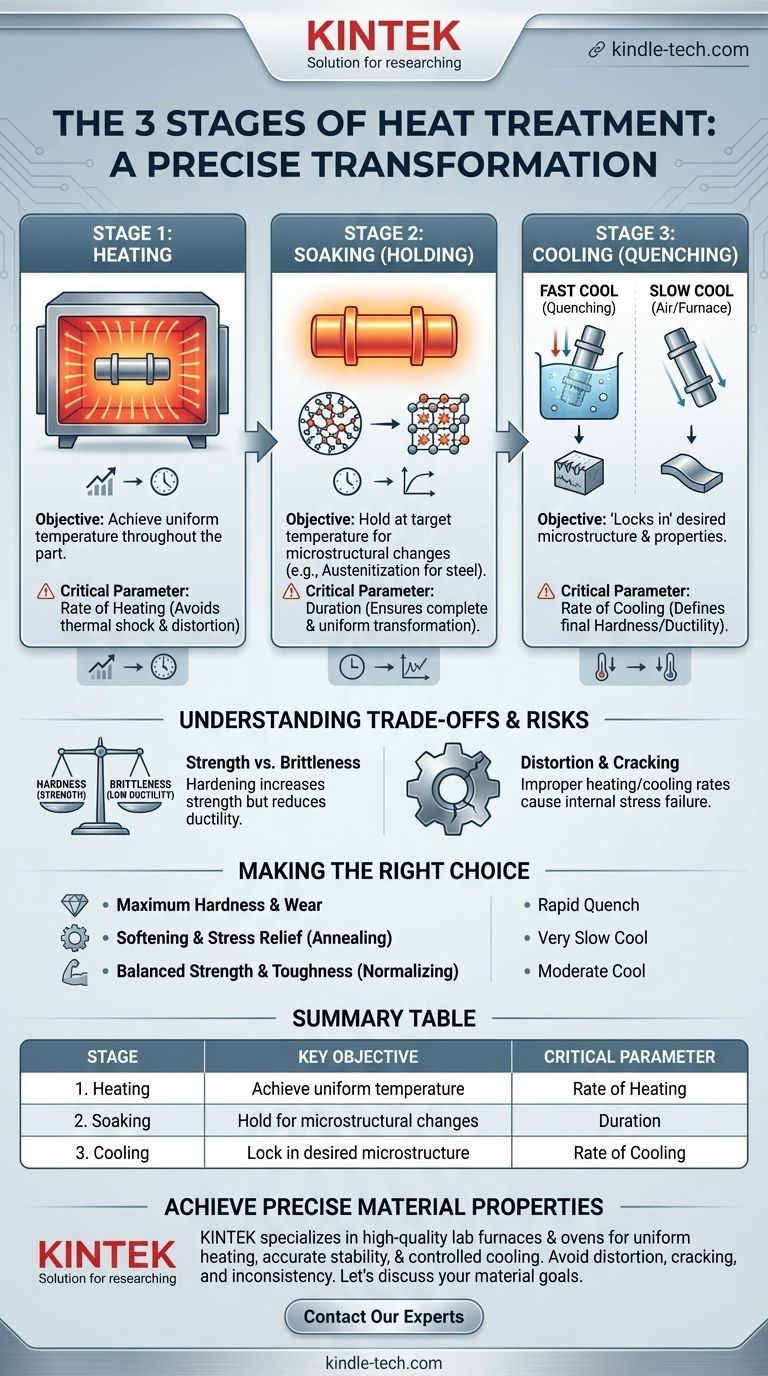
In short, the three stages of heat treatment are heating, soaking, and cooling. This fundamental process is not simply about changing a metal's temperature; it is a precise method for manipulating its internal crystal structure to achieve specific, desirable mechanical properties like hardness or ductility.
The core principle of heat treatment is that how you heat, hold, and cool a metal is just as important as the temperatures you reach. Each stage serves a distinct purpose in transforming the material's internal microstructure to achieve a desired engineering outcome.

The Goal of Heat Treatment: A Change from Within
Before examining the stages, it's critical to understand the objective. Heat treatment is used to intentionally alter a material's physical and mechanical properties without changing its shape.
By controlling temperature and time, you are controlling the arrangement of atoms within the metal's crystal lattice. This internal transformation is what allows you to make a piece of steel harder, more ductile, or more resistant to wear.
The Three Foundational Stages Explained
Every heat treatment process, from simple stress relief to complex hardening, is built upon these three sequential stages. The specific parameters of each stage define the final outcome.
Stage 1: Heating
The initial stage involves heating the material in a controlled manner to a predetermined temperature. The goal is to achieve a uniform temperature throughout the entire part.
The rate of heating is critical. Heating a component too quickly can cause internal stresses, distortion, or cracking due to thermal shock, especially in complex geometries or thick sections.
Stage 2: Soaking (or Holding)
Once the material reaches the target temperature, it is held, or "soaked," at that temperature for a specific amount of time. This is not an idle pause; it is when the crucial microstructural changes occur.
For steel, this is typically the stage where the crystal structure transforms into a phase called austenite. The duration of the soak ensures this transformation is complete and uniform throughout the material's cross-section.
Stage 3: Cooling (or Quenching)
Cooling is arguably the most decisive stage, as the rate of cooling "locks in" the desired microstructure and its corresponding properties.
A very fast cool, known as quenching (using water, oil, or polymers), traps the atoms in a hard, brittle structure like martensite. A slow cool (in still air or inside a furnace) allows a softer, more ductile structure to form. The choice of cooling medium is a key process variable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Heat treatment is a powerful process, but it requires a deep understanding of its inherent trade-offs. Achieving one property often comes at the expense of another.
The Strength vs. Brittleness Dilemma
The most common trade-off is between strength and brittleness. Hardening a metal almost always increases its strength but reduces its ductility, making it more brittle and susceptible to fracture under impact. This is why many hardened parts undergo a secondary, lower-temperature treatment called tempering to restore some toughness.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
Improper control over heating or cooling rates is the primary cause of failure. Uneven temperature changes create internal stresses that can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack during the process.
Surface vs. Core Properties
In thicker components, it can be challenging to achieve a uniform cooling rate. The surface may cool much faster than the core, resulting in a part that is very hard on the outside but softer on the inside. While sometimes desirable (as in case hardening), this differential must be carefully managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters for each of the three stages depend entirely on the material and the desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use a rapid cooling rate (quench) after a proper soak to form a martensitic structure.
- If your primary focus is to soften the metal and relieve internal stress (annealing): Use a very slow cooling rate, often by letting the part cool down inside the turned-off furnace.
- If your primary focus is a balanced combination of strength and toughness (normalizing): Use a moderate, controlled cooling rate, such as cooling the part in still air.
Mastering these three stages empowers you to precisely tailor a material's properties to meet any engineering demand.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Objective | Critical Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Heating | Achieve uniform temperature throughout the part. | Rate of Heating (to avoid thermal shock) |
| 2. Soaking | Hold at target temperature for microstructural changes. | Duration (for complete, uniform transformation) |
| 3. Cooling | Lock in the desired microstructure and properties. | Rate of Cooling (defines final hardness/ductility) |
Ready to achieve precise material properties with reliable heat treatment?
The three stages of heat treatment are foundational, but their success depends on precise control and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and ovens that provide the uniform heating, accurate temperature stability, and controlled cooling environments essential for successful heat treatment processes.
Whether you are hardening, annealing, or tempering, our equipment helps you avoid distortion, cracking, and inconsistent results. Let's discuss your specific material and property goals.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect heat treatment solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What type of insulation is used in a muffle furnace? Essential Materials for High-Temperature Performance
- What happens in the muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- How is the sintering temperature related to the melting temperature? A Guide to Solid-State Bonding
- How do you cool a muffle furnace? Safeguard your equipment and samples from thermal shock.
- What is the mechanism of a muffle furnace? Master Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating



















