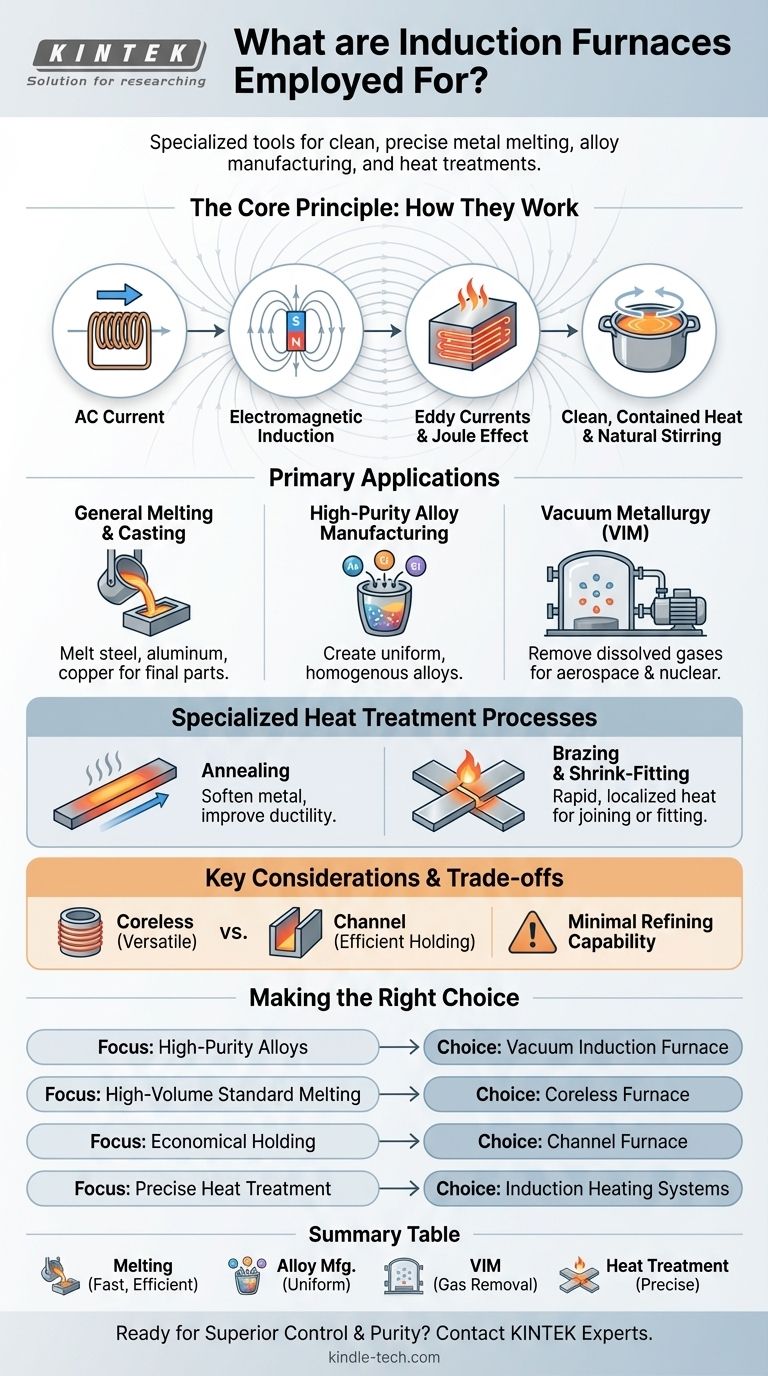
At its core, an induction furnace is a specialized tool for melting metals, manufacturing high-purity alloys, and executing precise heat treatments. Its applications range from melting common metals like steel, aluminum, and copper to producing superalloys for the aerospace industry and performing processes like annealing, brazing, and shrink-fitting.
The fundamental advantage of an induction furnace lies in its method: it uses non-contact electromagnetic induction to generate clean, contained, and highly controllable heat directly within the metal itself, ensuring uniformity and minimizing contamination.

The Core Principle: How Induction Furnaces Work
To understand why induction furnaces are so widely used, you must first understand the clean and efficient physics behind their operation.
Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a coil carrying a powerful alternating current to create a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive material, like metal, is placed within this field, electrical currents—known as eddy currents—are induced to flow inside it.
The Joule Effect
These induced eddy currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy into heat, a phenomenon known as the Joule effect. Because the heat is generated inside the material, the process is incredibly efficient and fast.
Natural Stirring Action
The intense magnetic fields also create a stirring action within the molten metal. This constant, gentle circulation is critical for manufacturing alloys, as it ensures all elements are mixed thoroughly for a completely uniform and homogenous final product.
Primary Applications in Metal Processing
The unique heating method of induction furnaces makes them indispensable for applications where purity, consistency, and control are paramount.
General Melting and Casting
The most common application is simply melting metals. Furnaces are used to melt everything from steel and iron to aluminum, copper, and precious metals. Once melted, the liquid metal is poured into a mold to create a final cast part.
High-Purity Alloy Manufacturing
The inherent stirring action and controlled environment make induction furnaces the ideal choice for creating high-performance alloys. The process ensures precise composition and optimal uniformity without introducing impurities from combustion byproducts.
Vacuum Metallurgy
For the most demanding applications, a vacuum induction furnace (VIM) is used. By melting the metal in a vacuum, producers can eliminate dissolved gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This is essential for creating the special steels and superalloys required for aerospace, missile, and atomic energy components.
Specialized Heat Treatment Processes
Beyond melting, induction heating is used for modifying the physical properties of solid metals with exceptional precision.
Annealing
Annealing is a process that softens a metal, increases its ductility, and reduces internal stresses. An induction furnace heats the material to a specific temperature and allows it to cool slowly, refining its crystal structure for improved workability.
Brazing and Shrink-Fitting
Induction technology can provide rapid, localized heat. This makes it perfect for brazing, where two pieces of metal are joined by a filler metal, and shrink-fitting, where a component is heated to expand it before being fitted onto another part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Furnace Types
While powerful, induction furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their types and limitations is key to using them effectively.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
The two main designs are coreless and channel furnaces. Coreless furnaces are versatile and widely used for melting a variety of metals. Channel furnaces are more energy-efficient for holding molten metal at temperature or for melting low-temperature alloys.
A Key Limitation: Minimal Refining
An induction furnace is a melting device, not a refining one. It does an excellent job of melting the charge material cleanly, but it offers very little capability to remove impurities that were present in the initial scrap or raw material.
Strategic Energy Management
Because induction furnaces consume significant power, facilities often use different types strategically. For example, a coreless furnace might be used for melting during off-peak hours, with the molten metal then transferred to a highly efficient channel furnace to be held for use during peak production hours, avoiding high electricity demand charges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best approach depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform alloys for critical applications: A vacuum induction furnace is the definitive choice for its ability to control the atmosphere and ensure compositional purity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume melting of standard metals: A coreless induction furnace offers the flexibility and power needed for a wide range of common metals like steel and iron.
- If your primary focus is holding molten metal economically: A channel induction furnace provides the highest energy efficiency for maintaining temperature over long periods.
- If your primary focus is precise, localized heat treatment: Induction heating systems designed for tasks like annealing or brazing offer unparalleled speed and control.
Ultimately, the induction furnace is a cornerstone of modern metallurgy because it provides a level of control over heat and material purity that is simply unattainable with older, combustion-based methods.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| General Melting & Casting | Fast, efficient melting of steel, aluminum, copper, etc. |
| High-Purity Alloy Manufacturing | Uniform composition and minimal contamination. |
| Vacuum Metallurgy (VIM) | Removes dissolved gases for aerospace & nuclear alloys. |
| Heat Treatment (Annealing, Brazing) | Precise, localized heating for improved material properties. |
Ready to achieve superior control and purity in your metal processing?
Whether you are melting high-purity alloys, performing precise heat treatments, or need an efficient holding solution, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial furnace technology can provide the right equipment for your specific goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction furnace solutions can enhance your laboratory or production efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity



















