In short, molybdenum is a versatile refractory metal prized for its exceptionally high melting point and durability. Its applications range from strengthening steel alloys and acting as a high-performance lubricant to forming critical components in industrial furnaces, electronics, and even advanced spacecraft.
The true value of molybdenum lies not in a single property, but in its unique combination of high-temperature stability, excellent wear resistance, and favorable economics compared to alternatives like tungsten. Understanding this balance is key to leveraging it effectively.
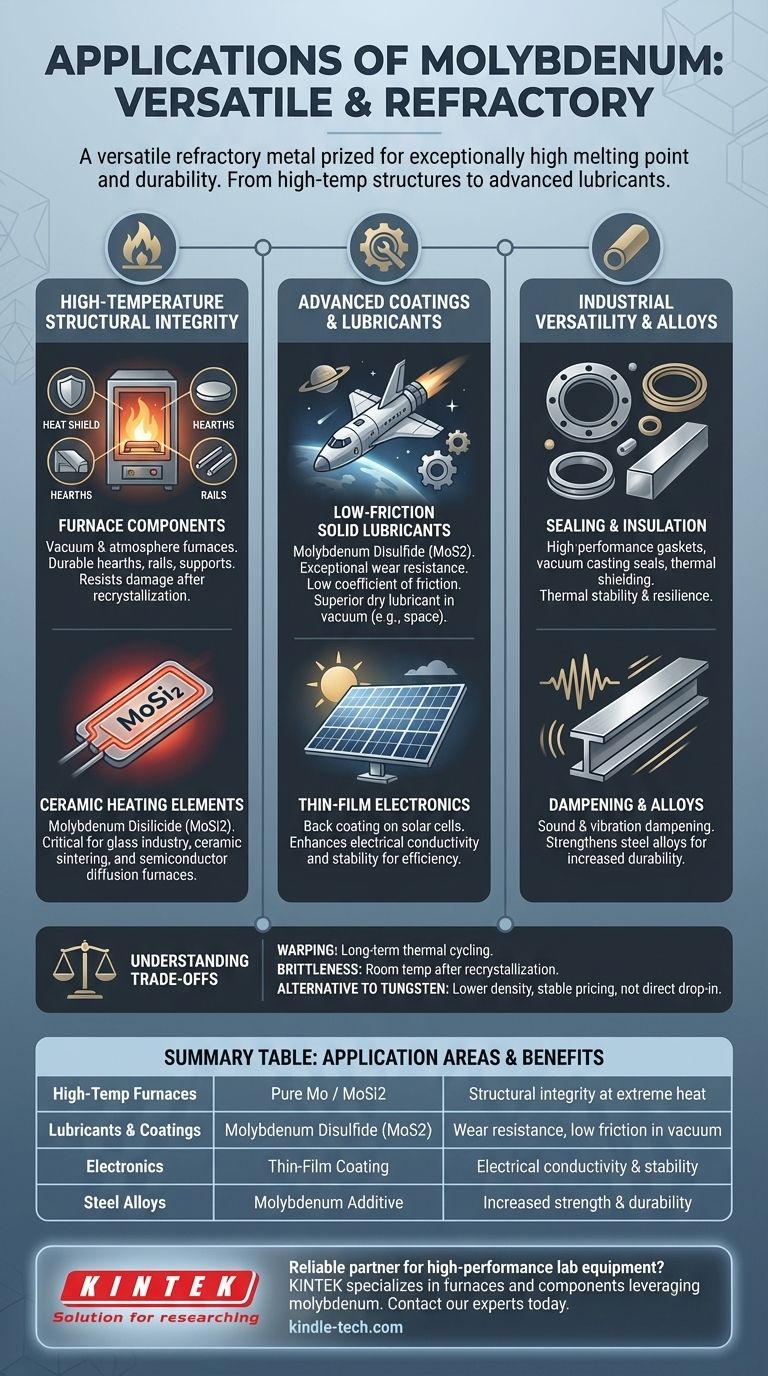
High-Temperature Structural Integrity
One of the primary drivers for using molybdenum is its ability to maintain strength at extreme temperatures where most other metals would fail.
Furnace Components
Molybdenum is a cornerstone material for constructing high-temperature vacuum and atmosphere furnaces. Its durability makes it ideal for hearth components, rails, and structural supports that must endure intense heat.
Thicker sections of molybdenum are remarkably robust, resisting damage even after a process called recrystallization, which can make other materials brittle.
Ceramic Heating Elements
In its compound form, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), it becomes a refractory ceramic used to create high-performance heating elements.
These elements are critical in the glass industry, for ceramic sintering, and in specialized heat treatment and semiconductor diffusion furnaces, where consistent and extreme heat is required.
Advanced Coatings and Lubricants
Molybdenum's utility extends to surface engineering, where it provides wear resistance and low-friction properties in demanding environments.
Low-Friction Solid Lubricants
Coatings based on molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) are used by organizations like NASA for their exceptional wear resistance and low coefficient of friction.
In the vacuum of space, where liquid lubricants would evaporate, MoS2 provides a durable, dry lubricating film that can outperform even Teflon and graphite.
Thin-Film Electronics
Molybdenum is also used as a thin-film coating on the back of solar panel cells. Its electrical conductivity and stability contribute to the efficiency and longevity of the photovoltaic device.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging molybdenum's specific challenges.
Warping Under Thermal Cycling
While durable, molybdenum components like furnace rails can warp after long-term, repeated thermal cycling. This deformation may require occasional maintenance, such as hot-straightening, to restore their original shape.
An Alternative, Not a Replacement
Molybdenum is often cited as an alternative to tungsten due to its lower density and more stable pricing. However, it is not a direct drop-in replacement. Tungsten has a higher melting point and density, making it superior for certain applications where maximum temperature resistance or mass is required.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many refractory metals, molybdenum can become brittle at room temperature after it has been heated past its recrystallization temperature. While thick components manage this well, it's a critical design consideration for thinner parts or those subject to mechanical shock.
Versatility in Industrial Products
Beyond high-tech applications, molybdenum's properties are leveraged in a variety of industrial products.
Sealing and Insulation
Due to its thermal stability and resilience, molybdenum is incorporated into materials for high-performance gaskets, seals for vacuum casting, and thermal shielding.
Dampening Properties
Its physical characteristics also make it a useful component in materials designed for vibration and sound dampening in specialized industrial equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting molybdenum depends entirely on the engineering problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat structural performance: Pure molybdenum and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are premier choices for furnace components and heating elements.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and low friction: Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) coatings provide a superior dry lubricant, especially in vacuum or high-load environments.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective alternative to tungsten: Molybdenum offers a balance of high-temperature performance and lower density at a more consistent price point.
Ultimately, molybdenum empowers engineers to solve challenges in heat, friction, and structural integrity where conventional materials fall short.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Molybdenum Form | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Furnaces | Pure Molybdenum / MoSi2 | Structural integrity at extreme heat |
| Lubricants & Coatings | Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) | Wear resistance, low friction in vacuum |
| Electronics | Thin-Film Coating | Electrical conductivity & stability |
| Steel Alloys | Molybdenum Additive | Increased strength & durability |
Need a reliable partner for high-performance lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in furnaces and components that leverage materials like molybdenum for superior thermal management. Whether you're designing for extreme temperatures or need durable, high-efficiency solutions, our expertise ensures your lab operates at peak performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs with precision-engineered equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance



















