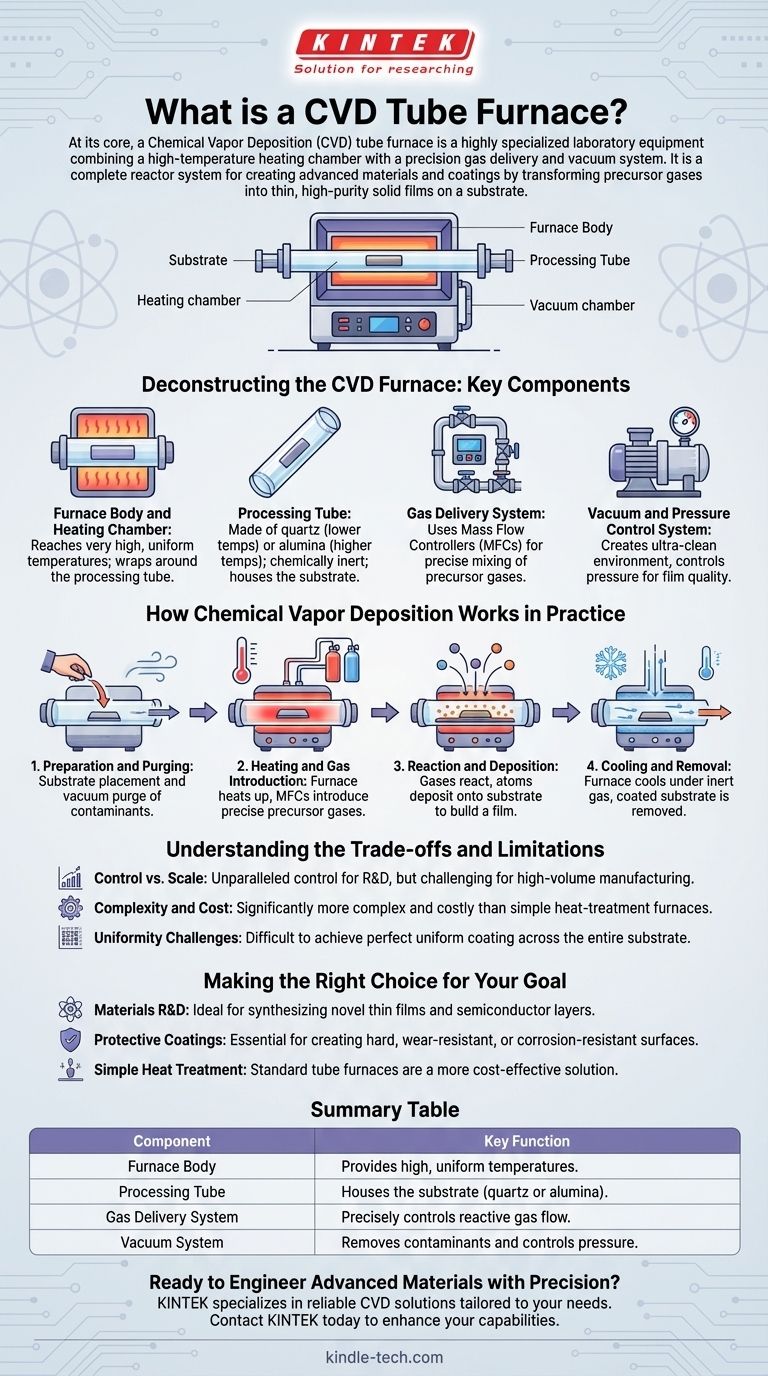
At its core, a CVD tube furnace is a highly specialized piece of laboratory equipment that combines a high-temperature heating chamber with a precision gas delivery and vacuum system. Its full name is a Chemical Vapor Deposition tube furnace, and its purpose is not merely to heat a sample, but to create a meticulously controlled environment. In this environment, reactive gases are introduced into the heated tube, where they decompose and deposit a thin, high-purity solid film onto a target material, known as a substrate.
A CVD tube furnace is not just for heating; it is a complete reactor system. Its primary purpose is to enable the creation of advanced materials and coatings by controlling a chemical reaction where gases transform into a solid layer on a surface.
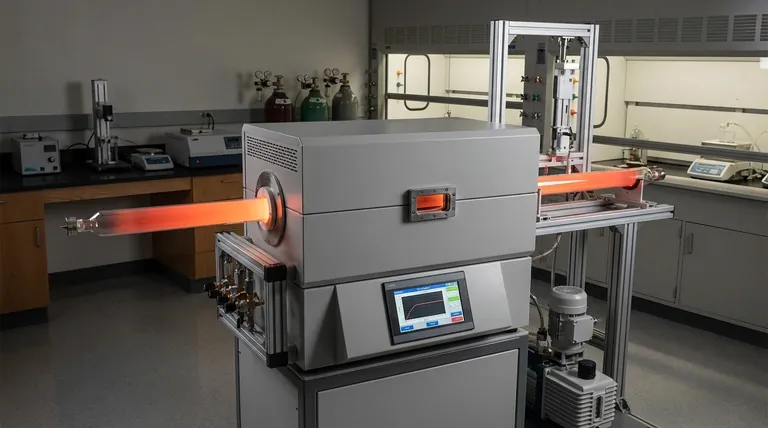

Deconstructing the CVD Furnace: Key Components
To understand what a CVD furnace does, you must first understand its constituent parts. It is an integrated system where each component plays a critical role in the deposition process.
The Furnace Body and Heating Chamber
The foundation of the system is a tube furnace. This consists of a heating chamber, typically insulated with alumina ceramic fiber, that houses heating elements. This assembly is designed to reach very high and uniform temperatures, wrapping around a central processing tube.
The Processing Tube
This tube, often made of quartz (for lower temperatures) or alumina (for higher temperatures), is the heart of the reactor. It must be chemically inert and capable of withstanding extreme heat. The substrate you wish to coat is placed inside this tube.
The Gas Delivery System
This is what truly defines a CVD system. It uses Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs), which are high-precision digital valves that control the exact flow rate of multiple gases. This allows for the precise mixing of precursor gases required for the chemical reaction.
The Vacuum and Pressure Control System
A vacuum pump is used to first evacuate the processing tube of all air and contaminants, creating an ultra-clean environment. During the process, the system actively controls the pressure, which is a critical variable for influencing the quality and characteristics of the deposited film.
How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works in Practice
The synergy of these components enables a precise, multi-step process for creating new materials layer by layer.
Step 1: Preparation and Purging
A substrate is carefully placed inside the processing tube. The system is then sealed, and the vacuum pump purges the tube of ambient air, particularly oxygen and water vapor, which could interfere with the reaction.
Step 2: Heating and Gas Introduction
The furnace ramps up to the target reaction temperature, which can be several hundred or even over a thousand degrees Celsius. Once stable, the MFCs begin introducing a precise, pre-programmed mixture of precursor gases into the tube.
Step 3: Reaction and Deposition
The high temperature provides the energy needed to cause the precursor gases to react or decompose. As they do, the atoms of the desired material are "deposited" onto the surface of the substrate, slowly building a thin, uniform film.
Step 4: Cooling and Removal
After the desired film thickness is achieved, the gas flow is stopped, and the furnace begins to cool down. This is often done under the flow of an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation. Once at a safe temperature, the coated substrate is removed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a CVD tube furnace is a specialized tool with specific considerations. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution for thermal processing.
Control vs. Scale
Laboratory CVD furnaces offer unparalleled control over the deposition process, making them ideal for research and development. However, they are typically designed for small samples and are not suited for high-volume, large-scale manufacturing without significant engineering.
Complexity and Cost
The integration of a vacuum system, high-precision gas handling, and advanced digital controls makes a CVD furnace significantly more complex and costly than a simple heat-treatment or annealing furnace.
Uniformity Challenges
Achieving a perfectly uniform coating thickness and composition across the entire surface of a substrate can be challenging. It is highly dependent on gas flow dynamics, temperature gradients along the tube, and depletion of the precursor gases as they travel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right equipment depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: A CVD tube furnace is the ideal tool for synthesizing novel thin films, testing new precursor gases, or fabricating semiconductor layers.
- If your primary focus is applying protective or functional coatings: This furnace is essential for creating hard, wear-resistant, or corrosion-resistant surfaces on small, high-value components.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment or annealing: A standard tube furnace without the complex gas delivery and vacuum systems is a much more cost-effective and simpler solution.
Ultimately, a CVD tube furnace empowers you to engineer materials at the atomic level, molecule by molecule.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Furnace Body | Provides high, uniform temperatures for the reaction. |
| Processing Tube | Houses the substrate; made of quartz or alumina. |
| Gas Delivery System | Precisely controls the flow of reactive precursor gases. |
| Vacuum System | Removes contaminants and controls pressure for purity. |
Ready to Engineer Advanced Materials with Precision?
A CVD tube furnace is more than just a heater—it's a complete reactor system for synthesizing high-purity thin films and coatings. If your research or production involves semiconductors, protective coatings, or novel material development, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your goals.
We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our CVD solutions can enhance your capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the components of MOCVD? A Detailed Breakdown of This Advanced Deposition System
- What is the function of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) equipment? Precision Growth for BDD Electrodes
- What is a vacuum coating machine? A Guide to High-Performance Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the CVD process reaction? A Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition Mechanisms
- What roles does a rotary vane vacuum pump play in atmospheric or micro-pressure CVD? Optimize Your Thin Film Quality
- What is the difference between PVD and CVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the steps involved in chemical vapour deposition? A Guide to the CVD Process
- What is CVD working mechanism? Unlock the Science of Building Materials Atom by Atom



















