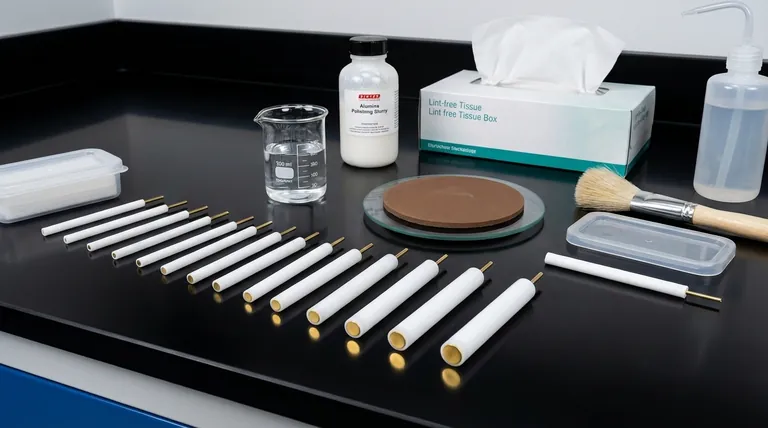
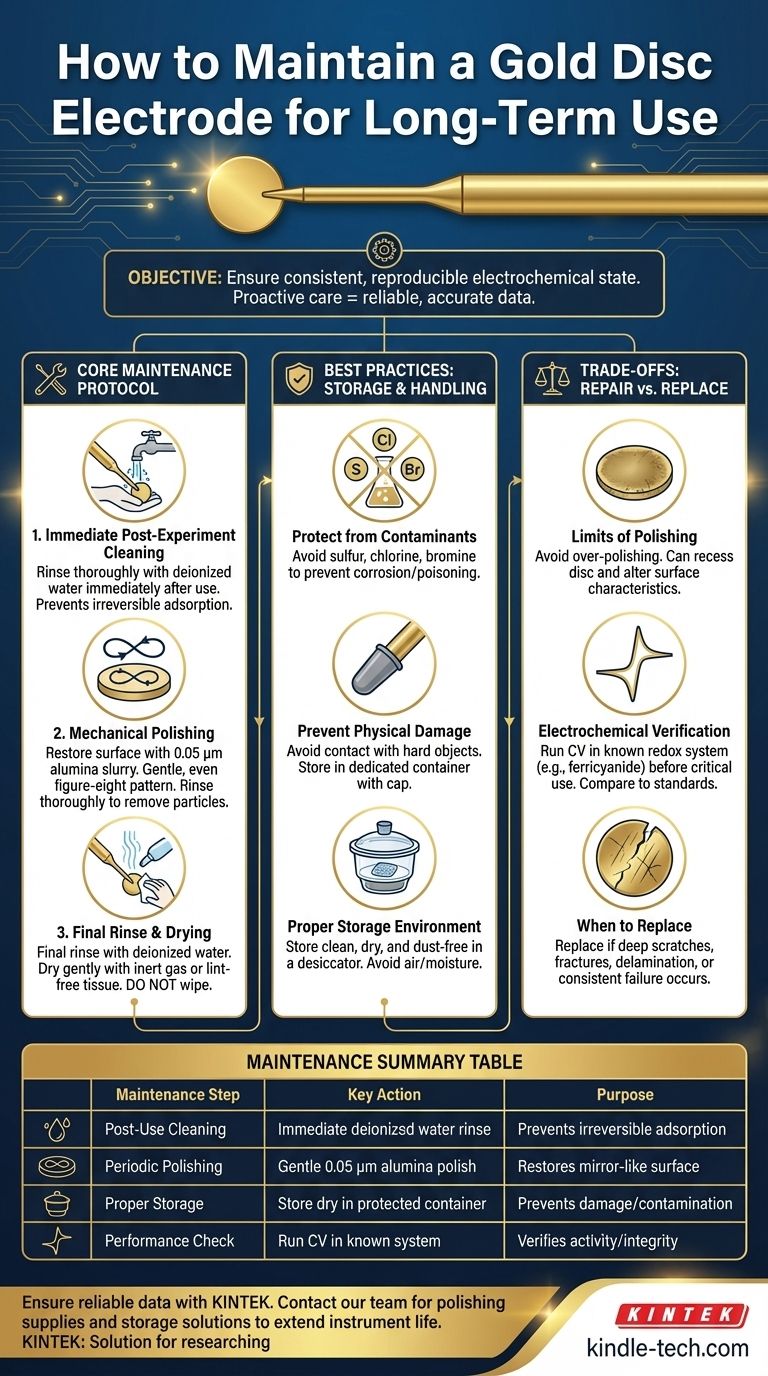
To properly maintain a gold disc electrode, you must implement a strict post-experiment cleaning protocol, employ periodic polishing to restore the surface, and adhere to specific storage and handling guidelines. The process begins with immediate rinsing after use, followed by mechanical polishing with alumina slurry for stubborn contaminants, and concludes with careful drying and storage in a protected environment.
The core objective of electrode maintenance is not merely to clean the surface, but to ensure a consistent and electrochemically reproducible state for every experiment. Proactive care is the foundation of reliable and accurate electrochemical data over the long term.
The Core Maintenance Protocol
A disciplined maintenance routine is essential for preserving the electrode's performance. This involves a cycle of cleaning, polishing, and verification performed consistently.
Step 1: Immediate Post-Experiment Cleaning
The most critical step is cleaning the electrode immediately after removing it from the electrolyte. This prevents residual species from drying and adsorbing irreversibly onto the gold surface.
Rinse the electrode tip thoroughly with high-purity, deionized water. For non-aqueous electrolytes, you may need to rinse with a compatible high-purity solvent first, followed by deionized water.
Step 2: Mechanical Polishing
When the surface is contaminated, tarnished, or scratched, mechanical polishing is required to restore a smooth, mirror-like finish.
Use a small amount of alumina polishing powder (a 0.05 µm slurry is a common choice) on a polishing pad. Gently press the electrode onto the pad and move it in a figure-eight pattern for a few minutes. This ensures even polishing across the surface.
After polishing, thoroughly rinse the electrode with deionized water to remove all alumina particles. Sonication in deionized water for a minute can help dislodge any stubborn abrasive particles.
Step 3: Final Rinse and Drying
After any cleaning or polishing step, a final rinse with deionized water is necessary. Some protocols also include a final rinse with a volatile solvent like ethanol to aid in drying.
Gently dry the electrode surface using lint-free filter paper or a soft tissue. You can also use a gentle stream of an inert gas like nitrogen or argon. Never wipe the electrode, as this can re-introduce scratches.
Best Practices for Storage and Handling
How you store and handle the electrode between experiments is just as important as how you clean it.
Protecting from Chemical Contamination
Gold is relatively inert, but it is susceptible to certain contaminants. Keep the electrode away from any environment containing sulfur, chlorine, or bromine, as these elements can corrode the surface and poison its electrochemical activity.
Preventing Physical Damage
The electrode surface is delicate. Avoid letting it come into contact with hard objects, which can cause scratches or deformation. When not in use, always store the electrode in its dedicated container, often with a protective cap over the tip.
Proper Storage Environment
Once clean and dry, store the electrode in a clean, dry, and dust-free container. Long-term exposure to air or moisture should be avoided. A desiccator or a sealed container is an ideal storage location.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replace
Knowing the limits of maintenance is crucial for data integrity. Aggressive recovery attempts can sometimes do more harm than good.
The Limits of Polishing
While polishing is an effective cleaning method, over-polishing can be detrimental. Excessive polishing can recess the gold disc below its insulating shroud, altering the diffusion characteristics at the electrode. It can also change the surface roughness, which affects the real surface area and can alter reaction kinetics.
Electrochemical Verification
Before critical measurements, you should verify the electrode's performance. Run a cyclic voltammogram (CV) in a well-characterized redox system (e.g., a potassium ferricyanide solution). Compare the peak separation and peak shape to theoretical or previously established values. A poorly performing electrode will show broadened peaks or a large peak separation.
When to Replace the Electrode
An electrode must be replaced if it exhibits signs of severe damage. This includes deep scratches that polishing cannot remove, fractures in the insulating shroud, or delamination of the gold coating. If an electrode consistently fails electrochemical verification even after thorough cleaning, it has reached the end of its functional life and must be replaced to ensure experimental accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance protocol should match the demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is routine qualitative analysis: A thorough rinse after each use and occasional polishing when the surface appears fouled may be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is high-precision quantitative research: A full polishing and electrochemical verification cycle is mandatory before each set of critical experiments.
- If your primary focus is long-term electrode lifespan: Meticulous handling, immediate post-use cleaning, and proper dry storage are your most important priorities.
Ultimately, disciplined maintenance transforms your electrode from a consumable into a reliable, long-term scientific instrument.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Post-Use Cleaning | Immediate rinse with deionized water | Prevents irreversible adsorption of contaminants |
| Periodic Polishing | Gentle polishing with 0.05 µm alumina slurry | Restores a smooth, mirror-like surface |
| Proper Storage | Store dry in a dedicated, protected container | Prevents physical damage and chemical contamination |
| Performance Check | Run a CV in a known redox system (e.g., ferricyanide) | Verifies electrochemical activity and surface integrity |
Ensure your research is built on a foundation of reliable data. Proper electrode maintenance is critical for accurate electrochemical measurements. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the materials needed for meticulous electrode care.
Our experts can help you select the right polishing supplies and storage solutions to extend the life of your instruments. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's precision and longevity goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the operating principle of a gold disc electrode in an electrochemical system? Unlock Precision with a Stable Interface
- What are the key precautions for a gold disc electrode? Ensure Accurate Results & Long Lifespan
- What are the necessary pretreatment steps before using a gold disc electrode? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- How should a gold disc electrode be handled during an experiment? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the key aspects of maintaining and caring for a gold plate electrode? Preserve Performance and Extend Lifespan



















