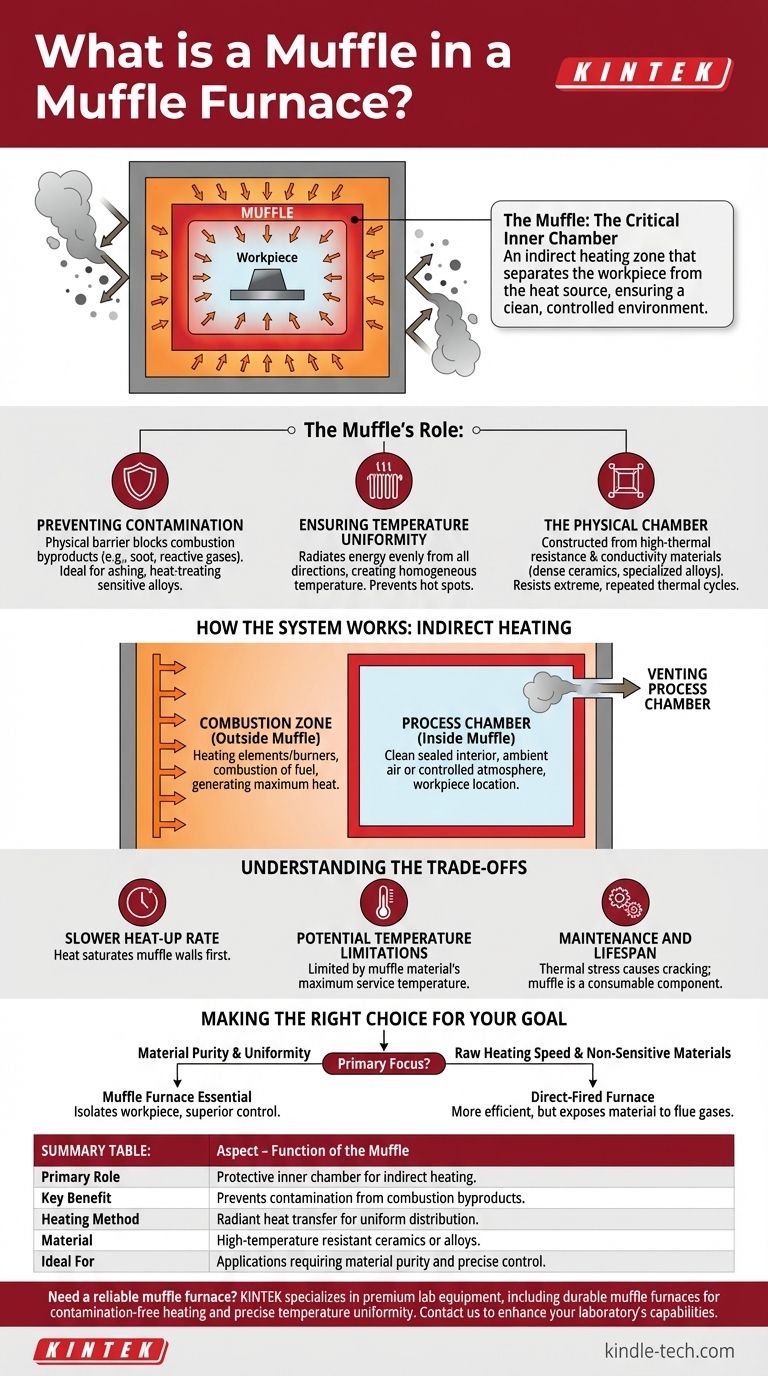
In a muffle furnace, the "muffle" is the critical inner chamber that separates the material being heated from the furnace's heat source. It is essentially a high-temperature, sealed box made of a heat-resistant material. This design allows heat to penetrate the muffle's walls and radiate onto the workpiece without any direct contact from flames or exposure to the byproducts of combustion.
The core principle of a muffle furnace is indirect heating. The muffle acts as a protective shield, allowing heat to radiate uniformly to the workpiece while isolating it from contaminants produced by the burning fuel.

The Muffle's Role: Creating a Controlled Environment
A muffle furnace is not just about generating high temperatures; it's about controlling the exact conditions under which a material is heated. The muffle itself is the component that makes this control possible.
Preventing Contamination
In a direct-fired furnace, byproducts from combustion—like soot or reactive gases—can settle on or react with the material being processed.
The muffle creates a physical barrier, ensuring the atmosphere inside the process chamber remains clean and predictable. This is vital for applications like ashing, heat-treating sensitive alloys, or chemical analysis where purity is paramount.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The muffle’s walls heat up and then radiate that energy evenly inward from all directions. This method of radiant and convective heat transfer provides a far more homogenous temperature environment than direct flame impingement, which can create hot spots.
This uniformity is critical for ensuring consistent results across the entire workpiece, from low-carbon steel production to the sintering of dental ceramics.
The Physical Chamber
The muffle is constructed from materials with high thermal resistance and conductivity, such as dense ceramics or specialized metal alloys.
It must be durable enough to withstand extreme, repeated temperature cycles while remaining efficient at transferring thermal energy from the outside to the inside.
How the System Works: Indirect Heating
The term "muffle furnace" describes a two-zone system. Understanding the distinction between what happens inside versus outside the muffle is key to grasping its function.
The Combustion Zone (Outside the Muffle)
This is the outer area of the furnace where the heating elements (in an electric furnace) or burners (in a gas furnace) are located.
The furnace is designed with sufficient space in this zone to ensure the complete and efficient combustion of fuel, generating the maximum amount of heat.
The Process Chamber (Inside the Muffle)
This is the clean, sealed interior where the workpiece is placed. The only gases present in this chamber are the ambient air (or a specific controlled atmosphere) and any gases released by the workpiece itself during heating.
Venting the Process Chamber
Even though the muffle protects from external contaminants, the heating process itself can generate smoke, fumes, or toxic gases from the material inside.
For this reason, muffle furnaces are equipped with an exhaust outlet. This allows for the safe removal of these internal byproducts, ensuring a safe operating environment and a clean chamber for the next run.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the muffle design offers significant advantages, it is important to recognize the associated engineering trade-offs.
Slower Heat-Up Rate
Because the heat must first saturate the muffle's walls before it can be transferred to the workpiece, a muffle furnace may have a slightly slower initial heat-up time compared to a direct-fired furnace.
Potential Temperature Limitations
The muffle itself has a maximum service temperature. The overall operating temperature of the furnace is limited by what the muffle material can safely and repeatedly withstand without degrading.
Maintenance and Lifespan
The muffle is subjected to immense thermal stress. Over time, repeated heating and cooling cycles can cause cracking or degradation, making it a consumable component that may eventually require replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a muffle furnace hinges on whether your process demands a clean, highly controlled heating environment.
- If your primary focus is material purity and avoiding contamination: A muffle furnace is essential, as it isolates your workpiece from the damaging byproducts of combustion.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature uniformity: The radiant heating provided by the enclosed muffle chamber offers superior control and consistency compared to direct-heating methods.
- If your primary focus is raw heating speed for non-sensitive materials: A direct-fired furnace might be a more efficient choice, provided your material will not be compromised by exposure to flue gases.
Ultimately, the muffle is the component that transforms a simple oven into a precise instrument for controlled thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Function of the Muffle |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Acts as a protective inner chamber for indirect heating |
| Key Benefit | Prevents contamination from combustion byproducts |
| Heating Method | Radiant heat transfer for uniform temperature distribution |
| Material | Made from high-temperature resistant ceramics or alloys |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring material purity and precise temperature control |
Need a reliable muffle furnace for your lab's high-temperature applications? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment, including durable muffle furnaces designed for contamination-free heating, precise temperature uniformity, and long-lasting performance. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace to meet your specific material processing needs. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's trusted solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heat transfer of a muffle furnace? Understanding Indirect Heating for Purity
- What temperature is needed for metal casting? Achieve Perfect Casts with the Right Superheat
- What is the capacity of a muffle furnace? Find the Right Size for Your Lab Needs
- How does heat affect material strength? Understanding Thermal Degradation and Creep Failure
- Why is the melting point different for different substances? The Key Role of Bond Strength



















