In the food industry, freeze-drying is a premium preservation method used to create high-quality, shelf-stable products by removing water without significantly damaging the food's structure, flavor, or nutritional value. This technology is the foundation for products like instant coffee, astronaut ice cream, and crispy fruit snacks, enabling long-term storage without refrigeration.
Freeze-drying is not simply about dehydration; it is a sophisticated process of preservation. Its primary advantage over other drying methods is its unique ability to maintain the original quality, nutrition, and structure of the food, making it the gold standard for high-value products.

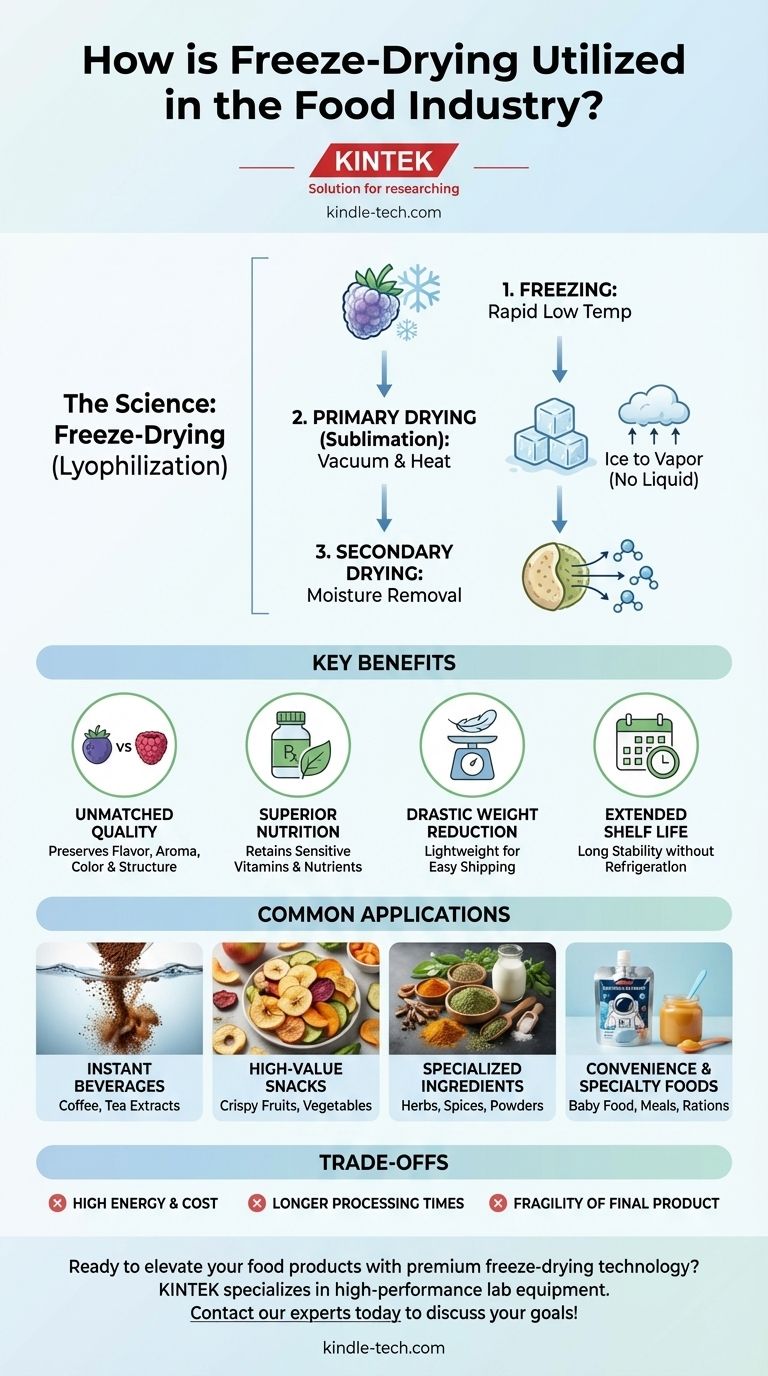
The Science of Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization)
To understand its applications, we must first understand the process. Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is fundamentally different from conventional heat-based dehydration.
The Principle of Sublimation
The core of freeze-drying is a physical process called sublimation. This is where a solid (ice) transforms directly into a gas (water vapor), completely bypassing the liquid phase.
By avoiding liquid water, the process minimizes the migration of solutes and the collapse of the food's cellular structure, which is what typically degrades quality in conventional drying.
The Three-Stage Process
Freeze-drying is a meticulous, multi-stage operation.
- Freezing: The food is rapidly frozen at very low temperatures. This locks water molecules in place as tiny ice crystals, preserving the product's physical structure.
- Primary Drying (Sublimation): The frozen food is placed in a high vacuum. A small amount of heat is applied, giving the ice crystals just enough energy to sublimate directly into vapor, which is then removed.
- Secondary Drying: After the free ice is gone, some water molecules remain bound to the food. The temperature is slightly increased to break these bonds, removing the final traces of moisture and ensuring maximum stability.
Key Benefits in Food Production
The industry chooses this complex method for several distinct and powerful advantages over simpler techniques like air or heat drying.
Unmatched Quality Preservation
Because the process avoids high temperatures, delicate compounds responsible for flavor, aroma, and color are left almost entirely intact. Freeze-dried products, when rehydrated, are remarkably similar to their fresh counterparts.
Superior Nutritional Retention
Heat can destroy sensitive vitamins and nutrients. Freeze-drying's low-temperature environment is far gentler, allowing it to preserve the nutritional value of the original food far more effectively than other preservation methods.
Drastic Weight Reduction and Shelf-Life Extension
Removing nearly all water content makes the final product incredibly lightweight, which is a major advantage for shipping and storage. Without water, microbial growth is inhibited, granting these foods an exceptionally long shelf life without the need for refrigeration or preservatives.
Common Applications in the Food Industry
Freeze-drying is applied where the final product's quality justifies the process's cost.
Instant Beverages
This is one of the most well-known applications. Freeze-drying coffee and tea extracts creates soluble granules that dissolve instantly in water while retaining the complex aroma and taste of the original brew.
High-Value Snacks
Fruits and vegetables are freeze-dried to create crispy, healthy snacks. This process maintains their vibrant color and intense flavor, offering a premium alternative to traditionally fried or baked chips.
Specialized Ingredients and Seasonings
The method is ideal for preserving the potent oils and flavors in herbs and spices. It is also used to create powdered ingredients like milk, eggs, or fruit powders for use in baking mixes, soups, and ready-to-eat meals.
Convenience and Specialty Foods
From nutritious baby food that rehydrates quickly to lightweight, long-lasting meals for astronauts and hikers, freeze-drying serves niche markets that demand both convenience and high quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, freeze-drying is not a universal solution. Its benefits must be weighed against its inherent limitations.
High Energy Consumption and Cost
The combination of deep freezing and maintaining a high vacuum is energy-intensive. This makes freeze-drying a significantly more expensive process per unit compared to conventional dehydration.
Longer Processing Times
Sublimation is a slow and deliberate process. A typical freeze-drying cycle can take many hours, or even days, which limits throughput and further adds to the operational cost.
Fragility of the Final Product
The porous, honeycomb-like structure left behind after sublimation makes freeze-dried foods very brittle and fragile. They require careful handling and robust packaging to prevent crushing and to protect them from moisture and oxygen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Deciding whether to use freeze-drying depends entirely on your product goals and market position.
- If your primary focus is premium quality and nutritional value: Freeze-drying is the ideal choice for creating a superior product that stands out in the market.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk dehydration: Conventional air or heat drying is a much more economical and faster method for products where some loss of quality is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is lightweight convenience for niche markets: Freeze-drying is perfectly suited for high-performance applications like camping food, emergency rations, or specialty ingredients where its benefits outweigh the cost.
Ultimately, understanding freeze-drying empowers you to select the precise preservation technology that aligns with your product's purpose and promise.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit in Food Industry |
|---|---|
| Quality | Preserves original flavor, aroma, color, and texture |
| Nutrition | Retains sensitive vitamins and nutrients better than heat drying |
| Shelf Life | Extends stability without refrigeration or preservatives |
| Weight | Drastically reduces weight for easier shipping and storage |
| Applications | Instant beverages, high-value snacks, specialty ingredients, convenience foods |
Ready to elevate your food products with premium freeze-drying technology? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for food research and development. Whether you're developing instant beverages, nutritious snacks, or long-lasting specialty foods, our solutions help you achieve superior quality and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the eutectic point in lyophilization? Master the Critical Temperature for Success
- How are freeze dryers used in the pharmaceutical industry? Extend Drug Shelf Life & Stability
- How should sample volume influence the choice of a lab freeze dryer? A Guide to Capacity, Specs & Cost
- Which industries commonly use lab freeze dryers? Preserve Sensitive Materials with Lyophilization
- What is a lyophilizer and how does it work? Unlock Superior Preservation for High-Value Materials



















