At its core, a coreless induction furnace is an advanced tool for melting, holding, and alloying a vast range of metals with exceptional speed and cleanliness. Its primary applications are found in modern foundries and metal processing facilities for melting iron, steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals, as well as for producing highly uniform alloys and feeding investment casting lines.
The true value of a coreless induction furnace lies not just in what it melts, but in how it melts. By using a powerful electromagnetic field to heat the metal directly, it provides unparalleled control over temperature and chemistry, free from the contamination inherent in fuel-fired methods.
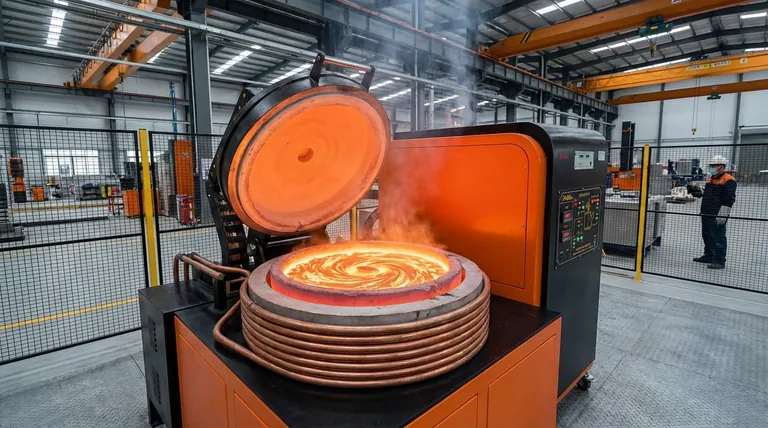

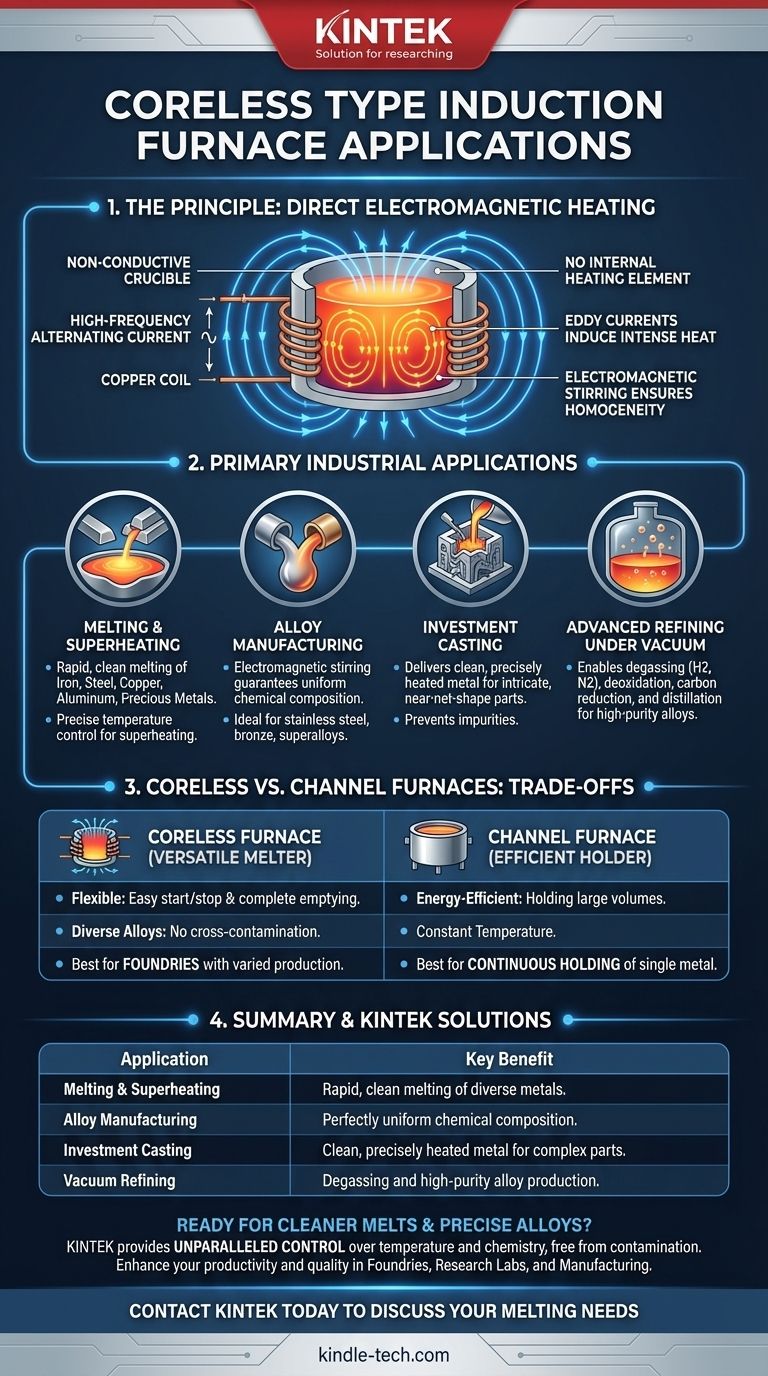
The Principle Behind the Process: Direct Electromagnetic Heating
How It Achieves Clean, Rapid Melting
A coreless induction furnace works without any internal heating element or flame. Instead, high-frequency alternating current is passed through a copper coil that surrounds a non-conductive crucible containing the metal charge.
This creates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. The field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, precise, and rapid heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
The Advantage of Electromagnetic Stirring
A secondary effect of the magnetic field is a vigorous stirring action within the molten metal bath. This electromagnetic stirring is critical, as it ensures all alloying elements are distributed perfectly, resulting in a completely homogenous and high-quality final product.
Primary Industrial Applications
Melting and Superheating
The most common use for coreless furnaces is the primary melting of scrap, ingots, and other raw materials. They excel at melting ferrous metals like iron and steel, as well as non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminum, and precious metals.
Their ability to reach and maintain precise temperatures also makes them ideal for superheating molten metal to the exact temperature required for casting.
Alloy Manufacturing
The natural stirring action makes coreless furnaces the preferred choice for manufacturing alloys. Whether creating specialized stainless steels, bronze, or complex superalloys, the furnace guarantees a uniform chemical composition throughout the entire melt.
Investment Casting Foundries
Investment casting requires extremely clean metal delivered at a precise temperature to produce intricate, near-net-shape parts. Coreless induction furnaces provide this level of control, preventing impurities and ensuring the molten metal fills the complex ceramic molds perfectly.
Advanced Refining Under Vacuum
When paired with a vacuum chamber, coreless induction furnaces enable sophisticated metallurgical processes. These applications include:
- Degassing: Removing undesirable dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen from the melt.
- Deoxidation: Reducing the oxygen content in steel melts.
- Carbon Reduction: Precisely adjusting carbon levels in stainless steel.
- Vacuum Distillation: Removing volatile elements like zinc from a melt.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
The term "induction furnace" can refer to two distinct designs. Understanding the difference is crucial for selecting the right tool for the job.
Coreless Furnaces: The Versatile Melter
Coreless furnaces are ideal for operations that require flexibility. They can be started and stopped easily, can be completely emptied between melts, and are excellent for producing a wide variety of different alloys without cross-contamination. They are the workhorse for foundries with diverse production needs.
Channel Furnaces: The Efficient Holder
A channel furnace has a separate "channel loop" of molten metal that is always kept hot. They are exceptionally energy-efficient for holding large volumes of a single type of molten metal at a constant temperature. However, they are not flexible, cannot be easily emptied, and are poorly suited for frequent alloy changes. They often serve as holding units for metal melted in a coreless furnace.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right furnace technology depends entirely on your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse materials and alloys: The flexibility of a coreless induction furnace is unmatched.
- If your primary focus is holding a large quantity of a single metal: A channel furnace offers superior energy efficiency for holding and superheating.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity or specialty alloys: A coreless furnace, potentially integrated with a vacuum system, provides the necessary chemical control.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment like hardening or brazing: You should investigate induction heating systems, which use the same principles but are configured for surface treatment rather than melting.
Ultimately, the coreless induction furnace is the definitive choice for modern metal processing that demands flexibility, purity, and precision.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Melting & Superheating | Rapid, clean melting of iron, steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals. |
| Alloy Manufacturing | Electromagnetic stirring ensures perfectly uniform chemical composition. |
| Investment Casting | Delivers clean, precisely heated metal for intricate, high-quality castings. |
| Vacuum Refining | Enables degassing, deoxidation, and carbon control for high-purity alloys. |
Ready to achieve cleaner melts and more precise alloys?
As a specialist in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK understands the critical need for reliable and efficient melting solutions. A coreless induction furnace from KINTEK can transform your metal processing by providing unparalleled control over temperature and chemistry, free from contamination.
Whether you're in a foundry, a research lab, or a manufacturing facility, our expertise can help you select the right equipment to enhance your productivity and product quality.
Contact KINTLAB today to discuss how a coreless induction furnace can meet your specific melting and alloying needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What is the primary function of vacuum melting equipment in Ti-Zr-Ni alloy preparation? Ensure Purity and Phase Stability
- How does vacuum arc melting equipment facilitate Ti-Cr-Al-Nb alloy prep? Precision High-Temp Melting Explained
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Clean Metal Joining



















