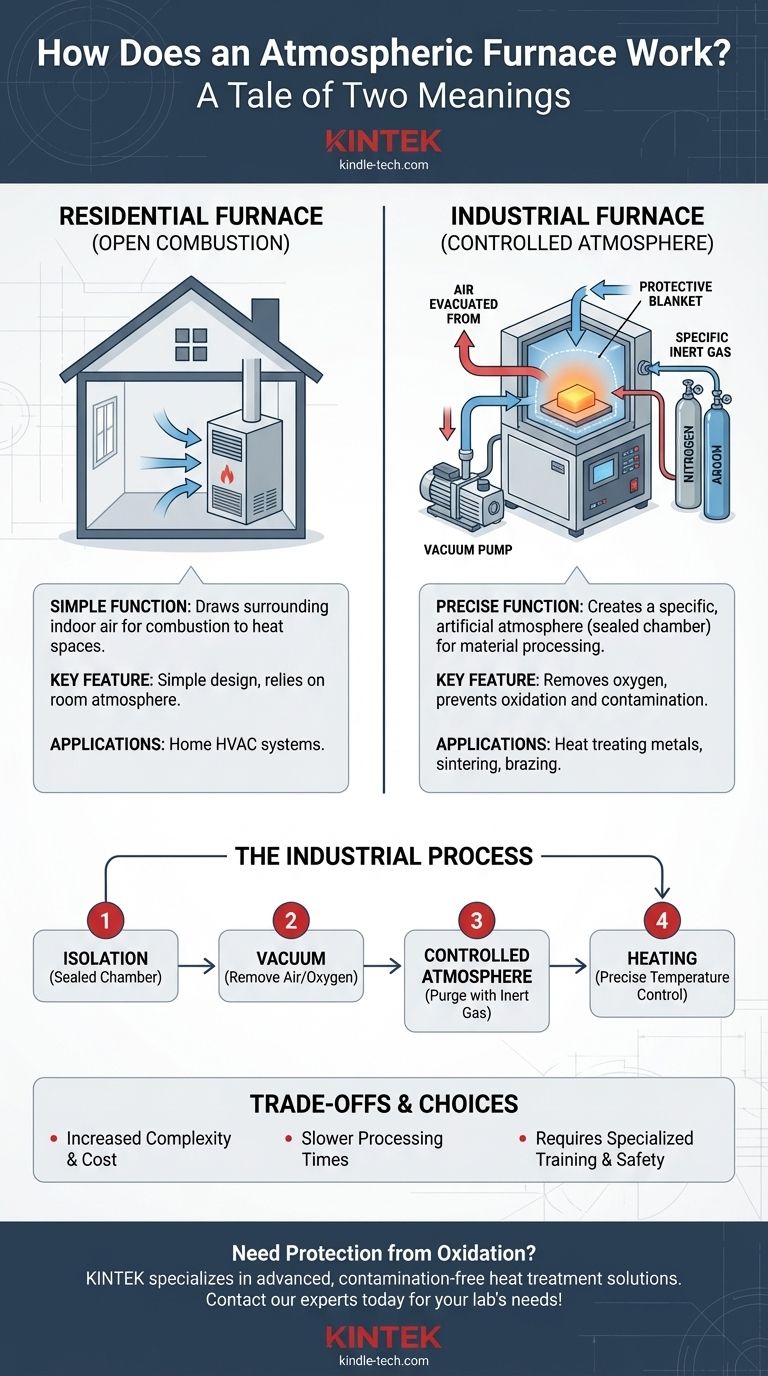
Crucially, the term "atmospheric furnace" has two distinct meanings. For residential heating, it refers to a simple furnace that uses the surrounding air (the atmosphere) for combustion. In a scientific or industrial context, it means the opposite: a highly-controlled furnace where the internal atmosphere is precisely managed—often by removing the air and replacing it with specific gases to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
The core function of an industrial atmospheric furnace is not just to heat a material, but to do so within a sealed chamber where the gaseous environment is precisely controlled. This control is the key to preventing contamination and achieving specific material properties that would be impossible in open air.

Clarifying the Two Meanings
The ambiguity of the term "atmospheric furnace" is a common point of confusion. The correct interpretation depends entirely on the context: home heating versus industrial processing.
The Residential Furnace (Open Combustion)
In HVAC, an atmospheric furnace is a basic design that draws air directly from the room it's in.
A grill on the unit pulls this indoor air into a combustion chamber. There, it mixes with a fuel like natural gas, allowing the burners to operate. This design is simple but relies on the surrounding atmosphere for its function.
The Industrial Furnace (Controlled Atmosphere)
In materials science and manufacturing, an atmospheric furnace is a sophisticated piece of equipment. Its purpose is to create a specific, artificial atmosphere around a sample during heat treatment.
These furnaces are fully sealed to isolate the internal chamber from the outside air. This allows operators to remove oxygen and other reactive gases, which is critical for high-temperature processing of sensitive materials.
How a Controlled-Atmosphere Furnace Works
The operation of an industrial atmospheric furnace follows a precise sequence to create the perfect environment for heat treatment.
The Principle of Isolation
The entire process begins with sealing the sample inside a work chamber or tube.
This chamber must be airtight to prevent any leaks of outside air, which contains about 21% oxygen. Oxygen is highly reactive at high temperatures and is the primary cause of oxidation (like rust on steel) and material degradation.
Achieving a Vacuum
Once the chamber is sealed, a vacuum pump is used to remove the air.
This step is critical because it evacuates the oxygen, moisture, and other contaminants that were inside the chamber. Reaching a near-perfect vacuum ensures the starting environment is as clean as possible.
Introducing the Controlled Atmosphere
After the vacuum is established, the chamber is backfilled or "purged" with a specific gas.
For many applications, an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is used. These gases do not react with the material being heated, creating a protective blanket that prevents oxidation during the heating cycle. In other processes, specific reactive gases might be introduced to intentionally alter the material's surface.
The Heating Process
Only after the atmosphere is established does the furnace begin to heat the sample.
The heating itself can be accomplished through various methods, such as electric resistance coils (like in a muffle furnace) or electromagnetic induction. The method of heating is separate from the method of controlling the atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for many processes, controlled-atmosphere furnaces come with inherent complexities compared to heating in open air.
Increased Complexity and Cost
The need for a perfectly sealed chamber, vacuum pumps, gas delivery systems, and precise controllers makes these furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than simple ovens.
Slower Processing Times
The extra steps of sealing the chamber, pumping down to a vacuum, and purging with gas add considerable time to each processing cycle. This can impact overall throughput.
Safety and Maintenance
Working with vacuum systems and high-pressure gas cylinders requires specialized training and safety protocols. The complex components also demand a more rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure leak-free performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of furnace depends entirely on how the material interacts with air at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is simple heating of non-reactive materials: A standard laboratory oven or muffle furnace that operates in the open air is often sufficient, simpler, and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is protecting a material from oxidation: A controlled-atmosphere furnace is non-negotiable. It is the only way to reliably heat reactive metals and composites without causing degradation.
- If your primary focus is altering a material's surface chemistry: You need a specialized atmospheric furnace capable of handling specific active gases, such as those used for carburizing or nitriding.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about mastering the environment in which that heat is applied.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Function | Atmosphere | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Furnace | Space Heating | Uses surrounding air for combustion | Home HVAC systems |
| Industrial Furnace | Material Processing | Sealed chamber with inert/reactive gases | Heat treating metals, sintering, brazing |
Need a furnace that protects your materials from oxidation? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including controlled-atmosphere furnaces designed for precise, contamination-free heat treatment. Our solutions ensure your sensitive materials achieve the desired properties without degradation. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your lab's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is controlled atmosphere important? Mastering Preservation and Industrial Processes
- What are the advantages of a sealed quench furnace? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Consistency & Efficiency
- What is furnace atmosphere? A Guide to Controlled Heating for Superior Results
- Why are atmosphere-controlled furnaces used for solid electrolyte impurities? Optimize Your Battery Research Now
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Why is hydrogen gas used in annealing furnace? For Superior Surface Purity & Faster Cycle Times
- What is the primary function of a controlled nitrogen atmosphere in Si3N4 + SiC? Ensure Superior Ceramic Stability
- What are the advantages of using an atmosphere furnace for low-temperature sintering? Optimize Solid-State Electrolytes



















