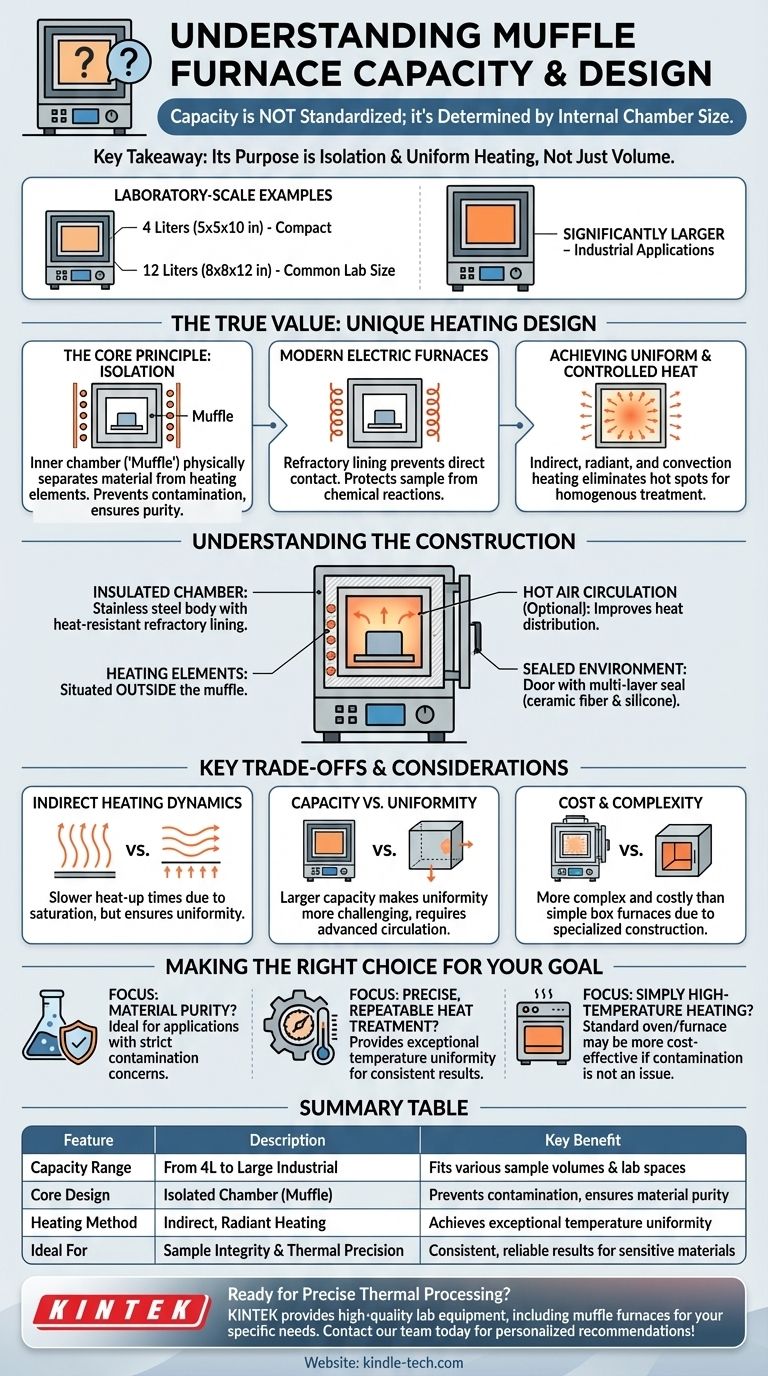
The capacity of a muffle furnace is not standardized; it is determined by the internal chamber size of a specific model. For example, common laboratory-scale models can range from a compact 4 liters (with a chamber size of 5 x 5 x 10 inches) to 12 liters (8 x 8 x 12 inches) and significantly larger for industrial applications.
The critical takeaway is not the specific volume of a muffle furnace, but its fundamental design purpose: to heat materials within an isolated chamber, protecting them from the contaminants of the heat source and ensuring exceptional temperature uniformity.

What Defines a Muffle Furnace Beyond Its Size?
While capacity is a practical specification, the true value of a muffle furnace lies in its unique method of heating. This design directly impacts the quality and reliability of your results.
The Core Principle: Isolation
The defining feature of this furnace is the "muffle"—an inner chamber that physically separates the material being processed from the heating elements.
In older fuel-fired furnaces, this was essential to prevent byproducts of combustion from contaminating the samples.
Modern Electric Furnaces
In modern electric muffle furnaces, the principle of isolation remains critical. The refractory material of the muffle ensures there is no direct contact between the high-temperature heating elements and the sample.
This prevents any potential chemical reactions or contamination, ensuring the purity of the material being treated.
Achieving Uniform and Controlled Heat
The muffle design is fundamental to achieving highly uniform temperatures.
The entire inner chamber is heated, which then transfers heat to the workpiece through a combination of radiant and convection methods. This indirect approach eliminates hot spots that can occur with direct element exposure, resulting in a homogenous treatment.
Understanding the Construction
The furnace's capacity and performance are a direct result of its specialized construction and materials.
The Insulated Chamber
The furnace body is typically a box-shaped cabinet made of stainless steel, containing an inner chamber lined with heat-resistant refractory material.
This lining serves two purposes: it acts as the muffle for isolating the sample and provides excellent thermal insulation to prevent heat loss, making the furnace energy-efficient.
Heating and Circulation
High-temperature electric heating elements are situated outside the muffle. A hot air circulation system is often included to further improve the even distribution of heat throughout the chamber.
Sealing the Environment
The furnace door is a critical component for maintaining temperature and atmosphere. It often features a multi-layer seal, such as an inner ceramic fiber rope and an outer silicone ring.
This robust sealing, combined with a multi-point locking mechanism, ensures the internal environment remains stable and free from external contaminants during operation.
Key Trade-offs and Considerations
Understanding the inherent design trade-offs of a muffle furnace is key to determining if it is right for your application.
Indirect Heating Dynamics
The very isolation that protects your sample also means heating is indirect. Heat must first saturate the muffle, which then radiates it to the sample.
While this ensures uniformity, it can mean slightly slower heat-up times compared to furnaces where elements are exposed directly to the workload.
Capacity and Uniformity
As the furnace capacity increases, maintaining perfect temperature uniformity becomes more challenging.
Larger industrial models require more sophisticated air circulation systems and control logic to ensure that materials in the corners of the chamber are heated at the same rate as those in the center.
Cost and Complexity
The specialized construction, including the refractory-lined muffle and advanced sealing systems, makes these furnaces more complex and typically more costly than simple box furnaces of a similar size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace should be based on your primary objective, not just its internal volume.
- If your primary focus is material purity: The isolating nature of the muffle is its most significant advantage, making it the ideal choice for applications where contamination is a critical concern.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable heat treatment: The exceptional temperature uniformity provided by the indirect heating design ensures consistent results for sensitive materials and experiments.
- If your primary focus is simply high-temperature heating: A standard laboratory oven or furnace without a muffle might be a more cost-effective solution, provided sample contamination is not an issue.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize sample integrity and thermal precision over all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity Range | From compact 4L to large industrial models. | Fits various sample volumes and lab spaces. |
| Core Design | Isolated chamber (muffle) separates sample from heating elements. | Prevents contamination, ensures material purity. |
| Heating Method | Indirect, radiant heating from the heated muffle chamber. | Achieves exceptional temperature uniformity. |
| Ideal For | Applications where sample integrity and thermal precision are critical. | Consistent, reliable results for sensitive materials. |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your laboratory's specific capacity and purity requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including a range of muffle furnaces designed for precise thermal processing. Our experts can help you select the ideal model to ensure your materials are heated uniformly and protected from contamination.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an electric furnace? A Guide to Precision Heating
- How do you cool a muffle furnace? Safeguard your equipment and samples from thermal shock.
- What is the working principle of muffle furnace? Achieving Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and hot oven? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thermal Tool
- Can a muffle furnace be used for calcination? Achieve Pure, Controlled Thermal Decomposition



















