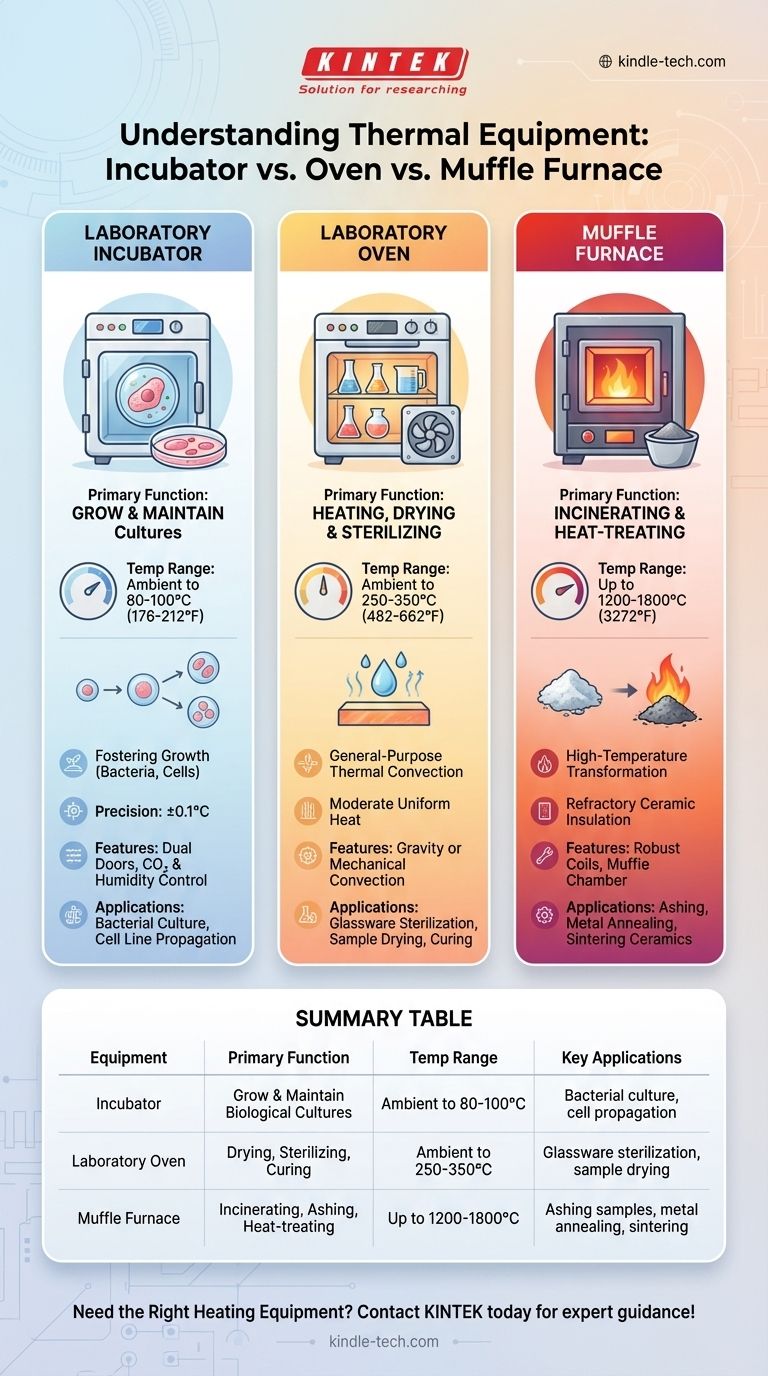
At their core, the difference between an oven, an incubator, and a muffle furnace comes down to their intended function and their operational temperature range. An incubator provides gentle, precise heat to grow and maintain biological cultures. A laboratory oven delivers moderate, uniform heat for drying, curing, or sterilizing. A muffle furnace generates extremely high temperatures to burn away substances or fundamentally alter materials.
While all three are essentially insulated boxes that heat things, they are not interchangeable. Using the wrong one can destroy your sample and damage the equipment. The key is to match the tool's specialized heating capability to your specific scientific or industrial goal.

The Laboratory Incubator: Fostering Growth
A laboratory incubator is a precision instrument designed to create the optimal environment for cultivating living organisms. Its primary goal is not just heating, but maintaining a stable, controlled atmosphere.
Primary Function
The core purpose of an incubator is to grow and maintain microbiological or cell cultures. It mimics the ideal environmental conditions required for organisms like bacteria, yeast, or animal cells to thrive.
Temperature Range
Incubators operate at relatively low temperatures, typically from just above ambient to around 80-100°C (176-212°F). They are designed for exceptional temperature stability, often holding a set point with a precision of ±0.1°C.
Key Features
Most incubators feature a dual-door design, with an inner glass door that allows for sample inspection without significantly disturbing the internal atmosphere. Many advanced models also offer humidity and CO₂ control to simulate physiological conditions for cell cultures.
Common Applications
You will find incubators in microbiology, molecular biology, and cell biology labs for tasks such as bacterial culture growth, cell line propagation, and biochemical assays.
The Laboratory Oven: Heating and Drying
A laboratory oven is a general-purpose workhorse for thermal convection. Its design is focused on providing uniform, stable heat at temperatures significantly higher than an incubator.
Primary Function
The main functions of an oven are drying, curing, sterilizing, and aging. The goal is typically to remove moisture from a sample or to induce a physical or chemical change through moderate heat.
Temperature Range
Laboratory ovens operate in a moderate temperature range, usually from ambient up to 250-350°C (482-662°F). They provide stable heat but without the ultra-fine precision of an incubator.
Key Features
Ovens are built for durability, often with stainless steel interiors and robust shelving. They may use gravity convection (for delicate samples) or mechanical convection (a fan) for faster heating and superior temperature uniformity.
Common Applications
Their use is widespread, from sterilizing lab glassware and drying chemical samples to curing polymers and performing materials testing.
The Muffle Furnace: High-Temperature Transformation
A muffle furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed to achieve extremely high temperatures. Its construction is fundamentally different from ovens and incubators to handle intense heat.
Primary Function
The furnace is used for applications that require incinerating, ashing, or heat-treating materials. The process fundamentally alters or destroys the sample, for example, by burning off all organic matter to determine the inorganic content (ash).
Temperature Range
Muffle furnaces operate at very high temperatures, typically starting around 300°C and going up to 1200°C, 1500°C, or even 1800°C (3272°F) depending on the model.
Key Features
These units feature thick, multi-layered refractory ceramic insulation to contain the extreme heat. The heating elements are robust coils that heat an inner chamber, or "muffle," which ensures the sample is heated uniformly by radiation, separate from the direct heating elements.
Common Applications
Furnaces are essential in materials science, analytical chemistry, and engineering for ashing food or chemical samples, heat-treating metals (annealing), sintering ceramics, and gravimetric analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these devices means understanding their core design differences. Using one for a task it wasn't designed for is inefficient at best and destructive at worst.
Temperature is the Primary Differentiator
The operational temperature range is the most significant factor. An incubator cannot sterilize glassware, and an oven cannot ash a sample. A furnace would instantly destroy a petri dish culture.
Precision vs. Power
An incubator prioritizes precision and stability over raw heating power. Its gentle heating system is designed to avoid temperature overshoots that could kill a culture. A furnace prioritizes raw power to reach extreme temperatures quickly and efficiently. An oven strikes a balance between the two.
Construction and Safety
The materials used in construction reflect their purpose. An incubator's plastic components or sensitive electronics would melt in a lab oven. The metallic interior of an oven would oxidize and degrade rapidly at the temperatures inside a muffle furnace, which is why furnaces rely on specialized ceramics.
Matching the Equipment to Your Task
Your choice must be driven by the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is cultivating biological samples: You must use an incubator for its low-temperature precision and atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing materials below 350°C: A laboratory oven is the correct and most efficient tool.
- If your primary focus is determining ash content, heat-treating metals, or testing materials at extreme temperatures: A muffle furnace is the only option.
Selecting the right thermal equipment is the foundational step toward achieving reliable and repeatable results in the lab.
Summary Table:
| Equipment | Primary Function | Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incubator | Grow and maintain biological cultures | Ambient to 80-100°C | Bacterial culture, cell propagation |
| Laboratory Oven | Drying, sterilizing, curing | Ambient to 250-350°C | Glassware sterilization, sample drying |
| Muffle Furnace | Incinerating, ashing, heat-treating | Up to 1200-1800°C | Ashing samples, metal annealing, sintering |
Need the Right Heating Equipment for Your Lab?
Choosing between an incubator, oven, or muffle furnace is critical for your research accuracy and sample integrity. KINTEK specializes in providing precisely the right lab equipment for your specific thermal applications.
We help you:
- Select the perfect equipment based on your temperature requirements and sample type
- Ensure reliable results with precision-controlled heating systems
- Protect your samples from thermal damage with the appropriate technology
Our team understands that using the wrong heating tool can destroy samples and compromise your work. Let us match you with the ideal solution from our range of incubators, ovens, and muffle furnaces.
Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss your laboratory heating needs and get expert guidance on the right equipment for your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is tempering the process of annealing? Understanding Their Opposing Goals in Heat Treatment
- How is a muffle furnace applied in assessing the high-temperature oxidation resistance of Ti/Al2O3 composites?
- What is a sintering oven? The Key to High-Performance Powder Metallurgy and 3D Printing
- What are the safety precautions for a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Burns, Fires, and Electrical Hazards
- What function does a muffle furnace serve in Mg-doped NASICON powder preparation? Master Solid-State Synthesis
- How does a muffle furnace with a PID controller impact doped zinc oxide nanoparticles? Precise Synthesis Control
- Why is a high-precision muffle furnace necessary for SDSS heat treatment? Achieve Superior Microstructural Stability.
- What is the objective of sintering? Transforming Powders into High-Performance Solid Parts



















