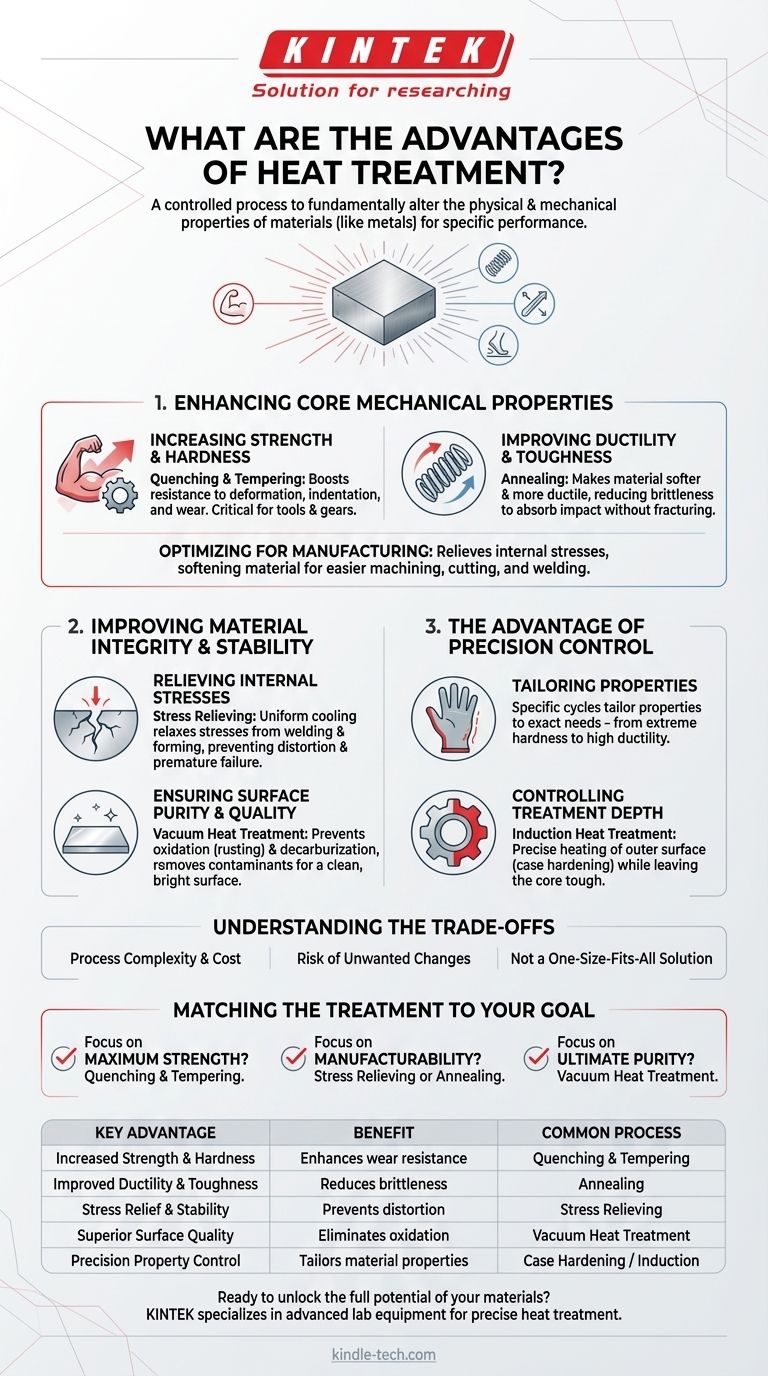
At its core, heat treatment is a highly controlled process used to fundamentally alter the physical and mechanical properties of a material, most commonly metals like steel. Its primary advantages are the ability to increase strength, improve ductility, relieve internal stresses, and introduce specific surface characteristics like wear resistance, making a component perfectly suited for its intended application.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a suite of sophisticated techniques. Its true advantage lies in the power to precisely engineer a material’s internal structure to achieve specific, predictable performance outcomes that are otherwise unattainable.

Enhancing Core Mechanical Properties
The most common reason for heat treatment is to change how a material behaves under stress. This is achieved by carefully heating and cooling the metal to manipulate its crystalline structure.
Increasing Strength and Hardness
Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering can significantly increase a material's hardness and tensile strength. This makes the final component more resistant to deformation, indentation, and wear, which is critical for tools, gears, and structural parts.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
Conversely, processes like annealing can make a material softer and more ductile. This reduces brittleness, allowing the material to bend or deform without fracturing, which is essential for parts that need to absorb impact or be formed into complex shapes.
Optimizing for Manufacturing
Some treatments are designed to prepare a material for subsequent work. By relieving internal stresses or softening the material, it becomes much easier to machine, cut, or weld, reducing tool wear and preventing warping or cracking during fabrication.
Improving Material Integrity and Stability
Beyond simple strength, heat treatment ensures the long-term reliability and cleanliness of a component. It addresses issues that arise from previous manufacturing steps or environmental exposure.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding and hot forming introduce significant internal stresses into a material. Heat treatment, specifically stress relieving, heats the part below its critical temperature and cools it uniformly, relaxing these stresses and preventing future distortion or premature failure.
Ensuring Surface Purity and Quality
Advanced methods like vacuum heat treatment provide a significant advantage by processing parts in a controlled environment. This prevents surface reactions like oxidation (rusting) and decarburization (loss of carbon, which reduces hardness).
This process also removes surface contaminants and degasses the metal, resulting in a clean, bright surface and improving properties like fatigue strength.
The Advantage of Precision Control
Modern heat treatment is not a brute-force method. Its value comes from the ability to apply changes with surgical precision, both in terms of temperature and location.
Tailoring Properties for Specific Needs
Different heating and cooling cycles produce vastly different results. This allows engineers to tailor the final properties of a component to its exact operational needs, whether that's extreme hardness for a cutting edge or high ductility for a fastener.
Controlling Treatment Depth
Techniques like induction heat treatment allow for precise control over the depth of heating. By adjusting the frequency of the current, one can harden just the outer surface of a part (case hardening) while leaving the core tough and ductile, creating a component with superior wear resistance and impact strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, heat treatment is a precise engineering process that requires careful consideration. Choosing the wrong method can be detrimental.
Process Complexity and Cost
Specialized treatments like vacuum processing offer superior results but require more sophisticated and expensive equipment. The benefits must be weighed against the increased cost and complexity of the operation.
Risk of Unwanted Changes
Improper control of heating or cooling rates can lead to negative outcomes. Overly rapid quenching can make a part too brittle and prone to cracking, while incorrect temperatures can fail to produce the desired properties, wasting time and resources.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The ideal heat treatment process is entirely dependent on the specific material alloy, the part geometry, and the desired final properties. A procedure that works perfectly for one type of steel may ruin another.
Matching the Treatment to Your Goal
To leverage the advantages of heat treatment effectively, you must align the process with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance: A process like quenching and tempering or case hardening is the most direct path to achieving a hard, durable surface.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability and stability: Stress relieving or annealing is critical to prepare materials for machining or to ensure dimensional stability after welding.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance: Vacuum heat treatment offers unparalleled control, preventing surface contamination and enhancing fatigue life for high-performance applications.
Ultimately, viewing heat treatment as a final, critical manufacturing step allows you to unlock the full potential of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Benefit | Common Process |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Strength & Hardness | Enhances wear resistance and durability | Quenching & Tempering |
| Improved Ductility & Toughness | Reduces brittleness, improves impact resistance | Annealing |
| Stress Relief & Stability | Prevents distortion, ensures dimensional accuracy | Stress Relieving |
| Superior Surface Quality | Eliminates oxidation, improves fatigue life | Vacuum Heat Treatment |
| Precision Property Control | Tailors material properties for specific applications | Case Hardening / Induction |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for precise heat treatment processes. Whether you're aiming for maximum hardness with quenching furnaces, superior purity with vacuum ovens, or precise control with tempering equipment, our solutions are designed to meet the exacting demands of your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your material performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing



















