At its core, dry ashing is a fundamental analytical technique used to determine the inorganic, or mineral, content of a sample. By using a high-temperature furnace to burn away all organic matter, the process isolates the non-combustible "ash," which is then weighed and analyzed. This method finds widespread application in food science for nutritional analysis, environmental testing for soil and water quality, and industrial quality control.
The primary purpose of dry ashing is not merely to measure the total amount of ash, but to prepare a sample for further analysis by cleanly separating its inorganic mineral components from its organic matrix.

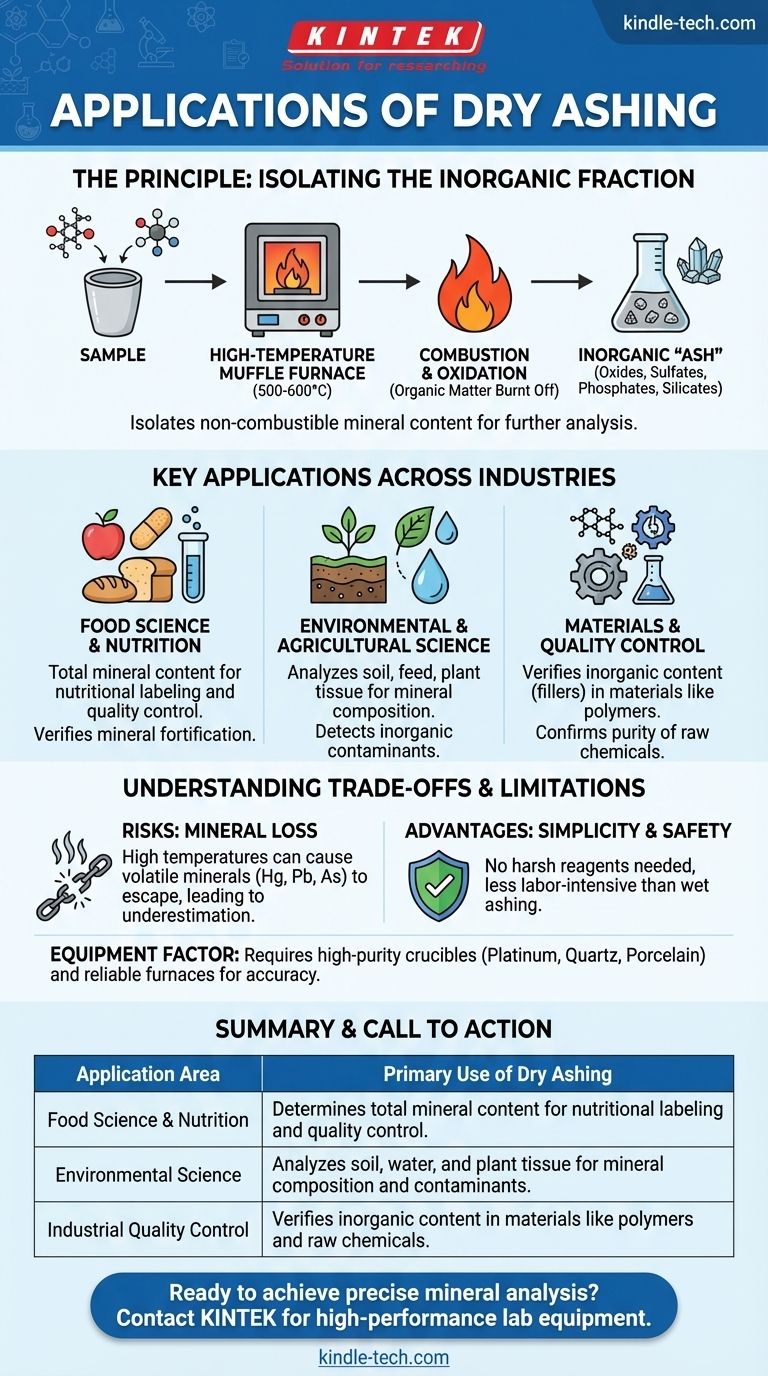
The Principle: Isolating the Inorganic Fraction
Dry ashing operates on a simple, yet powerful, principle: complete oxidation. By heating a sample in the presence of air, all organic material is burned off, leaving behind only the inorganic residue.
What is "Ash"?
The term "ash" refers to the non-combustible mineral residue left after a sample is completely burned. This residue consists of oxides, sulfates, phosphates, and silicates, which represent the total mineral content of the original material.
The High-Temperature Process
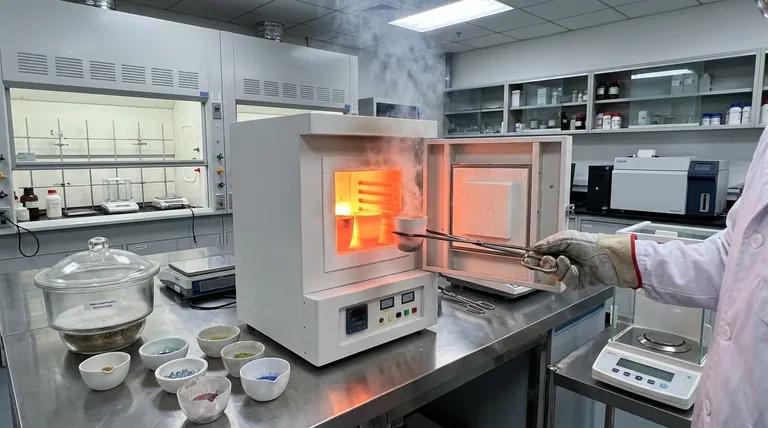
The technique involves placing a sample in an inert container—such as a quartz, porcelain, or platinum crucible—and heating it in a muffle furnace. Temperatures typically reach between 500°C and 600°C, ensuring that all organic compounds and volatile liquids are vaporized or oxidized into gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
The Goal: A Clean Sample for Analysis
While measuring the total ash content is useful, dry ashing is often a preparatory step. The resulting ash provides a concentrated, clean sample of the material's mineral components, which can then be dissolved and analyzed using more advanced techniques to identify and quantify specific elements like calcium, iron, or magnesium.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to isolate mineral content makes dry ashing a critical process in any field concerned with material composition, purity, or nutritional value.
Food Science and Nutrition
This is one of the most common applications. Food manufacturers use dry ashing to determine the total mineral content for nutritional labeling, ensuring products meet regulatory standards for essential minerals. It's the first step in verifying claims about a food's mineral fortification.
Environmental and Agricultural Science
Dry ashing is used to analyze soil, feed, and plant tissue samples. By determining the mineral composition, agronomists can assess soil fertility, while environmental scientists can detect the presence of inorganic contaminants in water or land.
Materials and Quality Control
In industrial settings, dry ashing helps verify the composition of materials. For example, it can be used to measure the amount of inorganic "filler" material in polymers or to confirm the purity of raw chemical ingredients.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, dry ashing is not suitable for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is crucial for ensuring accurate results.
The Primary Risk: Mineral Loss
The very high temperatures used can cause volatile minerals to be lost to the atmosphere, leading to an underestimation of their presence. Elements like mercury, lead, and arsenic can vaporize and escape, making this method unsuitable for their precise quantification.
The Advantage: Simplicity and Safety
A major benefit of dry ashing is its simplicity. It requires no harsh or corrosive reagents (like strong acids), making it generally safer and less labor-intensive than alternative methods like wet ashing.
The Equipment Factor
The accuracy of the results depends on the equipment used. The crucibles must be able to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading or reacting with the sample. Platinum offers the highest inertness, while porcelain and quartz provide cost-effective reliability for most common applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Selecting the proper sample preparation method is critical for achieving your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is total mineral content: Dry ashing is the standard, most straightforward, and cost-effective method.
- If you need to analyze volatile minerals (e.g., lead, mercury): You must consider a lower-temperature alternative, such as wet ashing, to prevent elemental loss.
- If you are analyzing trace elements in small quantities: Ensure you use high-purity crucibles (like quartz or platinum) and a clean furnace to avoid sample contamination.
Ultimately, understanding the composition of your sample is the first step toward controlling its quality and function.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use of Dry Ashing |
|---|---|
| Food Science & Nutrition | Determines total mineral content for nutritional labeling and quality control. |
| Environmental Science | Analyzes soil, water, and plant tissue for mineral composition and contaminants. |
| Industrial Quality Control | Verifies inorganic content in materials like polymers and raw chemicals. |
Ready to achieve precise mineral analysis in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces and crucibles essential for accurate dry ashing. Our solutions help food scientists, environmental researchers, and quality control professionals ensure reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a muffle furnace? Master Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- How does heat treatment affect surface roughness? Minimize Surface Degradation for Precision Parts
- What is the difference between a crucible and a furnace? Understanding the Heat Source and Container Partnership
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing



















