Yes, specialized flux for aluminum not only exists but is essential for many common joining processes like brazing and soldering. This is because aluminum instantly forms a tough, high-melting-point layer of aluminum oxide that prevents filler metals from bonding to the parent material. Aluminum flux is a chemically aggressive agent designed specifically to remove this oxide layer and protect the joint as it is being heated.
The central challenge in joining aluminum is defeating its tenacious, self-healing oxide layer. Your choice is not simply if a flux exists, but which fundamental strategy to use: chemically attacking the oxide with a flux or preventing its formation altogether in a controlled environment.
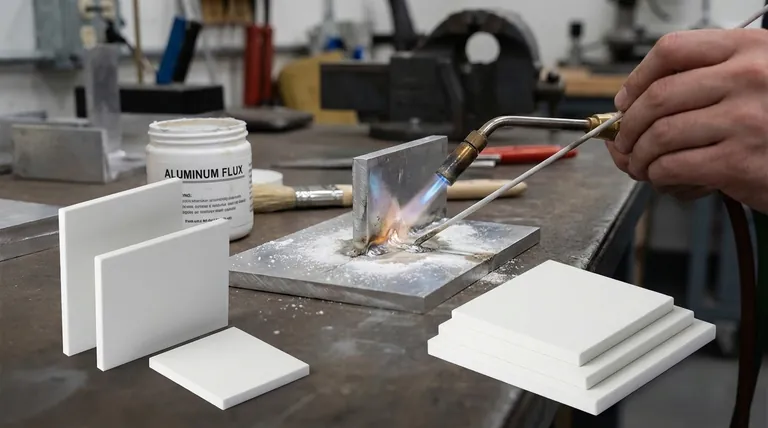

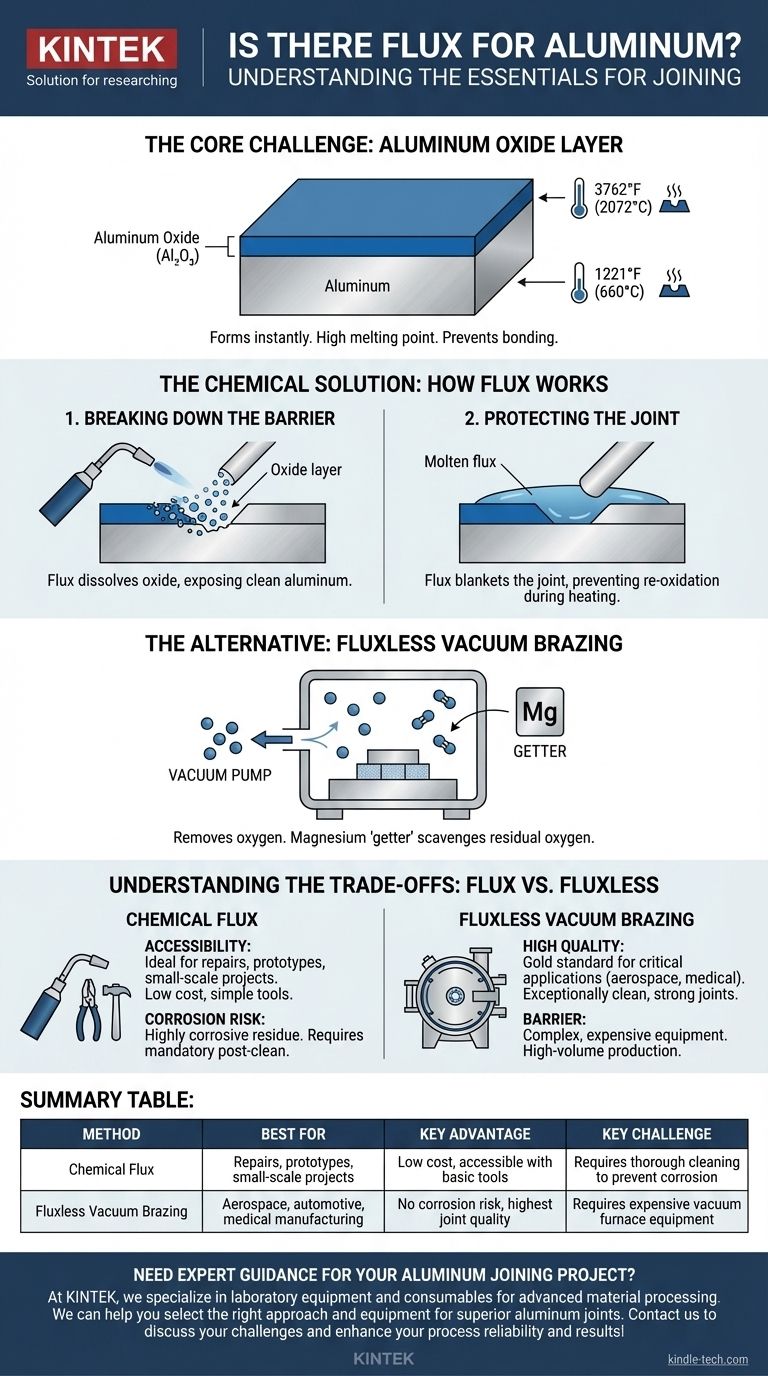
The Core Challenge: The Aluminum Oxide Layer
Why Aluminum is Different
Unlike iron that forms a porous rust, aluminum forms a thin, dense, and non-porous layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) the moment it's exposed to air.
This layer is incredibly useful, as it's what makes aluminum so resistant to corrosion. However, it is a significant barrier when you try to join the metal.
The Problem with the Oxide
The melting point of aluminum oxide is around 3762°F (2072°C), while the aluminum underneath melts at a much lower 1221°F (660°C).
This means that by the time you apply enough heat to melt the oxide layer, the base aluminum would have already melted and lost its shape. A chemical or environmental solution is required to remove the oxide at a lower temperature.
The Chemical Solution: How Aluminum Flux Works
Breaking Down the Barrier
Aluminum flux is a blend of reactive chemicals, typically containing chlorides and fluorides. When heated, these chemicals launch an aggressive attack on the aluminum oxide layer.
The flux dissolves the oxide, exposing the clean, raw aluminum underneath so the filler metal can flow into the joint and form a proper metallurgical bond.
Protecting the Joint
After removing the oxide, the molten flux blankets the joint area. This liquid shield prevents oxygen from reaching the clean aluminum, stopping the oxide layer from re-forming during the heating cycle.
The Alternative: Fluxless Brazing
Removing the Oxygen
An entirely different strategy avoids chemical flux altogether. Fluxless vacuum brazing, an industrial process, solves the oxide problem by changing the environment.
Parts are assembled with filler metal and placed inside a furnace. Powerful pumps remove the atmosphere, creating a deep vacuum that drastically reduces the amount of available oxygen. With no oxygen, the oxide layer cannot form.
The Role of a "Getter"
To ensure an ultra-pure environment, small amounts of magnesium are often added to the filler metal or placed in the furnace.
At brazing temperatures, the magnesium vaporizes and acts as a "getter". It actively seeks out and combines with any remaining oxygen molecules, effectively scavenging them from the vacuum chamber and protecting the parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Flux vs. Fluxless
The Case for Chemical Flux
The primary advantages of using a chemical flux are accessibility and cost. It allows aluminum to be brazed or soldered with simple tools like a torch.
This makes it the go-to method for repairs, one-off prototypes, and low-volume production where investing in a vacuum furnace is not feasible.
The Downsides of Flux
Aluminum fluxes are highly corrosive. If any flux residue is left on the part after joining, it will attract moisture from the air and aggressively corrode the aluminum parent metal and the joint itself over time.
This means a thorough, multi-step post-brazing cleaning process is not just recommended—it is absolutely mandatory to ensure the long-term integrity of the part.
The Case for Fluxless Brazing
Fluxless vacuum brazing produces exceptionally clean, strong, and reliable joints. There is zero risk of flux entrapment or post-braze corrosion from residue.
This makes it the gold standard for high-performance, critical applications in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing where joint failure is not an option.
The Barrier to Fluxless Brazing
The major disadvantage is the equipment. Vacuum furnaces are highly complex, expensive pieces of industrial machinery requiring significant capital investment and operator expertise. This method is only practical for high-volume, repeatable production environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the method you choose depends entirely on your application, resources, and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is accessibility for repairs or small-scale projects: A chemical aluminum flux is the correct and most practical choice, but you must be disciplined about cleaning the part thoroughly afterward.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible joint quality and repeatability in a production environment: Fluxless vacuum brazing is the superior industrial method that eliminates the risks associated with corrosive chemicals.
Choosing the right approach is about matching your strategy to the specific demands of your project.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Flux | Repairs, prototypes, small-scale projects | Low cost, accessible with basic tools | Requires thorough cleaning to prevent corrosion |
| Fluxless Vacuum Brazing | Aerospace, automotive, medical manufacturing | No corrosion risk, highest joint quality | Requires expensive vacuum furnace equipment |
Need expert guidance for your aluminum joining project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables for advanced material processing. Whether you're working with chemical fluxes or exploring fluxless brazing solutions, our team can help you select the right approach and equipment for your specific needs.
We serve laboratories and manufacturing facilities requiring precise thermal processing solutions. Let us help you achieve superior aluminum joints with the right technology and support.
Contact us today to discuss your aluminum joining challenges and discover how KINTEK can enhance your process reliability and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Reagent Wide Mouth Fine Mouth Sample High Temperature Bottles
People Also Ask
- Which materials are used as high temperature resistance materials? A Guide to Superalloys, Ceramics & Composites
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What are the properties and handling precautions for alumina powder as a polishing material? Achieve a Flawless Finish with Precision



















