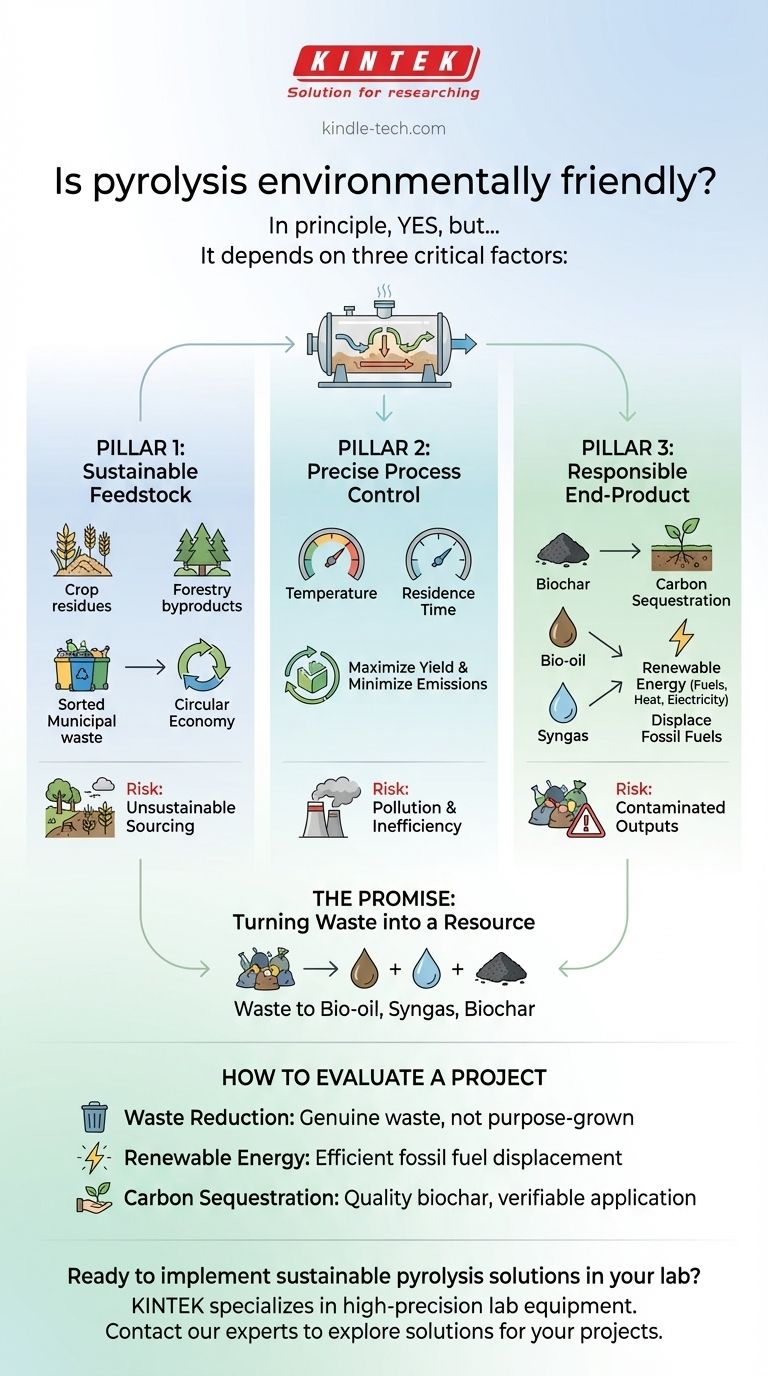
In principle, yes, pyrolysis is an environmentally friendly technology, but its actual impact depends entirely on how it is implemented. When managed correctly, pyrolysis converts waste materials into renewable energy and valuable products, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and can even capture carbon from the atmosphere. However, poor execution can lead to pollution and unsustainable resource use.
The environmental friendliness of pyrolysis is not inherent in the process itself. It is a direct result of three critical factors: the sustainability of the feedstock, the precision of the process control, and the responsible application of the end-products.

The Promise: Turning Waste into a Resource
Pyrolysis is a method of thermal decomposition, heating organic materials like biomass in the absence of oxygen. Because no burning occurs, the process breaks down materials into valuable new substances instead of just releasing their energy as heat and smoke.
From Problematic Waste to Valuable Products
Pyrolysis provides a powerful pathway to process materials that would otherwise end up in a landfill.
This includes agricultural residues, wood scraps, and even components of municipal solid waste. The process creates three primary outputs: bio-oil, syngas, and biochar.
A Pathway to Renewable Energy
The bio-oil can be refined into transportation fuels, and the syngas (a mix of hydrogen and carbon monoxide) can be used to generate heat or electricity.
These products create a renewable energy source from waste, directly reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and the pollution associated with their extraction and combustion.
The Three Pillars of "Green" Pyrolysis
To be considered environmentally friendly, a pyrolysis operation must be built on a foundation of sustainable practices from start to finish.
Pillar 1: Sustainable Feedstock Sourcing
The single most important factor is the source of the raw material, or feedstock.
Using genuine waste products—such as crop residues, forestry byproducts, or sorted municipal waste—is highly beneficial. This approach creates a circular economy.
Conversely, if the demand for feedstock leads to deforestation or the harvesting of purpose-grown crops that displace food agriculture, the environmental benefit is completely negated.
Pillar 2: Precise Process Control
The efficiency and cleanliness of the operation are determined by technical parameters like temperature and residence time (how long material stays in the reactor).
A well-controlled process maximizes the yield of valuable products and ensures that harmful emissions are not created. Poor control can lead to inefficient conversion and the release of pollutants.
Pillar 3: Responsible End-Product Application
The final products must be used in an environmentally sound way. The most powerful example of this is biochar.
Biochar is a stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. When added to soil, it does not decompose for hundreds or thousands of years. This process of carbon sequestration effectively locks atmospheric carbon into the ground, actively removing it from the carbon cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While the potential is enormous, it is critical to acknowledge the potential downsides when evaluating any pyrolysis project.
The Risk of Unsustainable Sourcing
The primary risk is creating a market that incentivizes unsustainable harvesting of biomass. Any credible project must have a transparent and verifiable supply chain that relies on legitimate waste streams.
The Problem of Contaminated Feedstock
When using mixed waste streams like municipal solid waste, there is a risk of contamination from plastics, heavy metals, or other hazardous materials. This requires sophisticated sorting systems and process controls to ensure these contaminants don't end up in the final products or released as pollution.
The Challenge of Inefficient Operations
A poorly designed or operated facility is not environmentally friendly. It can be energy-negative (using more energy than it produces) and fail to properly convert materials, resulting in pollution and waste instead of valuable resources.
How to Evaluate a Pyrolysis Project
To determine if a specific application is truly beneficial, analyze it based on its primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Verify that the feedstock is genuinely a waste material being diverted from landfills, not a purpose-grown resource.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: Scrutinize the process's energy efficiency and confirm that the resulting bio-oil or syngas is effectively displacing fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: Investigate the quality of the biochar produced and ensure there is a clear, verifiable plan for its application in soil.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a technology whose environmental benefit is realized not by its existence, but by its disciplined and responsible execution.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmentally Friendly | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Uses genuine waste (e.g., agricultural residues) | Unsustainable sourcing (e.g., deforestation) |
| Process Control | Maximizes product yield, minimizes emissions | Inefficient operations causing pollution |
| End-Products | Biochar sequesters carbon; bio-oil/syngas replace fossil fuels | Contaminated outputs from poor waste sorting |
Ready to implement sustainable pyrolysis solutions in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-precision lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research, helping you optimize feedstock conversion, process control, and product quality. Contact our experts today to explore how our solutions can advance your waste-to-energy or carbon sequestration projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















