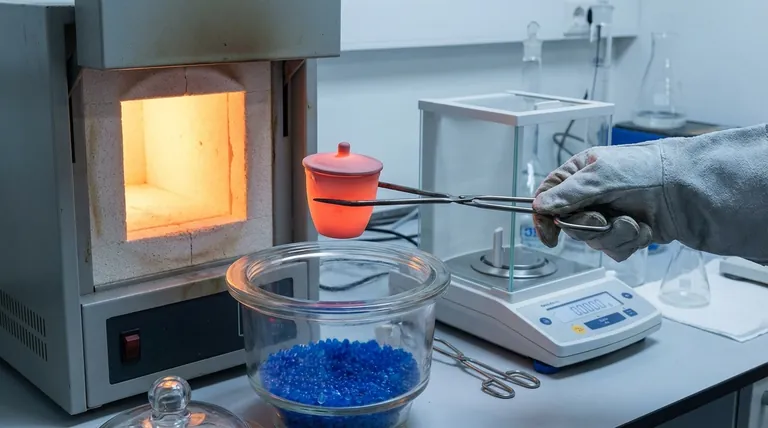

Why a Crucible is More Than a Heating Dish
A crucible's primary function in a laboratory is to hold a substance for heating to a very high temperature. While this seems simple, its most critical application is in gravimetric analysis, where precise mass measurements before and after heating are used to determine a substance's composition.
The Goal: Achieving Constant Mass
The entire procedure is designed to isolate one variable: the mass of the non-volatile residue of your sample.
To do this, you must first ensure the crucible itself has a stable, or constant mass. This is achieved by removing all volatile substances, primarily adsorbed water, which can otherwise cause significant measurement errors.
The Standard Procedure for Accurate Results
Following a strict, methodical process is essential for safety and for obtaining reliable, repeatable data. Each step serves a specific purpose in eliminating potential sources of error.
Step 1: Preparation and Initial Firing
Before introducing your sample, the crucible must be prepared. It should be visually clean, but more importantly, it must be chemically and physically stable at high temperatures.
The first step is to heat the empty crucible with a lid, typically in a muffle furnace, at a temperature equal to or greater than what you will use for your sample. This initial firing burns off any residual oils, dust, or contaminants and drives off any water adsorbed onto the porcelain surface.
Step 2: Cooling in a Desiccator
A hot crucible cannot be weighed accurately, and if left to cool in open air, its porous surface will immediately begin adsorbing moisture, which adds mass.
Therefore, you must use crucible tongs to move the hot crucible from the furnace into a desiccator. This is a sealed container with a desiccant (a drying agent) that provides a dry atmosphere for the crucible to cool to room temperature without gaining mass from atmospheric water vapor.
Step 3: Weighing and Sample Addition
Once the crucible has completely cooled to room temperature inside the desiccator, use tongs to move it to an analytical balance and record its mass precisely.
You can then add your sample to the crucible and weigh it again to determine the initial mass of your sample by subtraction.
Step 4: The Main Heating Process
Place the crucible with the sample back into the muffle furnace or over a Bunsen burner.
It is critical to heat the sample gradually at first. Rapid heating can cause the sample to spatter out of the crucible, resulting in a loss of material and an inaccurate final measurement. Once initial reactions (like smoking or charring) subside, you can increase the heat to the final, high temperature required for the process (e.g., ashing).
Step 5: Final Cooling and Weighing
After the heating period is complete, repeat Step 2. Use tongs to move the crucible back into the desiccator and allow it to cool completely.
Once cool, weigh the crucible and its contents again. This new measurement is your first "final" mass.
Step 6: Repeating to Constant Mass
A single heating is rarely sufficient to guarantee a complete reaction. Professional lab work requires heating to constant mass.
This involves repeating the cycle of heating (Step 4), cooling (Step 5), and weighing until two consecutive mass readings are identical within the accepted tolerance of the experiment. This confirms that the reaction is complete and all volatile materials have been removed.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the potential mistakes is as important as knowing the correct procedure. These errors can compromise safety and ruin your results.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
Porcelain is extremely resistant to high temperatures but is vulnerable to thermal shock. Heating or cooling it too quickly can cause it to crack or shatter. Never place a hot crucible on a cold lab bench, and always heat samples gradually.
Contamination from Handling
Never handle a crucible with your bare hands after its initial firing. The oils and moisture from your skin will transfer to the surface, adding measurable mass and contaminating your experiment. Always use clean crucible tongs.
Incomplete Cooling
Weighing a crucible that is still warm will produce an inaccurate reading. The heat creates convection currents in the air around the balance pan, making the crucible appear lighter than it actually is. It must cool completely to room temperature inside the desiccator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of rigor you apply depends entirely on the purpose of your work.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy for quantitative analysis: You must follow every step, especially firing the empty crucible and repeating the heat-cool-weigh cycle until you achieve a constant mass.
- If your primary focus is simple melting or qualitative observation: The full constant mass procedure may be unnecessary, but proper handling with tongs and avoiding thermal shock remain critical for your safety and the longevity of the equipment.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a crucible is about discipline and understanding that every step is designed to protect the integrity of your results.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Purpose | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Firing | Remove moisture and contaminants | Heat empty crucible to high temperature |
| Cooling in Desiccator | Prevent moisture absorption | Use tongs to transfer to a sealed container with desiccant |
| Weighing & Sample Addition | Measure precise initial mass | Cool to room temperature before weighing on analytical balance |
| Main Heating Process | Initiate chemical change (e.g., ashing) | Heat gradually to avoid spattering, then increase temperature |
| Final Cooling & Weighing | Obtain final mass measurement | Repeat cooling in desiccator and weighing until constant mass is achieved |
Achieve precise and reliable results in your laboratory with the right equipment.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable porcelain crucibles designed for accurate gravimetric analysis. Our products help you eliminate errors from contamination and moisture, ensuring your experiments are both safe and reproducible.
Ready to enhance your lab's precision? Contact our experts today to find the perfect crucibles and accessories for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C



















