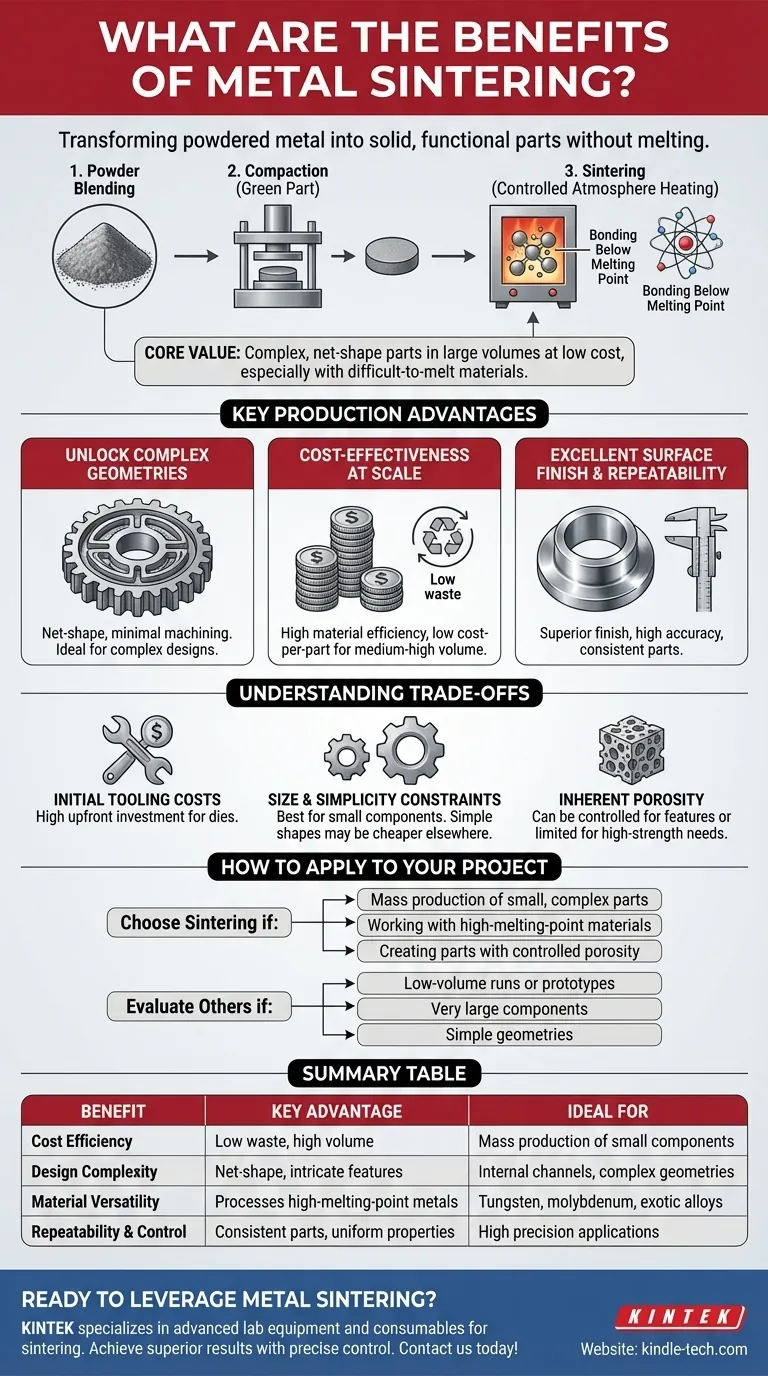
At its core, metal sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms powdered metal into a solid, functional part without ever melting the material. It achieves this by using heat and pressure to bond the particles together, unlocking significant advantages in cost, geometric complexity, and material versatility that are often unattainable with traditional methods like machining or casting.
Sintering's primary value lies in its unique ability to produce highly complex, net-shape parts in large volumes at a low cost per piece, especially when working with materials that are difficult or impossible to melt and machine.
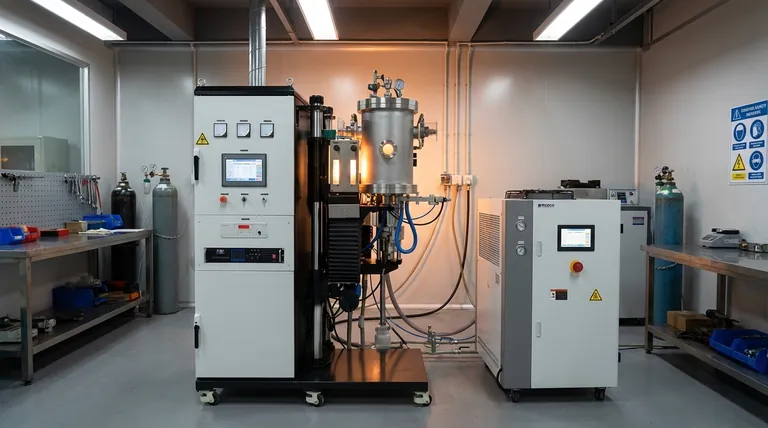

How Sintering Creates Value
The sintering process itself is the source of its key benefits. It involves three fundamental steps: blending metal powders, compacting them into a desired shape (a "green part"), and heating them in a controlled atmosphere furnace to bond the particles.
Bonding Below the Melting Point
The defining characteristic of sintering is that the heating phase occurs below the material's melting point.
This atomic-level diffusion fuses the particles together, developing "sintered necks" that reduce internal pores and dramatically increase the part's strength, density, and conductivity. This approach is far more energy-efficient than melting and casting.
Unlocking High-Performance Materials
Because it avoids melting, sintering is one of the few viable methods for manufacturing parts from materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum. This opens the door for high-strength, high-temperature applications like turbine blades and specialized tooling.
Achieving Superior Material Control
The process begins with precisely formulated powders. This gives manufacturers exceptional control over the final part's purity, uniformity, and grain size. The result is a highly repeatable operation that produces consistent parts with uniform properties and no risk of inclusions or binding contacts that can occur in casting.
Key Production Advantages
When applied correctly, sintering provides a powerful competitive edge in manufacturing. It excels where other processes struggle with cost, complexity, or consistency.
Unlocking Complex Geometries
Sintering is a net-shape or near-net-shape process. This means parts emerge from the tooling very close to their final dimensions, with intricate features like internal channels, non-machinable curves, or varying densities built-in.
This capability eliminates or drastically reduces the need for secondary machining, saving significant time and cost, especially for complex designs produced in mass.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
The process is remarkably efficient with raw materials, generating very little waste compared to subtractive methods like CNC machining.
While the initial investment in compaction tooling can be substantial, the low material waste and high production speed make the cost-per-part extremely low for medium- to high-volume production runs.
Excellent Surface Finish and Repeatability
Sintered parts typically have excellent surface finishes straight out of the furnace, often eliminating the need for post-processing steps like grinding or polishing. The use of robust tooling ensures that every part is a highly accurate and repeatable copy of the last.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every application. Objectivity requires understanding sintering's limitations to determine if it is the right fit.
Initial Tooling Costs
The primary drawback is the high upfront cost for the hardened steel dies and tooling required for compaction. This makes sintering economically unviable for prototypes, one-offs, or very low-volume production.
Size and Simplicity Constraints
The process is generally best suited for producing relatively small components. The immense pressure required for compaction makes manufacturing very large parts impractical or prohibitively expensive. Similarly, very simple geometries may be cheaper to produce with other methods.
Inherent Porosity
While the process significantly reduces porosity, it rarely eliminates it completely without secondary operations. For applications demanding absolute vacuum integrity or the highest possible fatigue strength, this residual porosity can be a limiting factor. However, this same feature can be leveraged to create parts with controlled porosity, such as self-lubricating bearings or filters.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific goals regarding cost, volume, material, and complexity.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing a small, complex metal part: Sintering is likely the most cost-effective and capable solution.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point or exotic materials: Sintering may be the only practical manufacturing option available.
- If your primary focus is a low-volume run or a very large component: You should evaluate CNC machining, casting, or fabrication first.
- If your primary focus is creating a part with controlled porosity: Sintering offers unique capabilities that other processes cannot replicate.
Ultimately, metal sintering provides a powerful strategic advantage when its strengths are aligned with the demands of the part and production scale.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Low material waste, high volume production | Mass production of small components |
| Design Complexity | Net-shape parts with intricate features | Internal channels, complex geometries |
| Material Versatility | Processes high-melting-point metals | Tungsten, molybdenum, exotic alloys |
| Repeatability & Control | Consistent parts with uniform properties | Applications requiring high precision |
Ready to leverage the power of metal sintering for your laboratory or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables required for sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our expertise can help you achieve superior results with precise temperature control and consistent performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities and drive efficiency in your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















