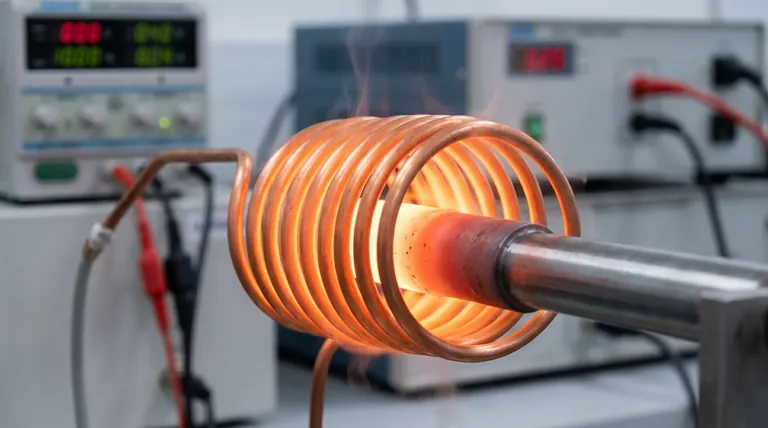
At their core, induction coils are specialized transformers used for non-contact heating of electrically conductive materials. By generating a powerful, high-frequency alternating magnetic field, they induce electrical currents directly within a target workpiece, causing it to heat up rapidly and precisely for applications like metal hardening, brazing, melting, and forging.
The fundamental purpose of an induction coil is to function as an antenna, shaping and directing a magnetic field. The coil's geometry is not arbitrary; it is meticulously engineered to control exactly where and how a metal part gets hot.
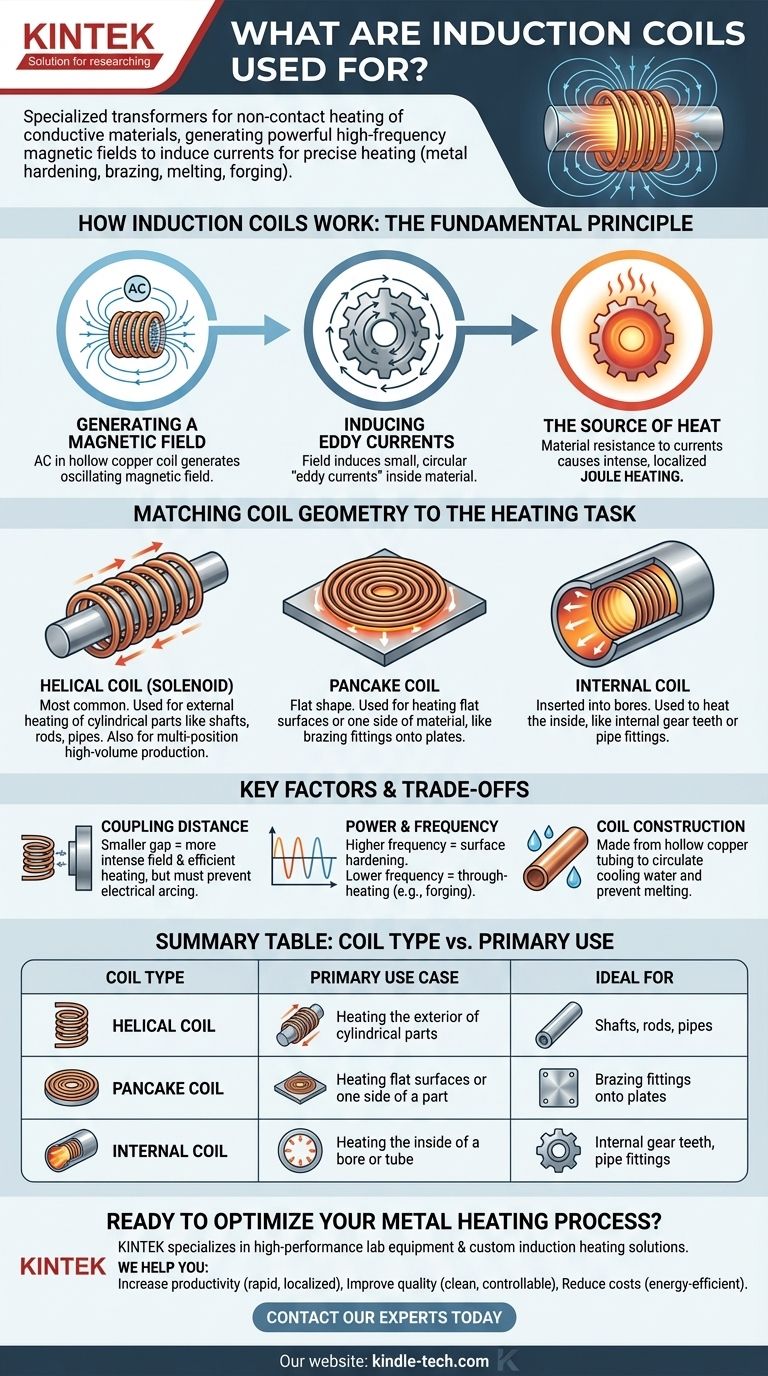
The Fundamental Principle: How Induction Coils Work
To understand what induction coils are used for, you must first understand the principle of induction heating itself. The process relies on two key physics concepts.
Generating a Magnetic Field
An induction coil is typically made from hollow copper tubing. A powerful alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, which, according to Ampere's Law, generates a concentrated and oscillating magnetic field in the space around and within the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a conductive workpiece (like a steel gear or copper pipe) is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces small, circular electrical currents inside the material. These are known as eddy currents.
The Source of Heat
The workpiece material has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance causes intense, localized heat to be generated directly within the part—a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This process is exceptionally fast, clean, and controllable.
Matching Coil Geometry to the Heating Task
The shape of the induction coil is the single most important factor in determining the success of an induction heating process. The goal is to design a coil that "couples" efficiently with the part, meaning the magnetic field lines intersect the area you wish to heat.
The Helical Coil
The most common design, a helical (or solenoid) coil, is essentially a copper tube wound into a spring-like shape. It is used for heating cylindrical parts like shafts, rods, and pipes from the outside. A multi-position helical coil is a variation used to heat several workpieces simultaneously for high-volume production.
The Pancake Coil
As its name suggests, a pancake coil is flat and spiral-shaped. It is used when the goal is to heat a flat surface or only one side of the material. The magnetic field is concentrated perpendicular to the face of the coil, making it ideal for applications like brazing a fitting onto a flat plate or heating the end of a large shaft.
The Internal Coil
When you need to heat the inside of a part, such as a pipe fitting or an engine cylinder, an internal coil is used. It is inserted into the bore, and its magnetic field expands outwards to induce currents on the part's inner surface. This is essential for tasks like shrink-fitting or hardening internal gear teeth.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
Simply choosing a coil shape is not enough. The efficiency and effectiveness of the heating process depend on several critical design and operational parameters.
Coupling Distance
The gap between the coil and the workpiece is called the coupling distance. A smaller gap results in a more intense magnetic field and more efficient heating. However, the gap must be large enough to prevent electrical arcing between the coil and the part.
Power and Frequency
The power supply's frequency determines the depth of heat penetration. Higher frequencies induce eddy currents that flow closer to the surface (the "skin effect"), which is ideal for surface hardening. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the part, which is better for through-heating applications like forging.
Coil Construction
Because of the immense currents flowing through them, induction coils generate significant heat themselves. They are almost always constructed from hollow copper tubing so that cooling water can be circulated through them to prevent the coil from melting during operation.
Choosing the Right Coil for Your Application
Your choice of coil must be directly informed by the geometry of your workpiece and your desired heating outcome.
- If your primary focus is heating the exterior of a cylindrical part: A helical coil is the standard choice for providing uniform, efficient heating around the circumference.
- If your primary focus is heating a flat surface or the end of a workpiece: A pancake coil is designed to concentrate the magnetic field onto a single plane.
- If your primary focus is heating the inside of a bore or tube: An internal coil is required to project the magnetic field outwards onto the inner surface of the part.
- If your primary focus is hardening a precise surface layer: You must use a high-frequency power source in addition to a closely coupled coil to limit heat penetration.
Ultimately, selecting the correct induction coil is about precisely matching its magnetic field geometry to your specific heating target.
Summary Table:
| Coil Type | Primary Use Case | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Helical Coil | Heating the exterior of cylindrical parts | Shafts, rods, pipes |
| Pancake Coil | Heating flat surfaces or one side of a part | Brazing fittings onto plates |
| Internal Coil | Heating the inside of a bore or tube | Internal gear teeth, pipe fittings |
Ready to optimize your metal heating process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including custom induction heating solutions. Whether your application requires surface hardening, brazing, or through-heating for forging, our expertise ensures you get the right coil geometry and system parameters for maximum efficiency and precision.
We help you:
- Increase productivity with rapid, localized heating.
- Improve quality with clean, controllable, and repeatable results.
- Reduce costs with energy-efficient and targeted heating.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect induction heating solution for your laboratory or production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















