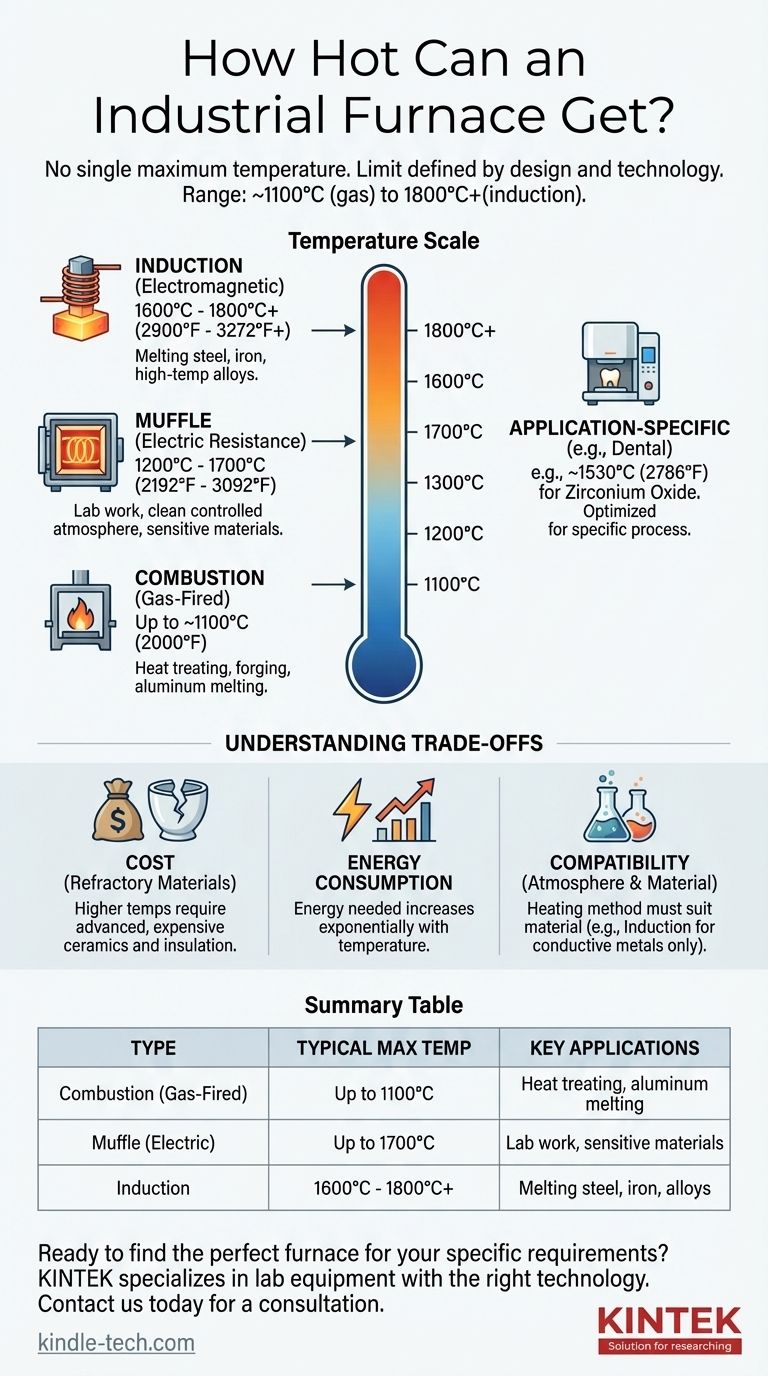
There is no single maximum temperature for an industrial furnace, as the limit is defined entirely by its design and heating technology. While a common natural gas furnace might reach around 1100°C (2000°F), specialized induction furnaces can exceed 1800°C (3272°F) for melting high-temperature metals.
The maximum temperature a furnace can achieve is a direct function of its heating method—such as combustion, electric resistance, or induction—and the physical limits of its construction materials. Your specific application, not a theoretical maximum, will determine the right furnace.
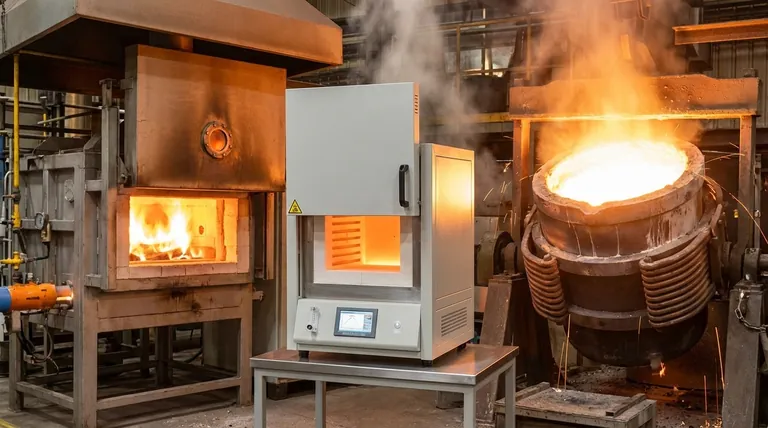

Furnace Temperature by Heating Technology
The term "industrial furnace" covers a vast range of equipment. Understanding the core heating technology is the key to understanding its temperature capabilities.
Combustion Furnaces (Gas-Fired)
Furnaces that burn fuel, like natural gas, are a common and cost-effective solution for many industrial processes.
They can reliably reach temperatures up to 1093°C (2000°F). This range is sufficient for applications like heat treating, forging, and melting lower-temperature metals like aluminum.
Muffle Furnaces (Electric Resistance)
Muffle furnaces use electric heating elements to heat a chamber, or "muffle," which isolates the material being heated from direct contact with the elements and any contaminants.
While typical models operate up to 1200°C (2192°F), specialized versions with advanced ceramic insulation and high-performance elements can reach maximum temperatures of 1700°C (3092°F). They are common in laboratories and for processes requiring a clean, controlled atmosphere.
Induction Furnaces (Electromagnetic)
Induction furnaces do not use conventional heating elements. Instead, they use a powerful electromagnetic field to directly heat a conductive material, like metal.
This method is extremely efficient and fast, allowing these furnaces to reach temperatures of 1600°C to 1800°C (2900°F to 3272°F), and sometimes even higher. They are the standard for melting steel, iron, and other high-temperature alloys.
Application-Specific Furnaces
Many furnaces are designed for a single purpose. For example, a dental furnace used for processing zirconium oxide materials is engineered to reach a specific maximum temperature of around 1530°C (2786°F).
This demonstrates that furnaces are often optimized for a specific process window rather than a universal maximum temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply choosing the furnace with the highest temperature rating is often a mistake. Higher temperatures introduce significant challenges and costs.
The Cost of Refractory Materials
The materials used to line a furnace and contain the heat are called refractories. As operating temperatures increase, the demands on these materials skyrocket.
Furnaces capable of exceeding 1500°C require advanced, and significantly more expensive, ceramics and insulation to function safely and efficiently.
Energy Consumption
The energy required to achieve and maintain temperature increases exponentially. Doubling the operating temperature can more than double the energy cost, making it a critical factor in operational budgets.
Atmosphere and Material Compatibility
The heating method itself is a crucial consideration. A combustion furnace introduces byproducts that can react with the material being heated.
An induction furnace is exceptionally effective for conductive metals but is completely ineffective for heating ceramics or other non-conductive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific requirements of your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating or melting non-ferrous metals: A gas-fired or standard electric resistance furnace (up to 1200°C) is often the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is melting steel, iron, or other high-temperature alloys: An induction furnace is the industry standard, providing the necessary temperatures of 1600°C or more.
- If your primary focus is laboratory work or processing sensitive materials: A muffle furnace provides a clean, controlled environment, with specialized models available for very high-temperature applications.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's capabilities to your precise material and temperature requirements is the key to a successful and efficient industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion (Gas-Fired) | Up to 1100°C (2000°F) | Heat treating, forging, melting aluminum |
| Muffle (Electric) | Up to 1700°C (3092°F) | Lab work, processing sensitive materials |
| Induction | 1600°C - 1800°C+ (3272°F+) | Melting steel, iron, high-temperature alloys |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your specific temperature and material requirements?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with the right furnace technology. Whether you need the clean environment of a muffle furnace or the high-temperature power of an induction system, our experts will help you select the most efficient and cost-effective solution for your process.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-temperature furnace in the austenitizing process of Q345 steel? Optimize Heat Treatment
- Can you temper any metal? No, and here’s why the process is exclusive to certain steels.
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- How are high-performance vacuum furnaces used in helium implantation annealing? Master Material Defect Visualization
- What is the working principle of vacuum brazing furnace? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Strength Metal Joining
- What role does a vacuum heat treatment furnace play in the final processing of Nb-Ti alloy powders? Restoring Ductility
- Why is a high vacuum brazing furnace necessary for nickel-based alloys? Achieve Oxidation-Free, High-Strength Joints
- What does bond strength depend on in braze welding? Master the 3 Keys to a Strong Joint



















