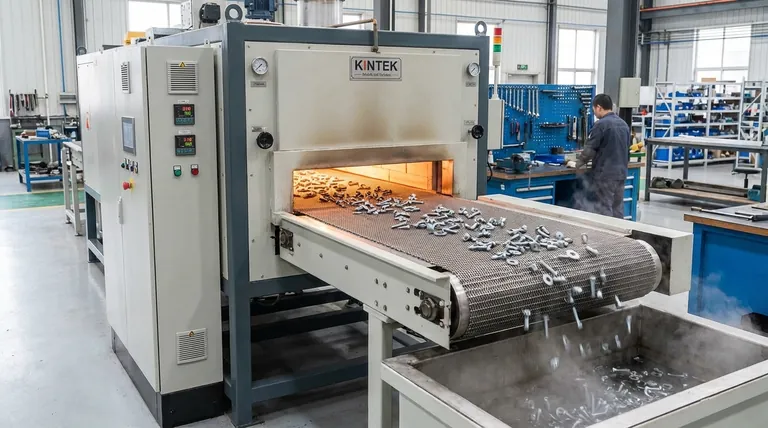
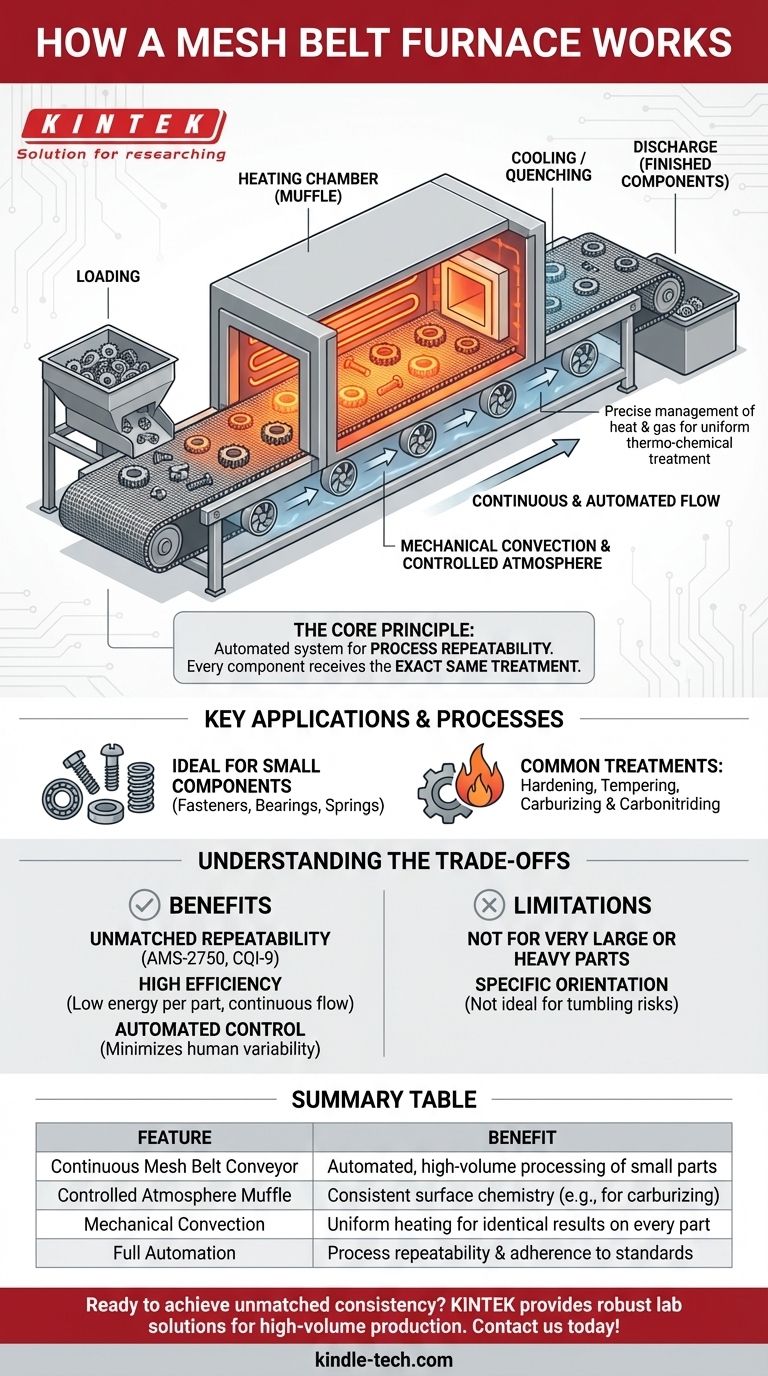
At its core, a mesh belt furnace operates like a highly controlled industrial oven with a conveyor belt. Workpieces are loaded onto a continuously moving metal mesh belt, which transports them through a heated chamber with a precisely managed atmosphere. This allows for consistent and automated heat treatment of large quantities of small parts.
The crucial insight is that a mesh belt furnace isn't just a heating device; it's an automated system designed for process repeatability. Its purpose is to ensure that every single component, from the first to the ten-thousandth, receives the exact same thermal treatment.

The Core Principle: Continuous and Uniform Processing
A mesh belt furnace achieves its consistency by breaking the process down into a seamless, automated flow. Each stage is optimized for uniformity.
The Conveyor System
The heart of the furnace is the mesh belt itself. This conveyor system, made of heat-resistant metal alloys, is what enables the continuous processing of parts. Parts are loaded at one end, travel through the furnace, and are discharged at the other.
The Heating Chamber (Muffle)
The belt travels through an enclosed chamber, often called a muffle. This muffle is supported by special ceramic elements to withstand the extreme temperatures and ensure a long service life.
Heat is generated by electric heating elements or gas burners positioned around the muffle, ensuring the chamber reaches and maintains the target temperature.
Controlled Atmosphere and Convection
For processes like carburizing or carbonitriding, the atmosphere inside the muffle is critical. The furnace is filled with a specific gas mixture to achieve the desired chemical reaction on the surface of the parts.
Highly efficient distribution of this atmosphere is achieved through mechanical convection, using internal fans and baffles to circulate the hot gas evenly. This ensures every surface of every part is exposed to the same conditions, preventing inconsistencies.
Fully Automated Control
The entire technological line is typically automated. A central control system monitors and manages belt speed, temperature zones, and atmosphere composition.
Service personnel are only responsible for loading parts onto the belt and collecting the finished components. This automation removes human variability and is the key to achieving identical, repeatable results.
Key Applications and Processes
Mesh belt furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They are specifically engineered for treating large volumes of relatively small parts where uniformity is essential.
Ideal for Small Components
This technology is the industry standard for treating parts like fasteners, bearings, springs, and other small stamped or machined elements. The belt allows for bulk loading and even processing that would be impractical in a batch furnace.
Common Heat Treatments
Mesh belt furnaces are used for a variety of thermo-chemical treatments, including:
- Hardening: Heating and rapidly cooling steel to increase its hardness and strength.
- Tempering: A secondary, lower-temperature treatment to reduce the brittleness that can result from hardening.
- Carburizing & Carbonitriding: Introducing carbon (and nitrogen) into the surface of a part to create a hard, wear-resistant outer case while maintaining a softer core.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a mesh belt furnace comes with inherent advantages and limitations.
The Benefit of Consistency
The primary advantage is unmatched repeatability. The combination of a synchronized belt, precise atmosphere control, and automated systems ensures homogeneous results across massive production runs, often adhering to strict standards like AMS-2750 and CQI-9.
The Benefit of Efficiency
These furnaces are designed for high-volume production, resulting in low energy consumption per part. The continuous flow minimizes heat loss from opening and closing doors, and efficient quenching systems further reduce the risk of part deformation.
The Limitation: Component Size and Weight
The defining trade-off is component size. Mesh belt furnaces are not suitable for very large or heavy parts. The belt has weight and size limits, and the bulk-processing nature is not ideal for components that require specific orientation or could be damaged by tumbling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on the parts you are processing and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, uniform parts: A mesh belt furnace offers the best combination of efficiency, automation, and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is treating large, heavy components or parts in specific fixtures: A batch furnace or a continuous pusher furnace, which moves parts on trays, is a more appropriate solution.
- If your primary focus is process development or treating small, unique batches: A laboratory or tube furnace provides the flexibility and precise control needed for research and development.
Ultimately, a mesh belt furnace excels by transforming heat treatment from a manual, batch-by-batch task into a seamless and highly reliable industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Mesh Belt Conveyor | Enables automated, high-volume processing of small parts |
| Controlled Atmosphere Muffle | Ensures consistent surface chemistry (e.g., for carburizing) |
| Mechanical Convection | Provides uniform heating for identical results on every part |
| Full Automation | Guarantees process repeatability and adherence to standards like AMS-2750 |
Ready to achieve unmatched consistency in your heat treatment process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions for high-volume production needs. Our expertise ensures your laboratory benefits from efficient, automated systems designed for reliability and repeatability.
Contact us today to discuss how a mesh belt furnace can optimize your production line!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















