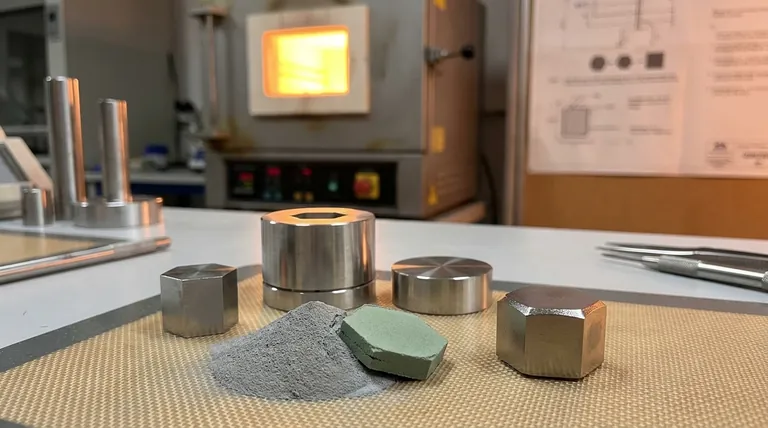
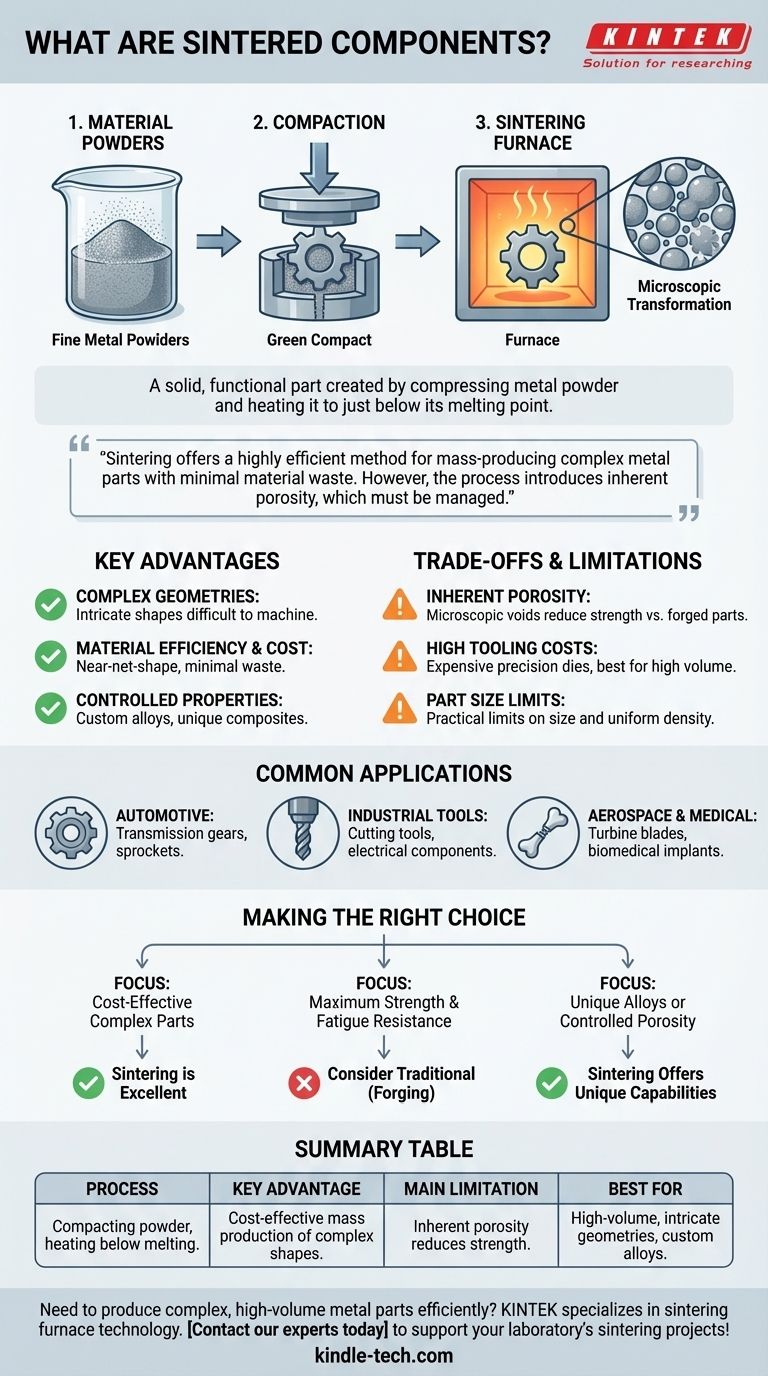
At its core, a sintered component is a solid, functional part created by compressing metal powder and heating it to just below its melting point. This process, known as powder metallurgy, fuses the individual powder particles together to form a strong, dense object without ever fully liquefying the material. The result is often a "net-shape" or "near-net-shape" part that requires little to no post-processing.
Sintering offers a highly efficient method for mass-producing complex metal parts with minimal material waste. However, the process introduces inherent porosity, which must be managed as it directly influences the component's final strength and performance characteristics.

How Sintering Transforms Powder into a Solid Part
To understand a sintered component, you must first understand the process. It is a precise method of transformation, not melting and casting.
The Starting Point: Material Powders
The process begins not with a solid block of metal, but with a fine powder. This can be a elemental metal like iron, a pre-made alloy, or a custom blend of different powders to achieve specific properties.
Step 1: Compaction
The powder is placed into a rigid die or mold that is the shape of the final part. It is then compressed under immense pressure, forming a fragile, "green" compact that holds its shape but has little structural strength.
Step 2: The Sintering Furnace
The green compact is then placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. It is heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's melting point, for a specific amount of time.
The Microscopic Transformation
During this heating stage, the powder particles fuse together at their contact points. The boundaries between individual particles, known as grain boundaries, expand and grow.
Simultaneously, the small voids or pores between particles gradually shrink and migrate towards the grain boundaries, where many of them are eliminated. The density of the part increases significantly, typically reaching about 95% of the material's theoretical maximum density.
Key Advantages of Sintering
Engineers and designers choose sintering for several strategic reasons that set it apart from traditional manufacturing methods like machining or forging.
Creating Complex Geometries
Sintering excels at producing parts with intricate shapes, internal holes, or unique features that would be difficult, expensive, or impossible to create by cutting away material from a solid block.
Material Efficiency and Cost
Because parts are formed to their final shape (net-shape), there is very little material waste. This is a major cost advantage over subtractive processes like machining, especially when using expensive materials.
Controlled and Unique Properties
By blending different types of powders, manufacturers can create custom alloys and composite materials. Furthermore, the inherent porosity can be controlled and even used as a feature, such as in self-lubricating bearings that are impregnated with oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. The primary trade-offs of sintering are directly linked to its powder-based origins.
Inherent Porosity
Even in a high-density part, the ~5% of remaining volume is porosity. These microscopic voids can act as stress concentrators, typically making sintered parts less strong than their forged or wrought counterparts. This is the single most important factor to consider.
High Initial Tooling Costs
Creating the precision dies for compacting the powder is expensive. This makes sintering most cost-effective for high-volume production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized over many thousands of parts.
Limitations on Part Size
There are practical limits to the size and complexity of parts that can be produced. Large or very long parts are difficult to compact with uniform density, which can lead to inconsistent properties throughout the component.
Common Applications of Sintered Components
You will find sintered components in a wide array of demanding, high-volume applications where their balance of cost and performance is ideal.
Automotive Industry
This is the largest user of sintered parts. They are commonly used for transmission gears, engine sprockets, and various actuators where complexity and cost are primary drivers.
Industrial and Electrical Tools
Many cutting tools for milling, drilling, and reaming are made from sintered tungsten carbide. Components in electrical switchgear are also commonly produced via sintering.
Aerospace and Medical
In high-value industries, sintering is used to create complex parts from exotic materials. This includes aerospace fuel valve components, turbine blades, and biomedical implants like porous prosthetic joints that encourage bone growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing a manufacturing process requires balancing your technical requirements with your economic goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice, especially when material waste from machining is a major concern.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue resistance: You should consider traditional manufacturing like forging or machining from solid billet, as sintering's inherent porosity is a mechanical limitation.
- If your primary focus is creating unique material alloys or controlled porosity: Sintering offers unique capabilities for creating custom material blends and self-lubricating parts that are difficult to achieve with other methods.
Understanding sintering empowers you to select a manufacturing process that aligns perfectly with your component's cost, complexity, and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Compacting metal powder and heating below melting point |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective mass production of complex shapes |
| Main Limitation | Inherent porosity reduces strength vs. forged parts |
| Best For | High-volume production, intricate geometries, custom alloys |
Need to produce complex, high-volume metal parts efficiently? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing, including sintering furnace technology. Our solutions help you achieve precise temperature control and consistent results for your R&D or production needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Grinding Bowl
People Also Ask
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation



















