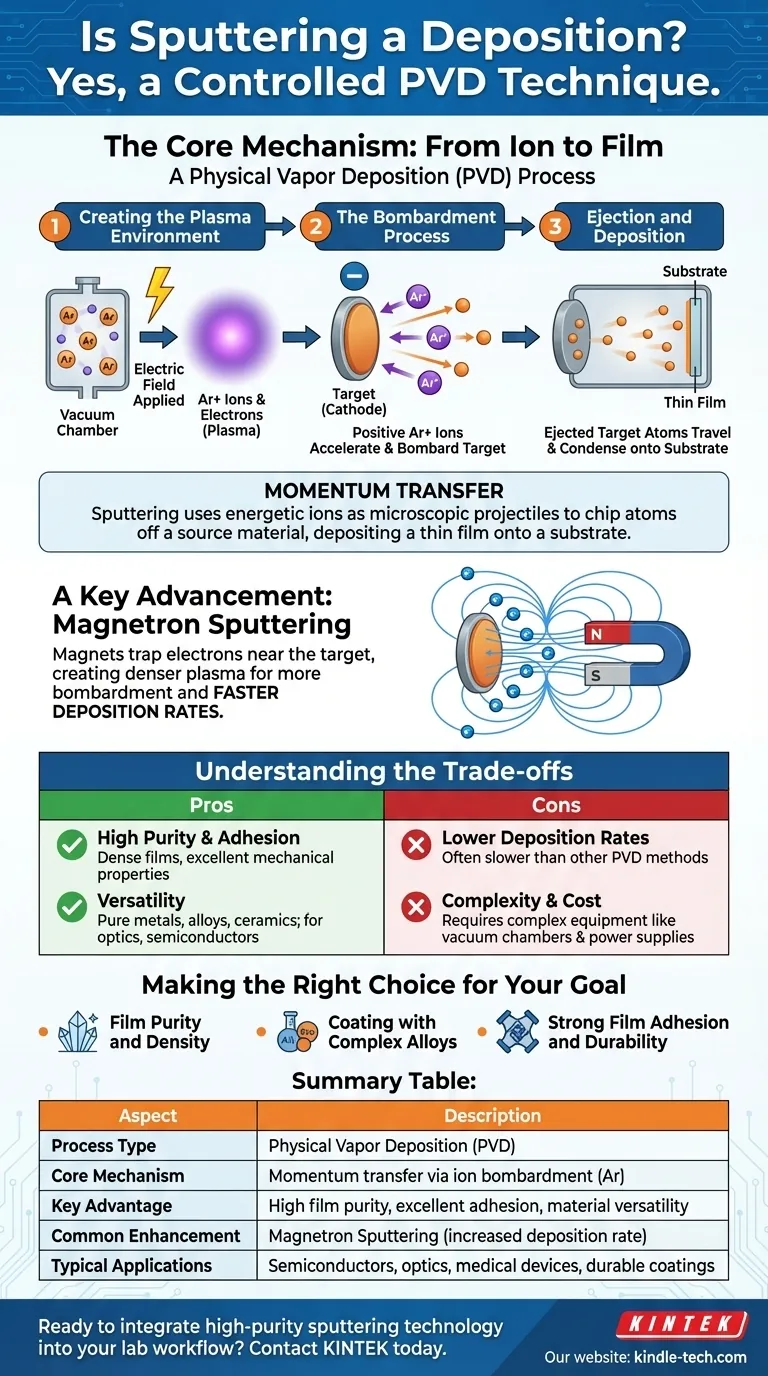
Yes, sputtering is a highly controlled deposition technique. It is a method of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) where a solid material, known as the "target," is bombarded with high-energy ions. This bombardment physically ejects or "sputters" atoms from the target, which then travel through a vacuum chamber and condense onto a component, forming an extremely thin and uniform coating.
At its core, sputtering is not a chemical reaction but a physical momentum transfer process. It uses energetic ions as microscopic projectiles to chip atoms off a source material, which then deposit as a thin film onto a substrate.
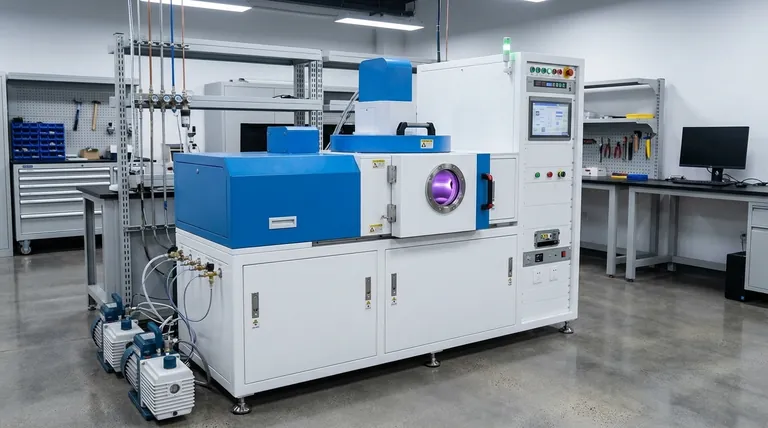

The Core Mechanism: From Ion to Film
To understand sputtering, it’s best to break it down into a sequence of events that happen inside a vacuum chamber. This process ensures the purity and quality of the final deposited layer.
Creating the Plasma Environment
The process begins by creating a near-vacuum and then introducing a small, controlled amount of an inert gas, almost always argon. An electric field is applied, which energizes the gas and strips electrons from the argon atoms, creating a glowing, ionized gas known as plasma.
The Bombardment Process
The source material to be deposited, the target, is given a negative electrical charge (making it a cathode). The positively charged argon ions from the plasma are then aggressively accelerated by the electric field, causing them to collide with the target at high velocity.
Ejection and Deposition
Each impact from an argon ion has enough kinetic energy to knock atoms loose from the target's surface. These ejected target atoms travel through the vacuum chamber until they strike the object being coated (the substrate), where they condense and build up, layer by layer, to form a thin film.
A Key Advancement: Magnetron Sputtering
While the basic sputtering process is effective, it can be slow. Modern systems almost always use magnetron sputtering to dramatically increase the efficiency and speed of deposition.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
In DC magnetron sputtering, powerful magnets are placed behind the target. This magnetic field traps the free electrons from the plasma, forcing them to stay close to the surface of the target.
The Impact on Efficiency
By trapping these electrons, the magnetic field significantly increases the probability that they will collide with and ionize more argon atoms. This creates a much denser plasma directly in front of the target, leading to more ion bombardment and, consequently, a much faster deposition rate even at lower gas pressures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sputtering is a powerful and versatile technique, but like any engineering process, it involves specific trade-offs. Understanding these is key to deciding if it's the right method for your application.
Pro: High Purity and Adhesion
Because sputtering is a physical process, the composition of the deposited film is extremely close to that of the source target. The kinetic energy of the deposited atoms also results in dense, well-adhered films with excellent mechanical properties.
Pro: Versatility
Sputtering can be used to deposit a vast range of materials, including pure metals, complex alloys, and even insulating ceramic compounds. This makes it a go-to process for advanced applications in optics, semiconductors, and medical devices.
Con: Lower Deposition Rates
Even with magnetron enhancement, sputtering can be slower than other PVD methods like thermal evaporation, especially for certain materials. This can be a factor in high-volume, low-cost production environments.
Con: Complexity and Cost
The equipment required for sputtering—including vacuum chambers, high-voltage power supplies, and magnetic assemblies—is complex and carries a higher capital cost than some simpler coating techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sputtering is a decision based on the required properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is film purity and density: Sputtering offers exceptional control, as it physically transfers material from a high-purity target directly onto your substrate.
- If your primary focus is coating with complex alloys: Sputtering excels at preserving the original composition (stoichiometry) of the target material in the final film.
- If your primary focus is strong film adhesion and durability: The energetic nature of the sputtered atoms creates a robust interface between the film and the substrate, resulting in a highly durable coating.
Ultimately, sputtering provides a precise and repeatable physical pathway for transforming a solid material into a high-performance thin film.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Mechanism | Momentum transfer via ion bombardment (e.g., Argon) |
| Key Advantage | High film purity, excellent adhesion, versatility with materials |
| Common Enhancement | Magnetron Sputtering (increased deposition rate) |
| Typical Applications | Semiconductors, optics, medical devices, durable coatings |
Ready to integrate high-purity sputtering technology into your lab workflow?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research and production needs. Whether you are working in semiconductor fabrication, developing new optical coatings, or creating durable medical device layers, our sputtering solutions offer the precision, reliability, and material versatility you require.
Let our experts help you achieve superior thin film results. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our sputtering systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















