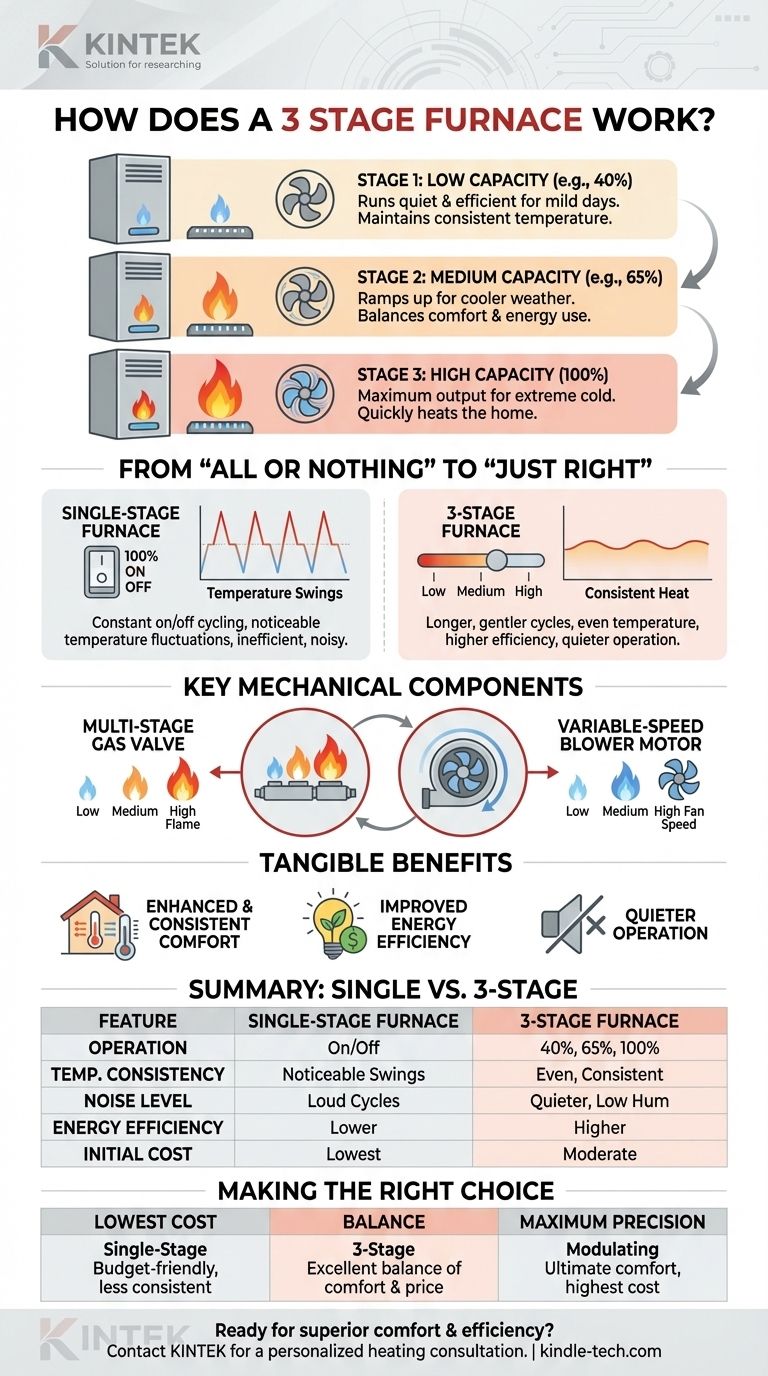
A 3-stage furnace operates at three distinct output levels to more accurately match your home's real-time heating needs. Unlike a basic furnace that can only run at 100% power, a 3-stage unit can also run at lower-capacity settings, such as 40% and 65%. This allows it to maintain a consistent temperature with greater efficiency and less noise.
A 3-stage furnace acts as a strategic middle ground between basic two-stage models and premium modulating systems. Its primary advantage is providing superior comfort and efficiency by running for longer periods at lower, quieter power levels, rather than constantly cycling on and off at full blast.

From "All or Nothing" to "Just Right"
To understand the value of a 3-stage system, you must first understand the limitations of a standard, single-stage furnace.
The Problem with Single-Stage Furnaces
A single-stage furnace operates like a light switch: it is either completely ON (100% capacity) or completely OFF.
This "all or nothing" approach creates noticeable temperature swings in your home. It runs at full power until the thermostat is satisfied, then shuts off, allowing the temperature to drop until it must blast on again. This constant starting and stopping, known as short cycling, is inefficient and noisy.
How a 3-Stage Furnace Solves This
A 3-stage furnace spends most of its time running on its lowest setting (e.g., 40% capacity). This low-and-slow approach is often all that's needed to maintain the desired temperature on mild to cool days.
Only when the outdoor temperature drops significantly will the furnace automatically ramp up to its second (e.g., 65%) or third (100%) stage to meet the increased demand for heat.
The Key Mechanical Components
This variable output is achieved through two main components working in tandem:
- A multi-stage gas valve that controls the flow of fuel, allowing for low, medium, or high flames.
- A variable-speed blower motor that adjusts the fan speed to precisely match the heat being produced, ensuring optimal air circulation for each stage.
The Tangible Benefits for Your Home
The ability to adjust heating output translates directly into a more comfortable and efficient home environment.
Enhanced and Consistent Comfort
Because the furnace runs for longer, gentler cycles, it circulates air more continuously. This eliminates the hot and cold spots common with single-stage systems, resulting in a far more even temperature from room to room.
Improved Energy Efficiency
A furnace is least efficient during startup. By avoiding the constant on-off cycle of a single-stage unit, a 3-stage furnace runs more efficiently, consuming less fuel over the course of a heating season.
Quieter Operation
Running at 40% capacity is significantly quieter than running at 100%. For most of the winter, the furnace will operate at a low, almost unnoticeable hum, eliminating the disruptive roar of a standard furnace kicking on.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While offering significant benefits, a 3-stage furnace is not the right choice for every situation. Objectivity requires weighing the pros and cons.
Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term Savings
A 3-stage furnace has a higher initial purchase price than a single or two-stage model. This cost must be balanced against the potential for long-term energy savings and the non-monetary value of increased home comfort.
Complexity and Maintenance
The system's advanced components, like the variable-speed motor and multi-stage gas valve, are more complex than their single-stage counterparts. While reliable, potential repairs can be more specialized and costly.
vs. Two-Stage and Modulating Furnaces
A 3-stage furnace offers a finer degree of control than a two-stage (low/high) model. However, it is not as precise as a fully modulating furnace, which can adjust its output in tiny 1% increments. A modulating furnace offers the ultimate in comfort and efficiency but comes at the highest price point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal furnace depends on balancing your desire for comfort with your budget and local climate.
- If your primary focus is the lowest initial cost: A single-stage furnace is the most budget-friendly option, but you must accept less consistent temperatures and higher operating noise.
- If your primary focus is a significant upgrade in comfort and efficiency: A 3-stage furnace provides an excellent balance of performance and price, delivering a noticeable improvement over basic models.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and maximum efficiency: A fully modulating furnace is the top-tier choice, offering the most stable heat and lowest operating costs at the highest initial investment.
Understanding these distinct performance tiers empowers you to select the system that truly matches your home's heating needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Stage Furnace | 3-Stage Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | On (100%) or Off | 40%, 65%, or 100% Capacity |
| Temperature Consistency | Noticeable swings | More even, consistent heat |
| Noise Level | Loud on/off cycles | Quieter, low hum operation |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (frequent startups) | Higher (longer, gentler cycles) |
| Initial Cost | Lowest | Moderate |
Ready to eliminate temperature swings and reduce your heating bills?
A 3-stage furnace from KINTEK provides the perfect balance of superior comfort, quiet operation, and energy efficiency for your home. Our experts specialize in helping homeowners select the ideal heating solution to match their specific needs and climate.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how a 3-stage furnace can transform your home's comfort.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What is the temperature resistance of a ceramic tube? It Depends on the Material—Find the Right Fit
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- How does a multi-heating zone horizontal tube furnace benefit alloy testing? Maximize Thermal Uniformity and Throughput
- What is a three zone furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Uniformity



















