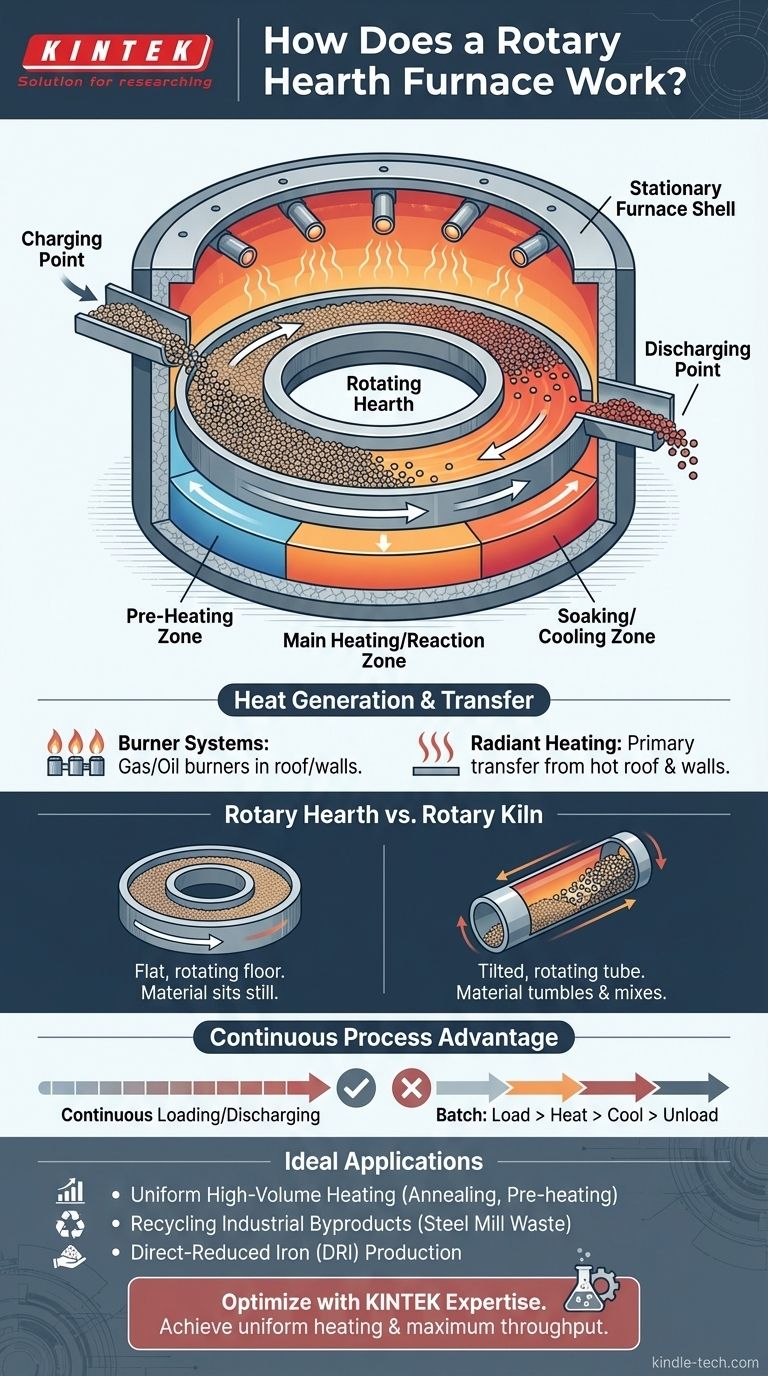
In essence, a rotary hearth furnace works by moving materials on a large, rotating circular floor (the hearth) through different, stationary heating zones contained within a fixed furnace shell. Material is loaded at one point, undergoes a precise thermal treatment as it travels in a circle, and is removed after completing nearly a full rotation.
The central principle of a rotary hearth furnace is not the rotation of the entire furnace, but the slow, continuous movement of the material-carrying hearth through fixed, specialized temperature zones. This allows for highly uniform, continuous, and controlled heat treatment.

The Core Components and Process Flow
A rotary hearth furnace is a sophisticated system for continuous thermal processing. Its design is based on moving the product through the heat, rather than heating and cooling the entire furnace chamber for each batch.
The Rotating Hearth
The "hearth" is the floor of the furnace. It is a large, donut-shaped or circular steel table lined with refractory materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures. This entire structure rotates slowly around a central axis.
The Stationary Furnace Shell
Enclosing the hearth is a fixed, insulated shell, also lined with refractory. This shell contains the heat, the atmosphere, and the heating systems. It has dedicated openings for loading raw material onto the hearth and for discharging the finished product.
Distinct Temperature Zones
The stationary shell is divided into several distinct zones, each with its own temperature controls. As the hearth rotates, it carries the material sequentially through these zones—for example, a pre-heating zone, a main heating or reaction zone, and a soaking or cooling zone.
Charging and Discharging
Material is continuously fed onto the hearth at a specific charging point. After traveling through the various zones for a set period (typically one full rotation, which can take anywhere from minutes to hours), the processed material is removed by a discharge mechanism, often located right next to the charging point.
How Heat is Generated and Transferred
The effectiveness of the furnace depends on precise and efficient heat application. This is managed through carefully placed heating systems within the stationary shell.
Burner Systems
Heat is most commonly generated by a series of gas or oil burners. These are strategically mounted in the roof and walls of the stationary shell, firing into the different temperature zones to maintain their specific setpoints.
Radiant Heating
The primary method of heat transfer is radiation. Heat radiates from the hot furnace roof, walls, and the combustion gases directly onto the surface of the material sitting on the hearth below. The slow rotation ensures every part of the load receives an equal amount of energy for exceptionally uniform heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
While highly effective, it's critical to distinguish the rotary hearth furnace from other designs that use the term "rotary." The provided references cause common confusion on this point.
Misconception: Rotary Hearth vs. Rotary Kiln
A rotary hearth furnace has a flat, rotating floor where material sits relatively still. In contrast, a rotary kiln (or rotary drum furnace) is a long, rotating tube or barrel that is tilted. Material tumbles and mixes as it travels from the high end to the low end, which is a fundamentally different process.
Advantage: Continuous vs. Batch Processing
Traditional "batch" furnaces require loading the entire chamber, heating it up, letting it soak, and cooling it down before unloading. A rotary hearth furnace operates continuously, with material constantly being loaded and discharged, which dramatically increases throughput and energy efficiency for high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The rotary hearth furnace is a specialized tool designed for specific industrial processes where uniformity and high throughput are paramount.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, uniform heating: The design's ability to move a continuous stream of product through fixed temperature zones is ideal for consistent heat treatment, annealing, or pre-heating.
- If your primary focus is recycling industrial byproducts: This technology excels at processing steel mill waste, such as dusts and sludges, to recover valuable iron units in a process known as direct reduction.
- If your primary focus is producing direct-reduced iron (DRI): The furnace provides the controlled atmosphere and temperature profile needed to convert iron ore pellets into metallic iron without melting them.
Ultimately, the rotary hearth furnace provides an elegant and efficient solution for continuous, high-temperature material processing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Rotating Hearth | Circular, refractory-lined floor that carries material in a continuous loop. |
| Stationary Furnace Shell | Fixed, insulated enclosure containing the heat, atmosphere, and heating systems. |
| Distinct Temperature Zones | Separate areas (e.g., pre-heat, heat, soak/cool) within the shell for precise thermal control. |
| Charging/Discharging | Mechanisms for continuous loading of raw material and unloading of finished product. |
| Burner Systems | Gas or oil burners mounted in the shell to generate heat in each zone via radiation. |
Optimize your high-volume thermal processing with KINTEK's expertise.
A rotary hearth furnace is the ideal solution for achieving uniform heating and maximum throughput in applications like annealing, pre-heating, or direct reduction. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables to meet the demanding needs of industrial and research laboratories.
Our team can help you determine if this continuous processing technology is right for your goals, ensuring energy efficiency and consistent product quality.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main difference between gasification and pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Biomass Conversion Process
- What are the benefits of a plastic pyrolysis plant? Turn Waste Plastic into Valuable Resources
- What are the uses of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy, Fuel, and More
- What is fast pyrolysis an overview? A Rapid Process for Converting Biomass to Bio-Oil
- What is the temperature and time for slow pyrolysis? Optimize Your Biochar Production Process
- What is the process of pyrolysis example? Transform Waste into Value with Thermal Decomposition
- What is the optimum temperature for pyrolysis? Target Your Desired Biochar, Bio-oil, or Syngas
- Is pyrolysis of plastic safe? Understanding the Critical Risks and Engineering Controls



















