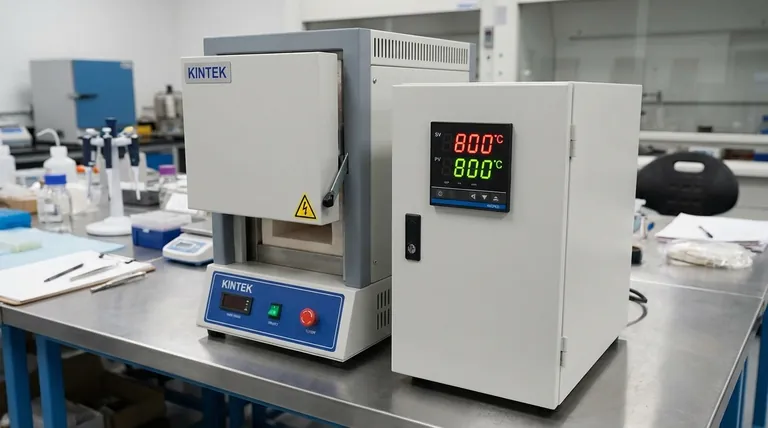
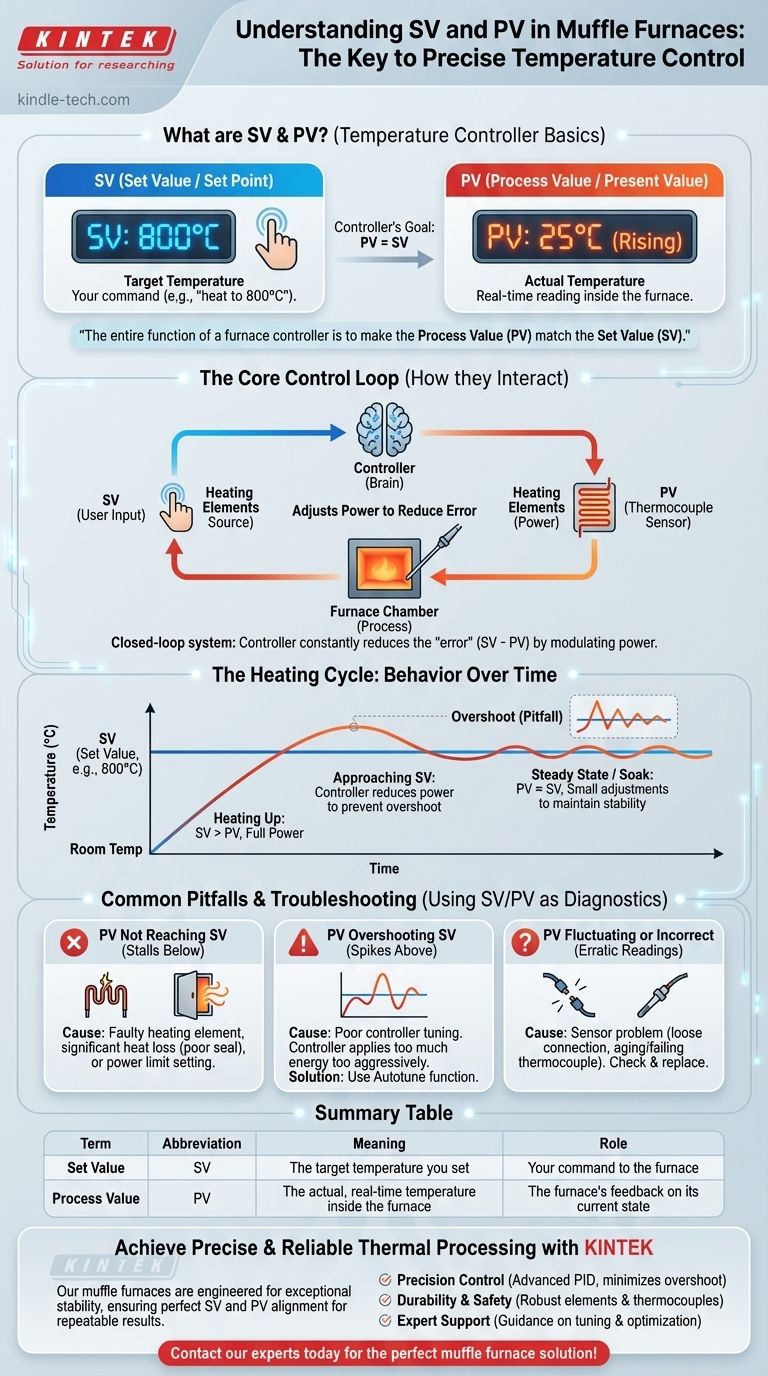
In the context of a muffle furnace, SV and PV are the two most critical values displayed on its temperature controller. SV stands for Set Value (or Set Point), which is the target temperature you want the furnace to reach. PV stands for Process Value (or Present Value), which is the actual, real-time temperature measured inside the furnace.
The entire function of a furnace controller is to make the Process Value (PV) match the Set Value (SV). Think of SV as your command—"heat to 800°C"—and PV as the furnace's real-time report on its progress toward that command.

The Core Function: How SV and PV Interact
Understanding the relationship between SV and PV is fundamental to operating any computer-controlled heating equipment. They are two halves of a closed-loop control system.
SV: Defining Your Target Temperature
The Set Value (SV) is the desired operational temperature. This is a user-defined input.
You determine the SV based on the requirements of your specific process, such as ashing, annealing, or material testing. Setting the SV is the first step you take when programming a heating cycle.
PV: Measuring the Real-Time Reality
The Process Value (PV) is the actual temperature inside the furnace chamber at any given moment. It is a measured value, not a setting.
This reading is provided by a sensor, typically a thermocouple, which is a robust probe designed to withstand extreme heat. The controller constantly monitors the thermocouple's signal to display the current PV.
The Controller: The Brain Closing the Loop
The furnace's temperature controller is the brain that connects the SV and PV. Its sole job is to constantly compare the two values.
The difference between SV and PV is known as the "error." The controller's goal is to reduce this error to zero by adjusting power to the heating elements. This is analogous to a thermostat in your home: you set the temperature (SV), it measures the room's air (PV), and it turns the heat on or off accordingly.
Understanding the Control Process
The interaction between SV and PV governs the furnace's behavior during both heating up and maintaining temperature.
The Heating Cycle: From Cold to Setpoint
When you first turn on the furnace, the PV is at room temperature while the SV is set high (e.g., 900°C). The controller sees a large error (SV > PV).
In response, the controller applies full power to the heating elements to raise the temperature as quickly as possible. As the PV gets closer to the SV, a smart controller (like a PID controller) will begin to reduce power to prevent overshooting the target.
Maintaining Stability: The Steady State
Once the PV reaches the SV, the controller's job shifts from rapid heating to precise maintenance. This is often called the "soak" or "dwell" period.
The controller will make small, continuous adjustments, pulsing power to the heating elements just enough to counteract heat loss to the surrounding environment. This ensures the PV remains stable and as close to the SV as possible for the duration of your process.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
The relationship between SV and PV is your primary diagnostic tool for identifying furnace problems.
Why is My PV Not Reaching SV?
If the PV stalls out well below the SV, it indicates the furnace cannot generate enough heat to reach the target.
This is typically caused by a faulty heating element, significant heat loss from a poorly sealed door, or a controller setting that is limiting the maximum power output.
Why is My PV Overshooting SV?
Overshoot occurs when the temperature climbs significantly past the setpoint before settling back down. This can ruin sensitive processes.
This is almost always a sign of poor controller tuning. The controller is applying too much energy too aggressively as it nears the setpoint. Most modern controllers have an autotune function that runs a test cycle to "learn" the furnace's thermal characteristics and optimize its own behavior.
What if the PV is Fluctuating or Incorrect?
An erratic, unstable, or clearly incorrect PV reading usually points to a sensor problem.
Check for a loose connection or a failing thermocouple. As thermocouples age, they can degrade and lose accuracy, requiring replacement.
Making Sense of Your Furnace's Display
Interpreting SV and PV correctly is the key to achieving repeatable and successful results in your thermal processes. Use the display as a window into the furnace's performance.
- If your primary focus is running a simple heating cycle: Set your desired temperature (SV) and monitor the PV until it stabilizes at that value before starting your process timer.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a problem: The relationship between SV and PV is your main diagnostic tool. If PV can't reach SV, investigate power and heat loss. If PV overshoots or oscillates, investigate the controller's tuning.
- If your primary focus is achieving high precision: Use the controller's "autotune" function before running critical processes to minimize the difference between PV and SV and prevent temperature overshoot.
Understanding the dynamic between your command (SV) and the system's response (PV) empowers you to control your thermal processes with precision and confidence.
Summary Table:
| Term | Abbreviation | Meaning | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set Value | SV | The target temperature you set | Your command to the furnace |
| Process Value | PV | The actual, real-time temperature inside the furnace | The furnace's feedback on its current state |
Achieve precise and reliable thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced muffle furnaces.
Understanding SV and PV is just the first step. Our laboratory equipment is engineered for exceptional temperature stability and control, ensuring your SV and PV values align perfectly for repeatable results in ashing, annealing, and material testing.
Let KINTEK empower your lab:
- Precision Control: Advanced PID controllers minimize overshoot and maintain tight temperature uniformity.
- Durability & Safety: Built with robust heating elements and thermocouples for long-lasting performance.
- Expert Support: Get guidance on controller tuning, troubleshooting, and optimizing your thermal processes.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What does a lab muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- How to use a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Operation
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace work? Achieve Contaminant-Free, Uniform Heating



















