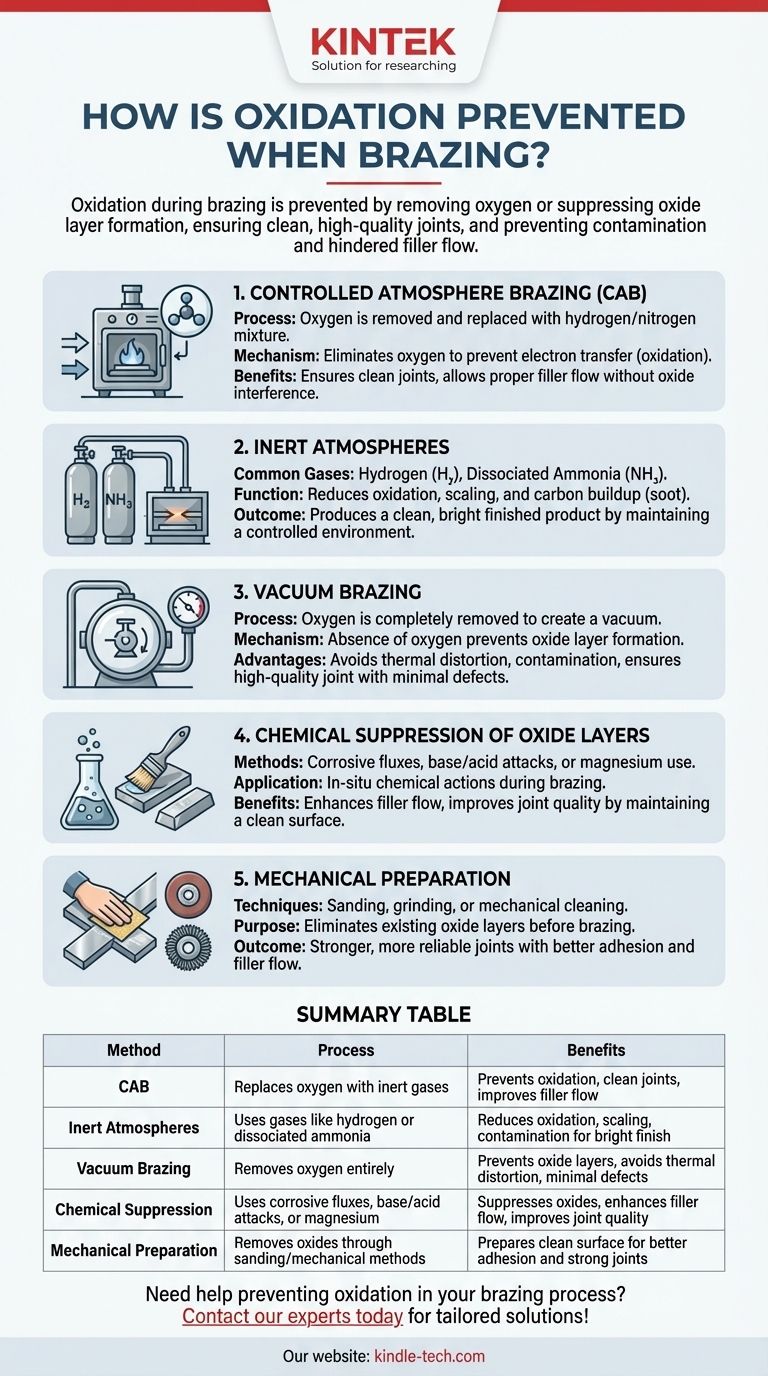
Oxidation during brazing is prevented through various methods that either remove oxygen from the brazing environment or chemically suppress the formation of oxide layers. Key techniques include controlled atmosphere brazing (CAB), which replaces oxygen with inert gases like hydrogen and nitrogen, and vacuum brazing, which eliminates oxygen entirely. Additionally, chemical methods such as using corrosive fluxes or mechanical preparation like sanding can suppress or remove oxide layers. These approaches ensure clean, high-quality joints by preventing oxidation, scaling, and contamination, which can otherwise hinder the flow of molten filler material and compromise the integrity of the brazed joint.

Key Points Explained:
-
Controlled Atmosphere Brazing (CAB):
- Process: Oxygen is removed from the brazing oven and replaced with a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen, creating an oxygen-free environment.
- Mechanism: By eliminating oxygen, the transfer of electrons from metal atoms to oxygen atoms (oxidation) is prevented.
- Benefits: Ensures a clean and high-quality joint by allowing the molten filler material to flow properly without interference from oxide layers.
-
Inert Atmospheres:
- Common Gases: Hydrogen and dissociated ammonia are frequently used to create inert atmospheres.
- Function: These gases reduce or eliminate oxidation, scaling, and carbon buildup (soot) during the brazing process.
- Outcome: Produces a clean and bright finished product by maintaining a controlled environment that prevents contamination.
-
Vacuum Brazing:
- Process: Oxygen is removed from the heating chamber, creating a vacuum environment.
- Mechanism: The absence of oxygen prevents the formation of oxide layers on the metal surfaces.
- Advantages: Avoids thermal distortion and contamination, ensuring a high-quality joint with minimal defects.
-
Chemical Suppression of Oxide Layers:
- Methods: Corrosive fluxes, base or acid attacks, or the use of magnesium can chemically suppress the aluminum oxide layer.
- Application: These chemical actions are performed in-situ during the brazing process to prevent oxidation.
- Benefits: Enhances the flow of the filler material and improves joint quality by maintaining a clean metal surface.
-
Mechanical Preparation:
- Techniques: Sanding or other mechanical methods can be used to remove oxide layers before brazing.
- Purpose: Prepares the metal surface by eliminating existing oxides, ensuring better adhesion and flow of the filler material.
- Outcome: Contributes to a stronger and more reliable brazed joint by starting with a clean, oxide-free surface.
By employing these methods, oxidation during brazing is effectively managed, leading to superior joint quality and performance. Each technique addresses the issue of oxidation from a different angle, whether through environmental control, chemical intervention, or mechanical preparation, ensuring that the brazing process yields optimal results.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere Brazing (CAB) | Replaces oxygen with inert gases (e.g., hydrogen, nitrogen) | Prevents oxidation, ensures clean joints, and improves filler material flow |
| Inert Atmospheres | Uses gases like hydrogen or dissociated ammonia | Reduces oxidation, scaling, and contamination for a clean, bright finish |
| Vacuum Brazing | Removes oxygen entirely from the heating chamber | Prevents oxide layers, avoids thermal distortion, and ensures minimal defects |
| Chemical Suppression | Uses corrosive fluxes, base/acid attacks, or magnesium | Suppresses oxide layers, enhances filler flow, and improves joint quality |
| Mechanical Preparation | Removes oxide layers through sanding or other mechanical methods | Prepares a clean surface for better adhesion and stronger joints |
Need help preventing oxidation in your brazing process? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















