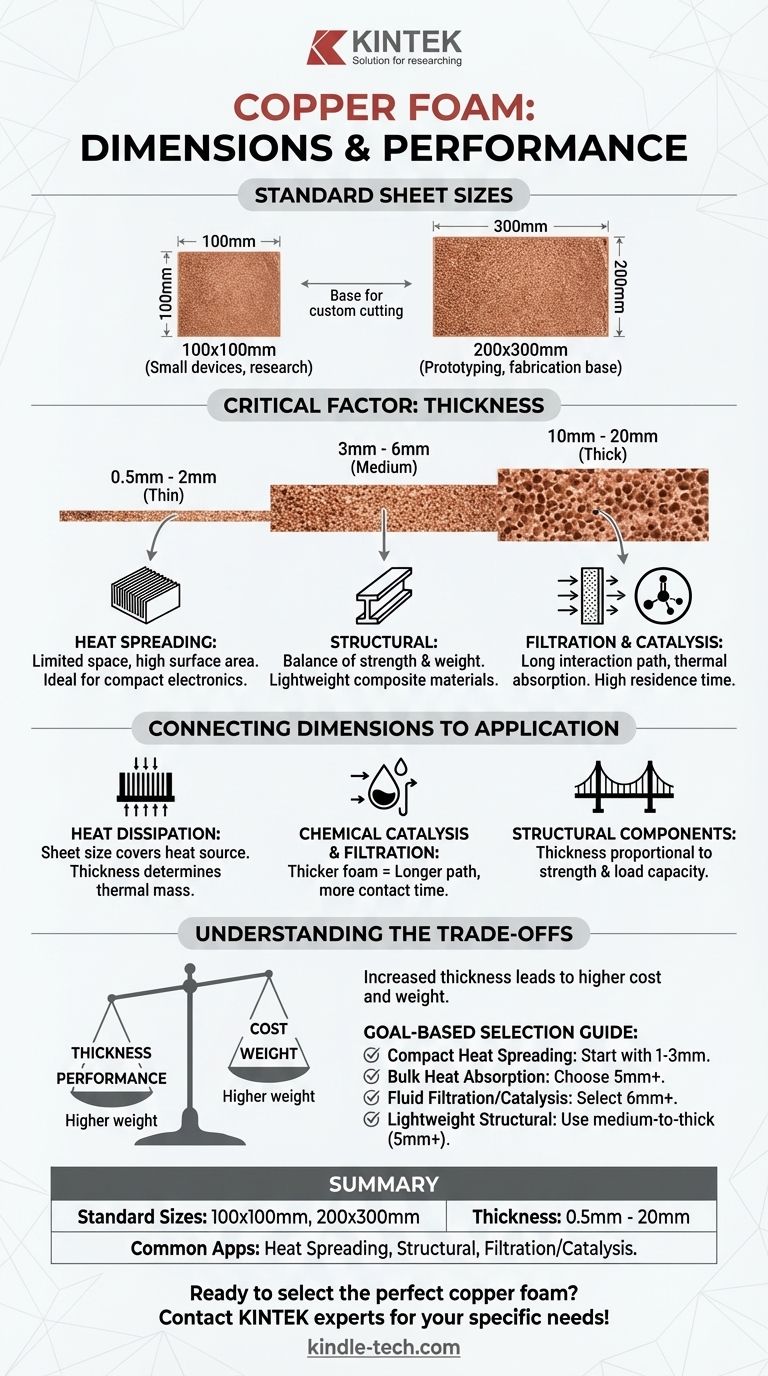
In short, commercially available copper foam is typically offered in standard sheet sizes of 100x100mm and 200x300mm. The material is produced in a wide range of thicknesses, commonly including 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.5mm, 1.6mm, 2mm, 3mm, 5mm, 6mm, 10mm, 15mm, and 20mm.
While knowing the standard sizes is a starting point, the critical decision is selecting a thickness that aligns with your specific technical goal, as this dimension directly dictates the material's thermal, structural, and filtration performance.

The Role of Physical Dimensions
The dimensions of copper foam are not arbitrary; they are directly linked to its intended function. Understanding how sheet size and thickness influence performance is key to successful implementation.
Standard Sheet Sizes
The common stock sizes of 100x100mm and 200x300mm are designed for accessibility. These dimensions are practical for laboratory research, prototyping, and integration into small- to medium-sized devices.
For applications requiring larger surface areas or custom shapes, these sheets serve as the base material for cutting and fabrication.
The Critical Factor of Thickness
The choice of thickness is the most important variable you will control. It directly impacts the material's properties and is a trade-off between performance, weight, and cost.
A thinner foam (e.g., 0.5mm to 2mm) is ideal for applications where space is limited but a high surface area is still needed, such as in compact heat spreaders.
Medium thicknesses (3mm to 6mm) offer a balance between thermal mass, fluid flow, and structural integrity, making them versatile for a range of applications.
Thicker foams (10mm and above) are chosen for tasks that demand significant thermal absorption, high mechanical strength, or a long interaction path for fluids in filtration or catalysis.
Connecting Dimensions to Application
The optimal size and thickness depend entirely on the problem you are trying to solve. The material's porous structure and high conductivity are leveraged differently in each use case.
For Heat Dissipation
In electronics cooling, copper foam excels due to its vast internal surface area. The sheet size must be sufficient to cover the heat-generating component.
The thickness determines the thermal mass and the capacity to draw heat away from the source. A thicker foam can absorb and dissipate more thermal energy.
For Chemical Catalysis and Filtration
For applications like wastewater treatment or catalytic converters, performance is a function of contact time.
A thicker foam creates a longer path, forcing a gas or liquid to have more residence time interacting with the copper's surface. The open-pore structure allows for high throughput with a relatively low pressure drop.
For Structural Components
As a structural material, copper foam's high strength-to-weight ratio is its primary advantage.
Here, thickness is directly proportional to its strength and hardness. Thicker sections provide greater rigidity and load-bearing capacity, useful in creating lightweight yet robust composite materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right dimensions requires balancing competing factors. Being aware of these compromises is crucial for avoiding common design pitfalls.
Thickness vs. Cost and Weight
The most obvious trade-off is that increased thickness leads directly to higher material cost and greater weight. You should always select the minimum thickness that meets your performance requirements to optimize for efficiency.
Porosity vs. Strength
While not a dimension you order directly, porosity is an inherent property that works in tandem with thickness. Higher porosity improves fluid flow and reduces weight but simultaneously decreases the material's overall mechanical strength.
Standard Sizes vs. Custom Fabrication
Relying on standard sheet sizes is excellent for rapid prototyping and validation. However, for scaled production or components with unique geometries, you must factor in the additional costs and lead times associated with custom water-jet cutting, stamping, or molding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use your primary objective to guide your selection of copper foam thickness.
- If your primary focus is compact heat spreading: Start with thinner foams (1-3mm) to maximize surface area in a small volume.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat absorption: Choose a thicker foam (5mm+) to provide the necessary thermal mass to manage heat spikes.
- If your primary focus is fluid filtration or catalysis: Select a thicker foam (6mm+) to increase the residence time and reaction efficiency.
- If your primary focus is a lightweight structural component: Use a medium-to-thick foam (5mm+) and pay close attention to the balance between its density and required mechanical strength.
Choosing the correct copper foam dimensions is a process of aligning the material's inherent properties with the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Dimension | Standard Options | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sheet Size | 100x100mm, 200x300mm | Lab research, prototyping, small-to-medium devices |
| Thickness | 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.5mm, 1.6mm, 2mm, 3mm, 5mm, 6mm, 10mm, 15mm, 20mm | Heat spreading (thin), structural components (medium), filtration/catalysis (thick) |
Ready to select the perfect copper foam for your project? The right dimensions are critical for achieving optimal performance in heat dissipation, filtration, or structural applications. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including copper foam, to meet your specific laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between thickness, porosity, and cost to find the ideal solution. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and leverage our expertise for your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Foam
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- What are the characteristics of copper foam? Unlock High-Performance Thermal and Electrical Solutions
- What electrostatic protection measures should be taken when using nickel and copper foam? Essential ESD Safety Protocols
- What are the common applications of copper foam? A Guide to Its High-Performance Uses
- What are the proper storage conditions for nickel and copper foam? A Guide to Preserving Performance

















