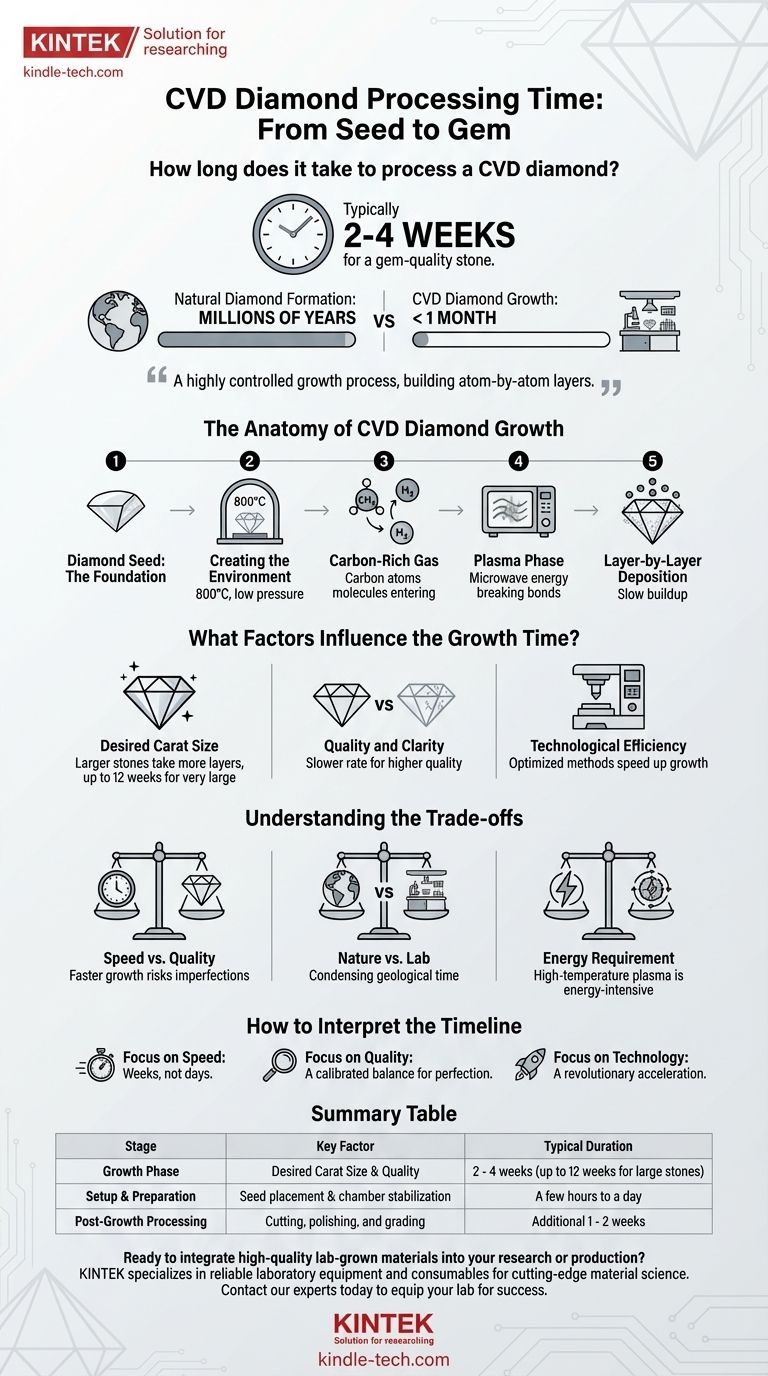
To be precise, processing a gem-quality CVD diamond typically takes between two and four weeks. For a standard one-carat stone, producers can complete the entire growth cycle in less than a month, a stark contrast to the millions of years required for natural diamond formation.
The creation of a CVD diamond is not an instantaneous event but a highly controlled growth process. The multi-week timeframe is dictated by the slow, deliberate, atom-by-atom layering of carbon required to build a high-quality crystal.
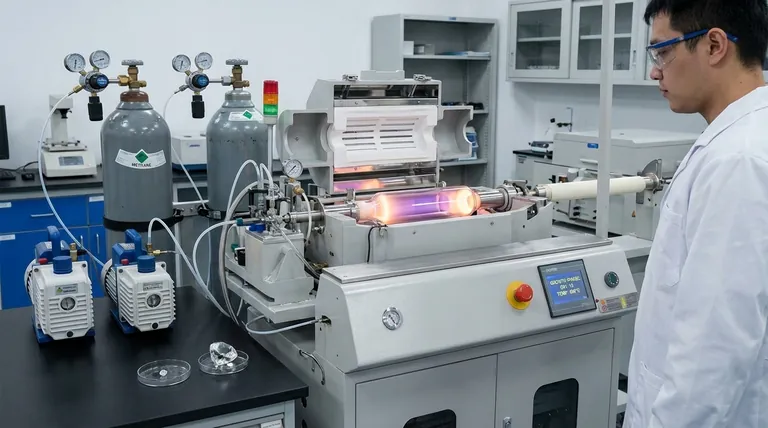

The Anatomy of CVD Diamond Growth
To understand why it takes several weeks, you must first understand the meticulous, step-by-step nature of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method.
The Diamond Seed: The Foundation
The entire process begins with a very thin slice of a pre-existing diamond, known as a seed. This seed acts as the template upon which the new diamond will grow.
Creating the Perfect Environment
This diamond seed is placed inside a sealed, low-pressure vacuum chamber. The chamber is then heated to an extreme temperature, typically around 800°C.
The Role of Carbon-Rich Gas
A mixture of gases, rich in carbon (like methane) and hydrogen, is introduced into the chamber. This mixture serves as the raw material for the new diamond.
From Gas to Crystal: The Plasma Phase
Energy, often in the form of microwaves, is used to energize the gas mixture until it ignites into a plasma. This breaks down the molecular bonds of the gases.
Layer-by-Layer Deposition
Within the plasma, pure carbon atoms are released. These atoms then settle down onto the diamond seed, bonding with its crystal structure and replicating it layer by layer, slowly building up the new diamond.
What Factors Influence the Growth Time?
The "two to four weeks" figure is a common benchmark, but the exact duration can vary based on several key factors.
Desired Carat Size
This is the most significant variable. A larger diamond requires more layers of carbon deposition, extending the necessary time in the chamber. Some very large stones can take up to 12 weeks.
Quality and Clarity Goals
Achieving a higher-quality, flawless diamond often requires a slower and more stable growth rate. Rushing the process can introduce imperfections into the crystal lattice.
Technological Efficiency
Top producers have refined their techniques and equipment over time. Their specific proprietary methods can influence the speed and efficiency of the growth cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The CVD process is a careful balance of scientific variables, and every choice involves a trade-off.
Speed vs. Quality
The fundamental tension in CVD growth is between speed and perfection. While it's possible to grow a diamond faster, doing so increases the risk of inclusions and structural flaws, resulting in a lower-quality stone.
A Stark Contrast to Nature
The weeks-long process of a CVD lab stands in dramatic opposition to the thousands or millions of years natural diamonds spend forming under immense heat and pressure deep within the Earth.
The Energy Requirement
Maintaining a high-temperature plasma chamber for weeks is an energy-intensive undertaking. This operational requirement is a significant factor in the cost and logistics of producing lab-grown diamonds.
How to Interpret the Timeline
Your understanding of the processing time depends on what you value most.
- If your primary focus is speed: Recognize that even the most advanced CVD methods require weeks, not days, to achieve gem-quality results.
- If your primary focus is quality: Appreciate that the 2-4 week timeframe represents a carefully calibrated balance, allowing for the meticulous layering needed for a flawless diamond.
- If your primary focus is the technology: View this multi-week process as a revolutionary acceleration, condensing a geological timescale into a manageable manufacturing cycle.
Understanding this deliberate, weeks-long process reveals how technology has mastered the art of creating one of nature's most valued materials.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Factor | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Phase | Desired Carat Size & Quality | 2 - 4 weeks (up to 12 weeks for large stones) |
| Setup & Preparation | Seed placement & chamber stabilization | A few hours to a day |
| Post-Growth Processing | Cutting, polishing, and grading | Additional 1 - 2 weeks |
Ready to integrate high-quality lab-grown materials into your research or production? The precise, controlled growth of CVD diamonds is just one example of how advanced lab equipment can revolutionize your work. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the reliable laboratory equipment and consumables needed for cutting-edge material science. Whether you're developing new semiconductors, advanced optics, or next-generation gemstones, our solutions support precision and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your lab for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















