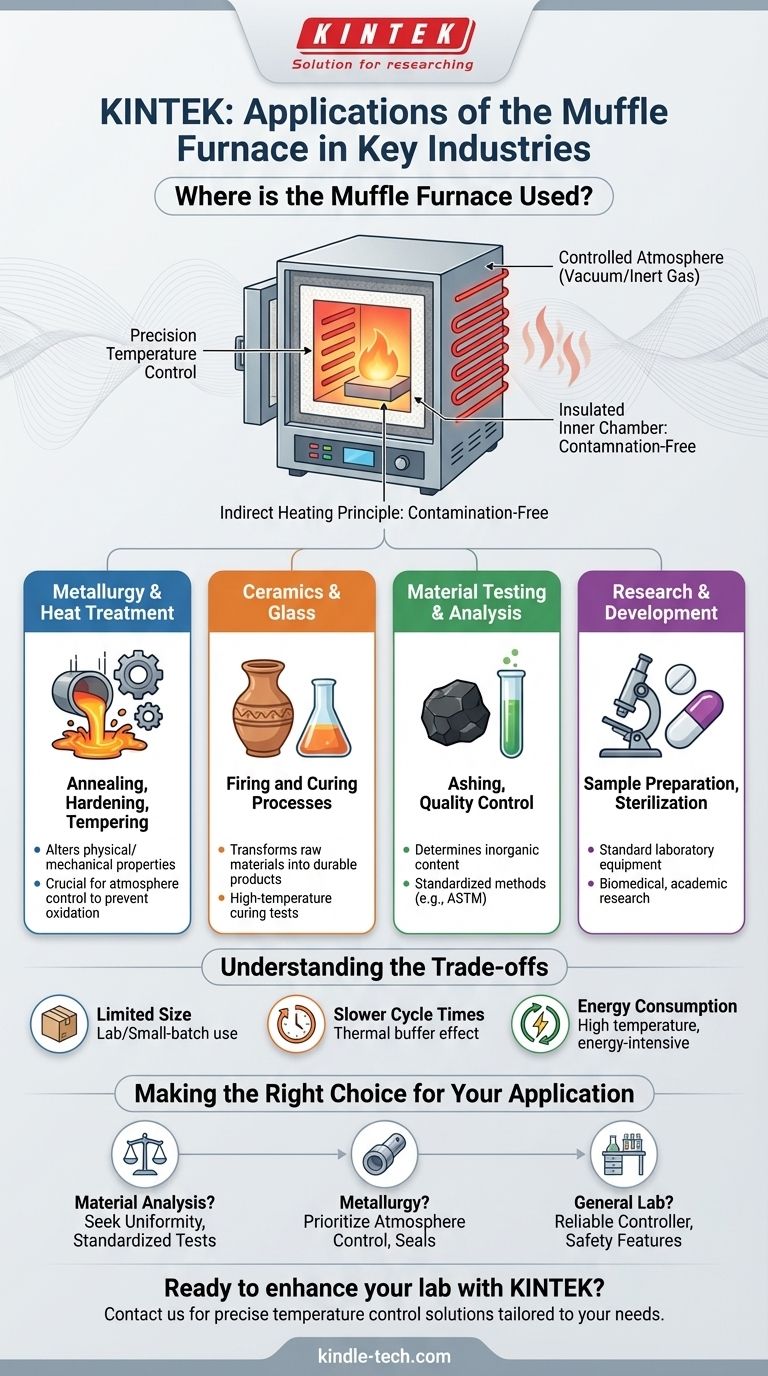
Fundamentally, the muffle furnace is a critical tool in any field that requires high-temperature, controlled thermal processing. Its applications are exceptionally broad, spanning industries such as metallurgy, ceramics, material science, and chemical analysis. You will find it used in sectors ranging from electric power and petrochemicals to biomedical research and agriculture.
The muffle furnace's value comes from its core function: providing a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment that is isolated from the contaminants of fuel and combustion. This simple principle makes it an indispensable tool for material testing, heat treatment, and sample preparation across countless scientific and industrial domains.

What Makes a Muffle Furnace So Versatile?
The widespread adoption of the muffle furnace is not due to a single-use case, but rather its fundamental design that serves several critical functions.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The name "muffle" refers to the furnace's core design feature: an insulated inner chamber that contains the sample.
This chamber is heated from the outside by heating elements. The sample never comes into direct contact with the source of heat, which prevents contamination from combustion byproducts. This ensures the integrity of the material being processed.
Precision Temperature Control
As the references note, these furnaces are equipped with thermocouples and sophisticated controllers. This allows for extremely precise and repeatable temperature cycles.
This level of control is non-negotiable for scientific research and quality control, where processes must be standardized to yield reliable results.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
Because the chamber is sealed, users can often modify the atmosphere inside. This may involve creating a vacuum or introducing specific gases like nitrogen or argon.
This capability is essential in metallurgy for processes like annealing or brazing, where oxygen would react with and damage the metal.
Key Applications Across Industries
Understanding the core function of clean, controlled heat allows us to see why the muffle furnace is essential in so many seemingly unrelated fields.
Material Testing and Analysis
In industries like coal, cement, and petrochemicals, the furnace is a workhorse for quality control. It is commonly used for ashing, a process where a sample is burned at high temperatures to determine its inorganic content.
Heat Treatment of Metals
The metallurgical industry relies heavily on muffle furnaces for treating metal parts to alter their physical and mechanical properties. Common processes include annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering (increasing toughness).
Firing and Curing Processes
In the ceramics and glass industries, furnaces are used to fire materials, transforming them from a raw state into a hard, durable final product. In the paint and coatings industry, they can be used for high-temperature curing tests.
Research and Development
For pharmaceutical, biomedical, and academic research, the muffle furnace is a standard piece of laboratory equipment. It's used for everything from sterilizing equipment to preparing samples for chemical analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, the muffle furnace is not the solution for every heating application. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Limited Chamber Size
Most muffle furnaces are designed for laboratory or small-batch use. They are generally not suitable for mass production or processing very large components, where larger industrial ovens are required.
Slower Cycle Times
The "muffle" that protects the sample also acts as a thermal buffer. This can result in slower heating and cooling rates compared to direct-fired furnaces, potentially increasing process time.
Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures that can exceed 1000°C (1800°F) is an energy-intensive process. The operational cost, particularly for frequent or prolonged use, can be a significant factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right tool, you must first define your goal. Different applications prioritize different features.
- If your primary focus is material analysis (e.g., ashing): Seek a furnace with certified temperature uniformity and a controller that can accurately follow standardized test methods (like those from ASTM).
- If your primary focus is metallurgical heat treatment: Prioritize a furnace with ports and seals that allow for atmosphere control to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory research: A versatile benchtop model with a reliable digital controller and robust safety features is the most practical choice.
By understanding its core function of providing clean, controlled heat, you can identify the critical role of the muffle furnace in nearly any technical field.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Material Testing | Ashing, Quality Control | Determines inorganic content of samples |
| Metallurgy | Annealing, Hardening | Alters physical/mechanical properties of metals |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing | Transforms raw materials into durable products |
| Research & Development | Sample Preparation, Sterilization | Supports pharmaceutical and academic labs |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a reliable muffle furnace?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific industry needs. Whether you're in material science, metallurgy, or chemical analysis, our muffle furnaces offer the precise temperature control and contamination-free environment required for accurate results.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover the perfect solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the maintenance of laboratory equipment? Ensure Data Integrity and Extend Equipment Lifespan
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is SV and PV in a muffle furnace? Master Temperature Control for Precision Results
- How does a muffle work? Achieve Clean, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the difference between oven incubator and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Heating Tool



















