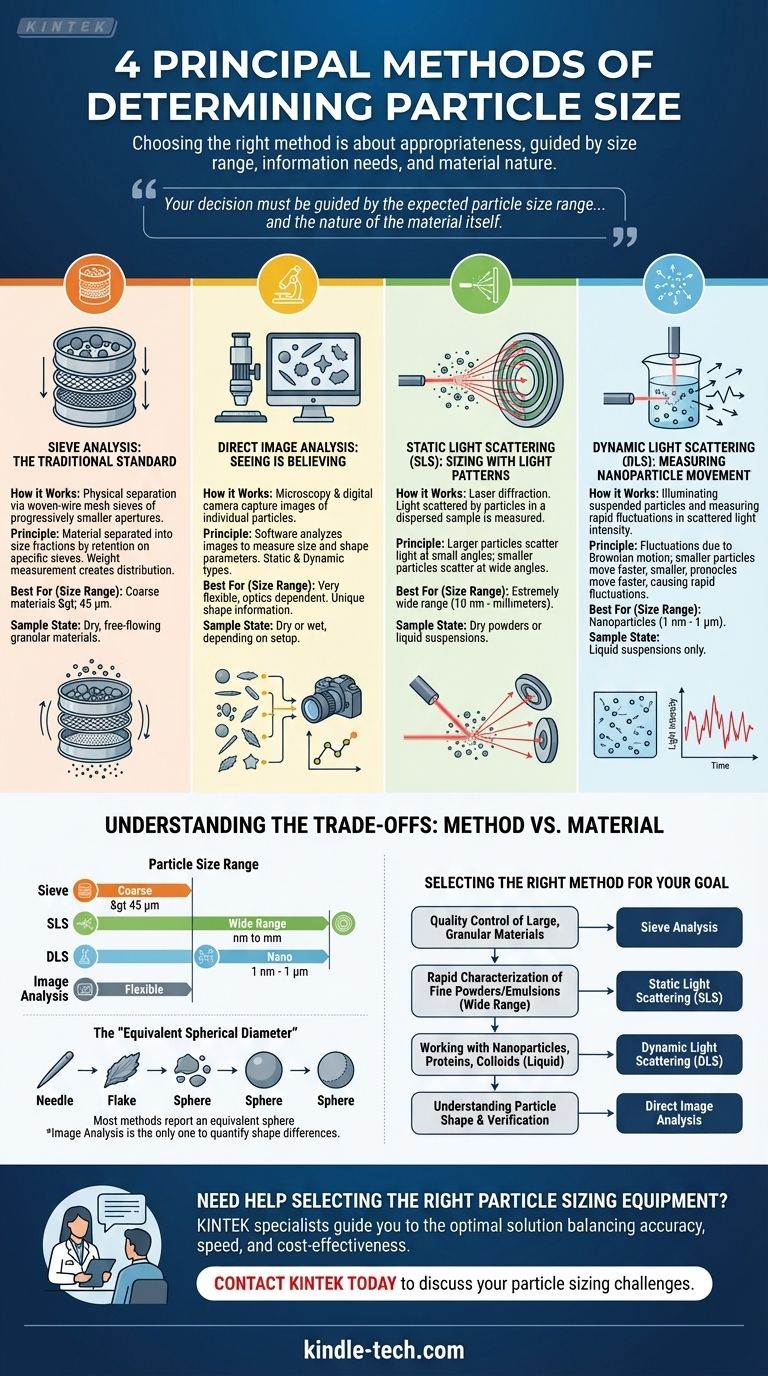
The four principal methods for determining particle size are sieve analysis, direct image analysis, static light scattering (also known as laser diffraction), and dynamic light scattering. While all four measure particle size, they operate on vastly different principles and are suited for different types of materials and size ranges. The choice of method is critical, as it directly impacts the accuracy and relevance of your results.
Choosing the right particle sizing method is not about finding the "best" one, but the most appropriate one. Your decision must be guided by the expected particle size range of your sample, the information you need (e.g., size vs. shape), and the nature of the material itself.

A Closer Look at Each Method
Each technique offers a unique window into the world of particles. Understanding how they work is the first step toward selecting the correct tool for your analysis.
Sieve Analysis: The Traditional Standard
Sieve analysis is the most traditional and intuitive method. It involves passing a sample through a stack of woven-wire mesh sieves, each with progressively smaller apertures.
The material is physically separated into different size fractions based on which sieve it is retained on. The weight of the material on each sieve is measured to create a particle size distribution.
This technique is robust, inexpensive, and ideal for characterizing larger, dry, free-flowing granular materials, typically those larger than 45 micrometers.
Direct Image Analysis: Seeing is Believing
This method uses microscopy and a digital camera to capture images of individual particles. Software then analyzes these images to measure various size and, critically, shape parameters.
There are two main types:
- Static Image Analysis: Particles are dispersed on a microscope slide and measured while stationary.
- Dynamic Image Analysis: Particles flow past the camera lens and are measured in motion.
Image analysis is unique in its ability to provide direct visual information and distinguish between particles of different shapes, not just sizes.
Static Light Scattering (SLS): Sizing with Light Patterns
Often called laser diffraction (LD), this is a highly popular and automated method. A laser beam is passed through a dispersed sample of particles, and the light they scatter is measured by a series of detectors.
The underlying principle is simple: larger particles scatter light at small angles, while smaller particles scatter light at wide angles. An algorithm then calculates the particle size distribution that would create the measured scattering pattern.
SLS is extremely fast and covers a very broad measurement range, from nanometers to millimeters, making it versatile for everything from fine powders to emulsions.
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS): Measuring Nanoparticle Movement
Dynamic Light Scattering is the gold standard for particles in the sub-micron and nanometer range. It works by illuminating particles suspended in a liquid and measuring the rapid fluctuations in scattered light intensity.
These fluctuations are caused by the random movement of the particles due to Brownian motion. Smaller particles move more quickly through the liquid, while larger particles move more slowly. The rate of this fluctuation is directly correlated to particle size.
DLS is exclusively for very small particles in a liquid suspension and cannot be used for dry powders directly.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Method vs. Material
No single method is perfect for all applications. The primary trade-offs are between the size range, the type of information you get, and the nature of your sample.
Particle Size Range
The effective range of each method is the most important differentiator.
- Sieve Analysis: Best for coarse materials > 45 µm (micrometers).
- Laser Diffraction (SLS): Extremely wide range, from ~10 nm to several millimeters.
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS): Specialized for the nano-scale, typically from ~1 nm to ~1 µm.
- Image Analysis: Very flexible, but dependent on the magnification and optics used.
The "Equivalent Spherical Diameter"
With the exception of image analysis, most methods do not "see" the particle's actual shape. They measure a property (like scattered light or volume) and report an equivalent spherical diameter.
This is the diameter of a perfect sphere that would produce the same signal. For non-spherical particles like needles or flakes, this can lead to different results between methods. Image analysis is the only way to quantify these shape differences.
Sample State: Dry vs. Wet
Your sample's natural state also guides the choice. Sieve analysis is typically performed on dry powders. DLS requires the sample to be suspended in a liquid. Laser diffraction and image analysis often have accessories to handle both dry powders and liquid suspensions.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Goal
To make an informed decision, align the method's strengths with your primary analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control of large, granular materials: Sieve analysis is your most reliable and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is rapid characterization of fine powders or emulsions across a wide size range: Static Light Scattering (Laser Diffraction) offers the best combination of speed, range, and automation.
- If your primary focus is working with nanoparticles, proteins, or colloids in a liquid: Dynamic Light Scattering is the industry standard for the sub-micron scale.
- If your primary focus is understanding particle shape or visually verifying results from other methods: Direct Image Analysis provides invaluable visual confirmation and shape metrics that no other method can.
Ultimately, understanding the principles behind each method empowers you to select the technique that will deliver the most accurate and relevant data for your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For (Size Range) | Key Principle | Sample State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sieve Analysis | Coarse materials (> 45 µm) | Physical separation by mesh size | Dry powders |
| Static Light Scattering (SLS/Laser Diffraction) | Wide range (10 nm - mm) | Light scattering angle | Dry powders or liquid suspensions |
| Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) | Nanoparticles (1 nm - 1 µm) | Brownian motion speed | Liquid suspensions |
| Direct Image Analysis | Shape analysis & verification | Microscopy & digital imaging | Dry or wet, depending on setup |
Need Help Selecting the Right Particle Sizing Equipment?
Choosing the correct method is critical for accurate and relevant results in your laboratory. The team at KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for all your particle characterization needs, from robust sieve shakers for granular materials to advanced laser diffraction systems for fine powders and nanoparticles.
We understand that every material is unique. Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution that balances accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your particle sizing challenges and discover how our solutions can enhance your analytical capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the different methods of sieving? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material
- Which Cannot be separated by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Particle Size Separation
- Can sieving be used to separate a solid substance from a liquid substance? Learn the Right Technique for Your Mixture
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis



















