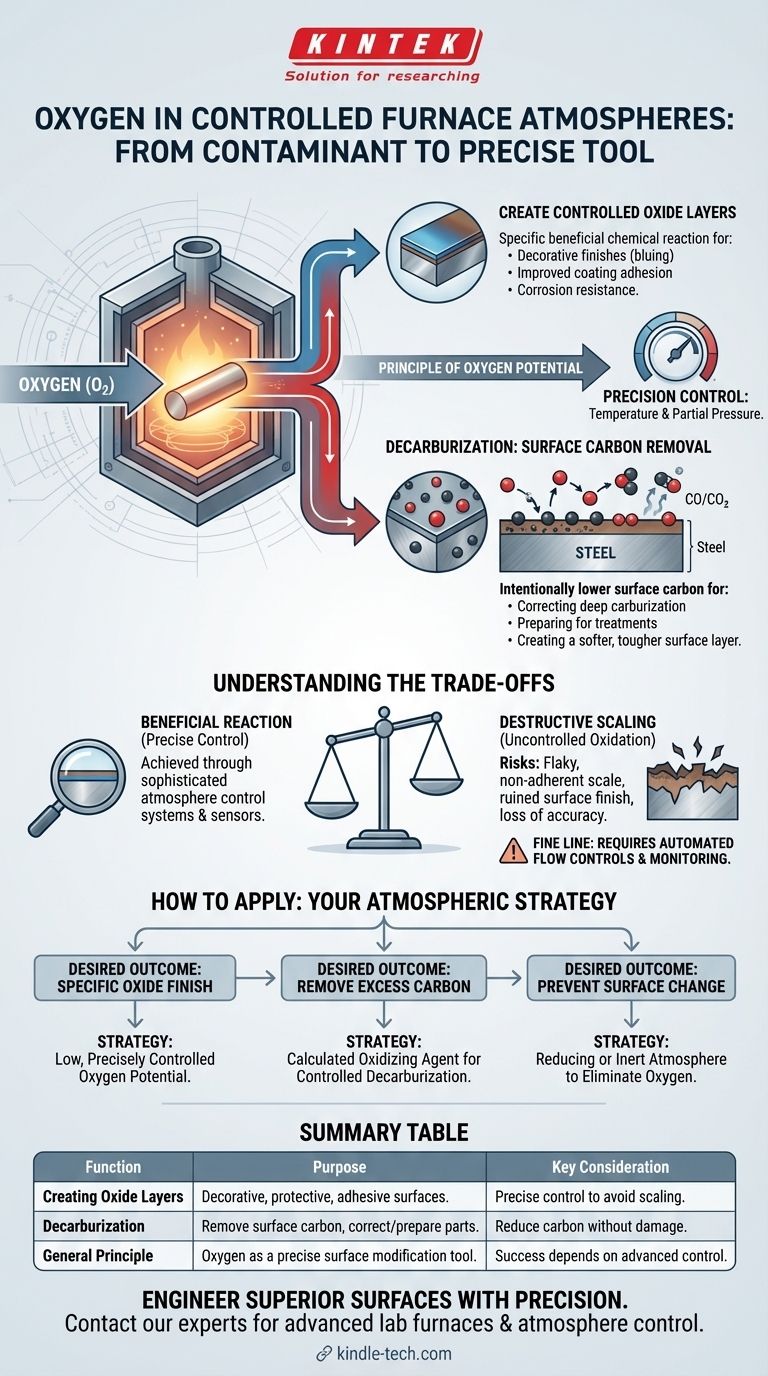
In a controlled furnace atmosphere, oxygen is used deliberately as a reactive agent to achieve specific surface modifications. Its primary functions are to create controlled oxide layers on metal surfaces and to react with carbon in steel to reduce its surface concentration in a process known as decarburization.
The key takeaway is that oxygen, often viewed as a contaminant to be eliminated, can be a precise tool in heat treating. Its role shifts from an unwanted agent of corrosion to a calculated ingredient for engineering specific surface properties when its concentration and reactivity are carefully managed.

The Purpose of Deliberate Oxidation
Introducing a controlled amount of oxygen into a furnace atmosphere is a form of surface engineering. The goal is not to create destructive rust or scale but to force a specific, beneficial chemical reaction at the part's surface.
Creating Specific Oxide Layers
Oxygen's most direct function is reacting with a metal to form a metal oxide. While uncontrolled oxidation is detrimental, a thin, uniform, and tenacious oxide layer can be highly desirable.
These controlled layers can serve as a decorative finish (like the blueing on firearms), improve paint or coating adhesion, or provide a specific type of corrosion resistance.
The Principle of Oxygen Potential
The process is governed by oxygen potential—the tendency of the furnace atmosphere to either give up or absorb oxygen atoms from the workpiece.
By precisely controlling the temperature and the partial pressure of oxygen (often by introducing it as part of a gas mixture like dissociated ammonia or endothermic gas), engineers can dictate the exact type and thickness of the oxide layer that forms.
Decarburization: The Intentional Removal of Carbon
In steel heat treatment, oxygen can be used to intentionally remove carbon from the surface of a part. This is a critical process for correcting or preparing a component.
The Decarburization Reaction
When introduced into a hot furnace, oxygen will react with the carbon (C) that is dissolved in the austenite phase of the steel. This reaction forms carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide (CO2), which are then carried away by the furnace atmosphere.
The result is a steel surface with a lower carbon content than its core.
Why Remove Surface Carbon?
This process is used to remedy parts that have been accidentally carburized too deeply. It can also be a preparatory step for other surface treatments or to create a softer surface layer for improved toughness or ductility while maintaining a hard, high-carbon core.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using oxygen as a reactive agent is a high-precision process with significant risks if not managed correctly. The line between a beneficial reaction and a destructive one is very fine.
The Risk of Scaling
The primary danger is uncontrolled oxidation, or scaling. If the oxygen potential is too high or the temperature is incorrect, a thick, flaky, and non-adherent oxide layer (scale) will form.
This scale is destructive, ruins the surface finish, and can lead to a loss of dimensional accuracy.
The Need for Precise Control
Successfully using oxygen requires sophisticated atmosphere control systems. This includes sensors to monitor gas composition (such as oxygen probes) and automated flow controls to maintain the precise gas mixture required for the desired reaction.
Without this level of control, attempting to use oxygen as a reactive agent is more likely to damage the workpiece than improve it.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your atmospheric strategy depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material's surface.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific oxide finish (e.g., bluing): You will need an atmosphere with a low but precisely controlled oxygen potential.
- If your primary focus is removing excess surface carbon: You will use a calculated amount of an oxidizing agent to achieve controlled decarburization without causing destructive scaling.
- If your primary focus is preventing any surface change (e.g., bright hardening): Your goal is the opposite—to use a reducing or inert atmosphere to eliminate oxygen and protect the part's surface chemistry.
Ultimately, mastering a furnace atmosphere means viewing every component, including oxygen, as a controllable variable for achieving a desired engineering outcome.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Creating Oxide Layers | Forms decorative, protective, or adhesive surfaces (e.g., bluing). | Requires precise control of oxygen potential to avoid destructive scaling. |
| Decarburization | Removes surface carbon from steel to correct carburization or prepare for treatment. | Must be carefully managed to reduce carbon without damaging the workpiece. |
| General Principle | Oxygen shifts from a contaminant to a precise tool for surface modification. | Success depends entirely on sophisticated atmosphere control systems. |
Ready to engineer superior surface properties with precision?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and atmosphere control systems designed for exacting heat treatment processes. Whether your goal is controlled oxidation, decarburization, or bright hardening, our equipment delivers the reliability and control you need.
Let's discuss how we can help you achieve your specific surface engineering outcomes. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















