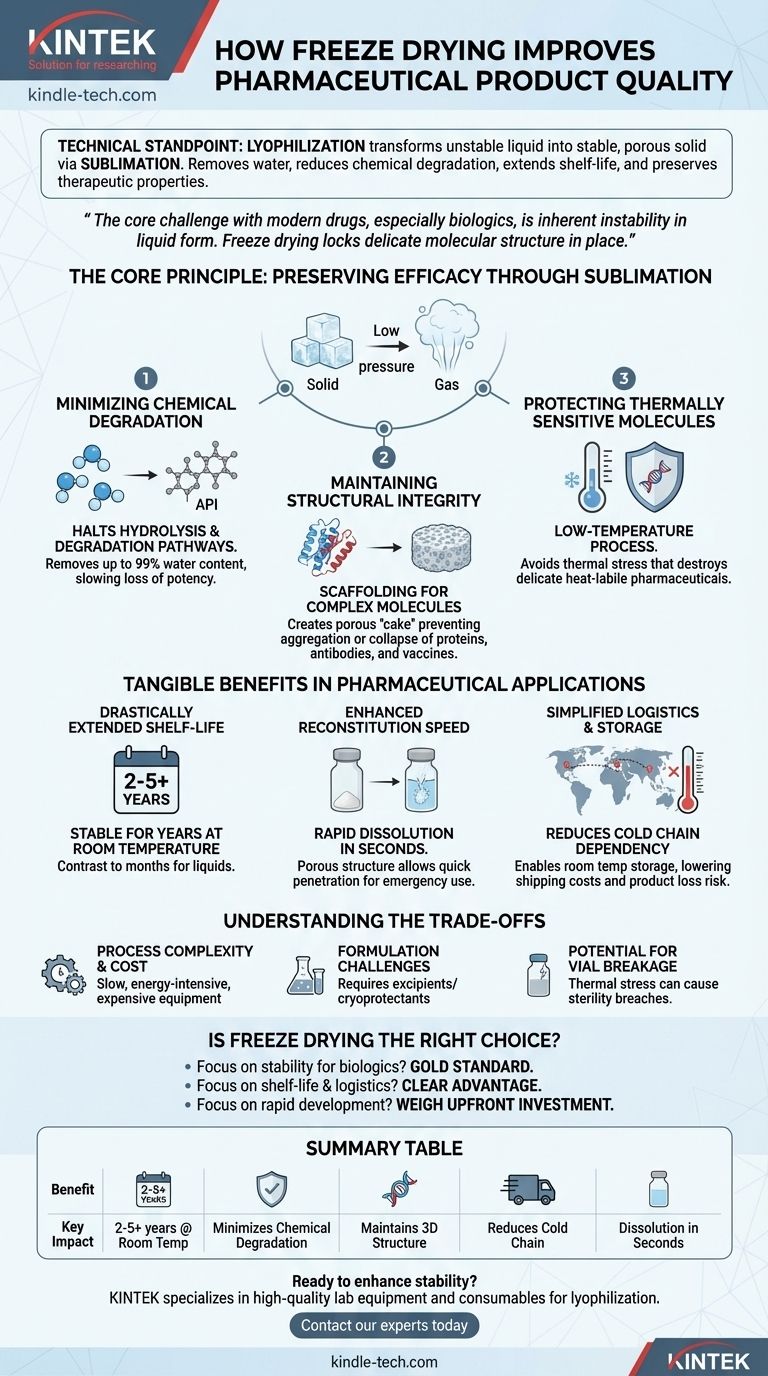
From a technical standpoint, freeze drying—or lyophilization—improves pharmaceutical quality by fundamentally transforming an unstable liquid product into a stable, porous solid. This is achieved by removing water via sublimation, which significantly reduces chemical degradation, extends shelf-life often to several years at room temperature, and creates a product that can be rapidly reconstituted for use while preserving its original therapeutic properties.
The core challenge with many modern drugs, especially biologics and vaccines, is their inherent instability in liquid form. Freeze drying solves this not by merely drying the product, but by locking its delicate molecular structure in place at low temperatures, ensuring its safety and efficacy are preserved from manufacturing to patient administration.

The Core Principle: Preserving Efficacy Through Sublimation
Lyophilization is a low-temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product, lowering the pressure, and then removing the ice by sublimation—the direct transition of a solid to a gas. This unique mechanism is the key to its quality-enhancing benefits.
Minimizing Chemical Degradation
Water is a primary medium for chemical reactions, particularly hydrolysis, which can break down and inactivate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). By removing up to 99% of the water content, freeze drying effectively halts these degradation pathways.
This dramatically slows the loss of potency over time, ensuring the drug delivers its intended therapeutic effect even after years in storage.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
For complex molecules like proteins, antibodies, and vaccines, their three-dimensional structure is essential to their function. Conventional heat-drying methods can cause this structure to denature and collapse, rendering the drug useless.
Freeze drying, however, removes water from a frozen state. This process acts like a scaffold, creating a porous, sponge-like "cake" that maintains the drug's original molecular dispersion and prevents aggregation or structural collapse.
Protecting Thermally Sensitive Molecules
Many advanced biologics are extremely sensitive to heat. The entire freeze-drying process is conducted at low or sub-zero temperatures, which avoids the thermal stress that would otherwise destroy these delicate products. This makes it the premier method for preserving heat-labile pharmaceuticals.
Tangible Benefits in Pharmaceutical Applications
The scientific principles of lyophilization translate directly into critical, real-world advantages for drug development, manufacturing, and distribution.
Drastically Extended Shelf-Life
The primary benefit of creating a dry, stable state is a massive extension of product shelf-life. Many freeze-dried pharmaceuticals are stable for two to five years or more at room temperature, a stark contrast to liquid formulations that may only last months even with refrigeration.
Enhanced Reconstitution Speed
The porous cake structure created during sublimation has a very large surface area. When a solvent (like sterile water) is added, it can quickly penetrate this structure, allowing the product to dissolve and be reconstituted in seconds. This is a critical advantage for emergency medicine and clinical convenience.
Simplified Logistics and Storage
By enabling room temperature storage, freeze drying can eliminate the need for a continuous and expensive "cold chain"—the refrigerated network required for storing and transporting many liquid biologics. This simplifies global distribution, reduces shipping costs, and lowers the risk of product loss due to temperature excursions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, freeze drying is not a universal solution. Objectivity requires acknowledging its significant challenges.
Process Complexity and Cost
Lyophilization is a slow, multi-day process that is highly energy-intensive. The specialized equipment is expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain, making it one of the costliest unit operations in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Formulation Challenges
You cannot simply put any liquid drug into a freeze dryer. Successful lyophilization often requires extensive formulation development, including the addition of excipients (like sugars or amino acids) that act as cryoprotectants and lyoprotectants to shield the API during freezing and drying stresses.
Potential for Vial Breakage
The freezing step induces significant thermal stress on the product's primary container (typically a glass vial). Without careful process optimization, this can lead to container breakage, resulting in sterility breaches and product loss.
Is Freeze Drying the Right Choice for Your Product?
The decision to use lyophilization is a strategic balance between quality requirements, logistical needs, and cost.
- If your primary focus is stability for a biologic or vaccine: Freeze drying is often the gold standard for preserving the structure and function of complex, temperature-sensitive molecules.
- If your primary focus is extending shelf-life and simplifying logistics: Lyophilization offers a clear advantage by enabling room-temperature storage and reducing or eliminating cold-chain dependency.
- If your primary focus is rapid development and low cost: You must weigh the superior quality of freeze drying against its significant investment in process development, cycle time, and capital equipment.
Ultimately, freeze drying is a strategic investment in product quality, trading upfront complexity for long-term stability and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Extended Shelf-Life | Stable for 2-5+ years at room temperature vs. months for liquids |
| Preserved Potency | Minimizes chemical degradation (e.g., hydrolysis) of APIs |
| Structural Integrity | Maintains 3D structure of proteins, antibodies, and vaccines |
| Simplified Logistics | Reduces or eliminates the need for expensive cold chain storage |
| Rapid Reconstitution | Porous cake structure allows for dissolution in seconds |
Ready to enhance the stability and shelf-life of your pharmaceutical products? The freeze drying process is a precise science requiring reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Our expertise can help you navigate the complexities of lyophilization to achieve superior product quality. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for drying nickel nanoparticle precursors? Prevent Hard Agglomeration Now



















