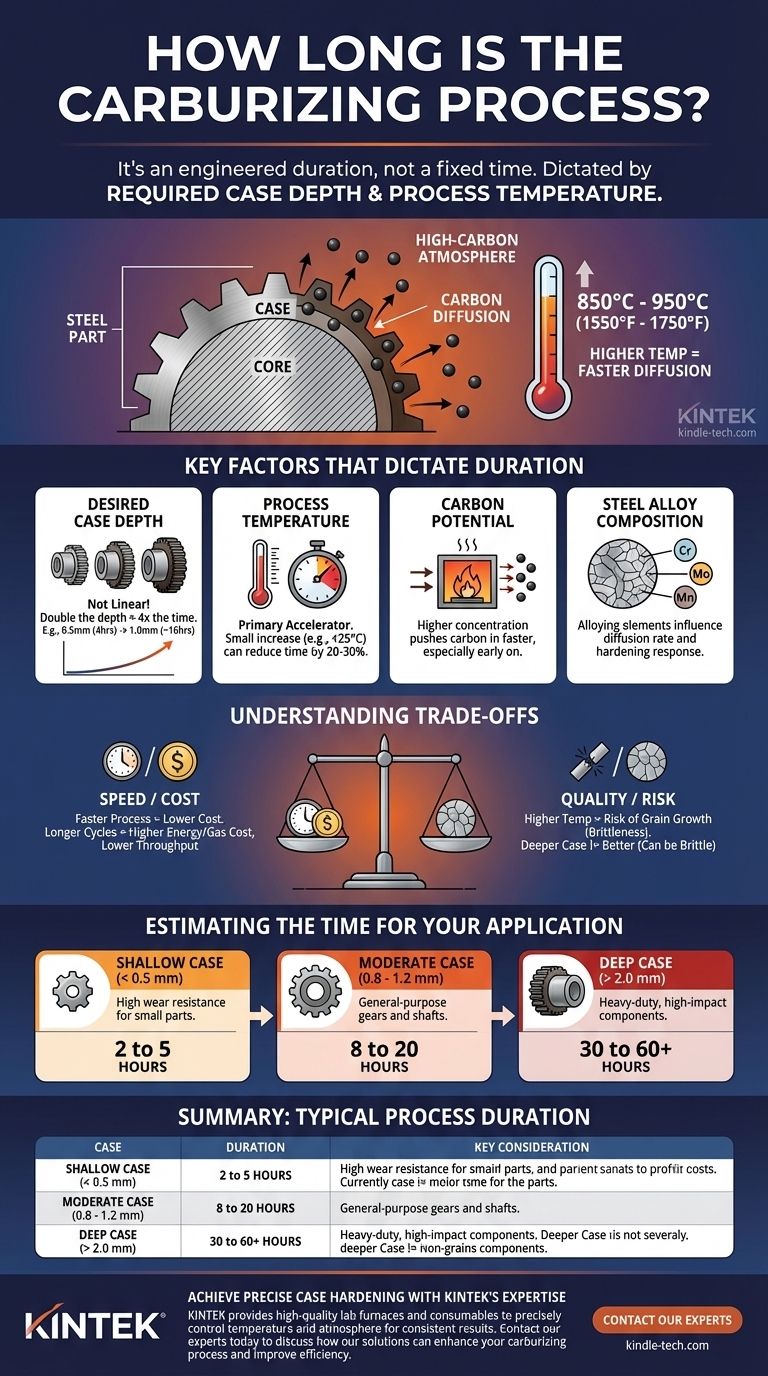
There is no single answer to how long the carburizing process takes, as the duration is engineered to meet a specific outcome. A shallow case might only require a few hours, while a deep, heavy-duty case can take 48 hours or more. The time is dictated almost entirely by the required case depth and the process temperature.
The duration of carburizing is not a fixed number but a critical process variable. It is governed by the laws of diffusion, where the required time increases exponentially—not linearly—with the target depth of the hardened layer.

What Governs Carburizing Time?
To understand the timing, you must first understand the mechanism. Carburizing is a heat treatment process that introduces carbon into the surface of low-carbon steel to create a hard, wear-resistant outer layer (the "case") while maintaining a softer, tougher interior (the "core").
The Principle of Diffusion
At its heart, carburizing is a diffusion-controlled process. Carbon atoms from a high-carbon atmosphere (like a gas or vacuum furnace) migrate into the surface of the steel. The rate of this migration is determined by fundamental physical laws.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary accelerator for diffusion. Most commercial carburizing is performed between 850°C and 950°C (1550°F to 1750°F).
A higher temperature significantly speeds up the rate at which carbon atoms can move through the steel's crystal lattice, reducing the required furnace time.
The Goal: Effective Case Depth (ECD)
The true objective is not just to add carbon but to achieve a specific Effective Case Depth (ECD). This is the depth from the surface at which the steel's hardness drops to a specific threshold, commonly 50 Rockwell C (HRC). All process parameters, especially time, are manipulated to achieve this target ECD.
Key Factors That Dictate the Duration
The duration of a carburizing cycle is a calculated result based on several interdependent factors.
Desired Case Depth
This is the most influential factor. The relationship between time and depth is not linear. Due to the nature of diffusion, achieving twice the depth takes approximately four times as long.
For example, if a 0.5 mm case takes 4 hours, a 1.0 mm case on the same part under the same conditions will take closer to 16 hours.
Process Temperature
As mentioned, a higher temperature accelerates the process. A small increase of 25°C can reduce the required cycle time by 20-30%. This makes temperature the main lever for balancing speed and cost.
Carbon Potential of the Atmosphere
The carbon potential refers to the concentration of available carbon in the furnace atmosphere. A higher potential creates a steeper "concentration gradient," pushing carbon into the steel more quickly, especially in the early stages of the process.
Steel Alloy Composition
The specific grade of steel matters. Alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, and manganese can influence how readily carbon diffuses into the surface and how the steel responds to the subsequent hardening (quenching) process, which can impact the total time required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply running the process faster or longer is not always better. It involves a series of critical engineering trade-offs.
Time vs. Cost
Longer cycle times directly increase costs. This includes the energy to run the furnace, the consumption of process gases, and the reduction in overall plant throughput. Every hour in the furnace has a price tag.
Temperature vs. Grain Growth
While raising the temperature speeds up the process, it comes with a significant risk. Excessively high temperatures can cause the crystalline grains within the steel to grow too large.
This condition, known as grain growth, can make the final part brittle and reduce its toughness, potentially leading to premature failure.
Case Depth vs. Core Properties
A deeper case is not always desirable. An excessively deep or high-carbon case can become brittle and prone to chipping. The goal is a balanced component with a hard, wear-resistant surface and a tough, ductile core that can absorb impact.
Estimating the Time for Your Application
To determine the right duration, you must first define your component's performance requirements. The cycle time is then engineered to meet that goal.
- If your primary focus is a shallow case (< 0.5 mm) for high wear resistance on small parts: The process can be relatively short, often completed in 2 to 5 hours.
- If your primary focus is a moderate case (0.8 - 1.2 mm) for general-purpose gears and shafts: Expect a common cycle time in the range of 8 to 20 hours.
- If your primary focus is a deep case (> 2.0 mm) for heavy-duty or high-impact components: You must plan for a multi-day process, often lasting 30 to 60 hours or more.
Ultimately, controlling carburizing time is a precise balancing act between achieving metallurgical goals and maintaining production efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Target Case Depth | Typical Process Duration | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Shallow (< 0.5 mm) | 2 - 5 hours | High wear resistance for small parts. |
| Moderate (0.8 - 1.2 mm) | 8 - 20 hours | Common for gears and shafts. |
| Deep (> 2.0 mm) | 30 - 60+ hours | For heavy-duty, high-impact components. |
Achieve precise case hardening with KINTEK's expertise.
Determining the optimal carburizing time is critical for balancing component performance with production costs. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab furnaces and consumables needed to precisely control temperature and atmosphere for consistent, reliable results.
Whether you're developing a new heat treatment protocol or optimizing an existing one, our team can help you select the right equipment to meet your specific case depth and metallurgical goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your carburizing process and improve your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting



















