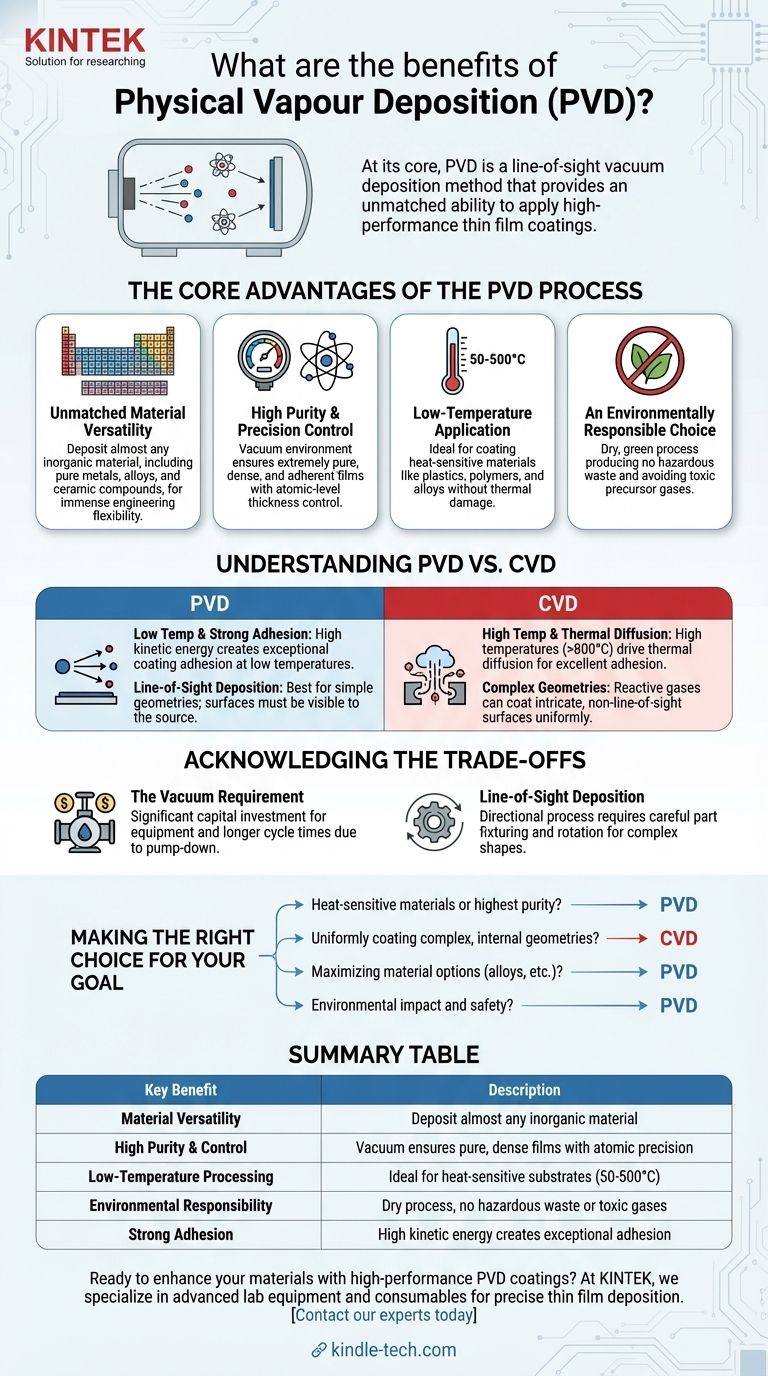
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a line-of-sight vacuum deposition method that provides an unmatched ability to apply high-performance thin film coatings. The primary benefits of PVD include its vast material versatility, exceptional coating purity and density, and its low processing temperature, which allows it to be used on a wide range of substrates without causing thermal damage.
The essential value of PVD lies in its precision and versatility. It allows engineers to deposit high-purity films from nearly any inorganic material onto substrates, including heat-sensitive plastics, at low temperatures—something high-temperature chemical methods cannot achieve.

The Core Advantages of the PVD Process
To truly understand PVD, we must look beyond a simple list of benefits and examine the principles that drive its adoption in industries from aerospace to medical devices.
Unmatched Material Versatility
PVD processes, such as sputtering or evaporation, function by physically liberating atoms from a source material (the "target") and depositing them onto a substrate.
Because this is a physical and not a chemical process, it can be used to deposit almost any inorganic material. This includes pure metals, alloys, and a wide range of ceramic compounds, offering immense flexibility in engineering a surface's properties.
High Purity and Precision Control
All PVD processes take place in a high-vacuum chamber. This environment is critical because it removes atmospheric gases that could otherwise react with the coating material and create impurities.
The result is an extremely pure, dense, and adherent film. This process allows for atomic-level control over the coating's thickness and structure, ensuring high quality and repeatable accuracy for high-volume production.
Low-Temperature Application
Perhaps the most significant advantage of PVD is its characteristically low processing temperature, typically ranging from 50 to 500°C.
This makes it the ideal method for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics, polymers, and certain metal alloys that would be damaged or destroyed by the high temperatures required for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
An Environmentally Responsible Choice
PVD is a dry, environmentally friendly process. It produces no hazardous waste, unlike wet plating processes, and does not rely on the often toxic precursor gases used in CVD.
This "green" characteristic simplifies regulatory compliance and creates a safer working environment.
Understanding the PVD vs. CVD Distinction
A common point of confusion is choosing between PVD and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While both create thin films, their mechanisms and ideal use cases are fundamentally different.
The Matter of Temperature and Adhesion
CVD relies on a chemical reaction at high temperatures (often >800°C), causing precursor gases to form a film on the substrate. This high heat promotes excellent coating adhesion through thermal diffusion into the substrate.
PVD, being a low-temperature process, is a "line-of-sight" deposition of energetic atoms. The adhesion is exceptionally strong due to the high kinetic energy of the depositing particles, but it is a fundamentally different mechanism than the thermal diffusion in CVD.
The Challenge of Complex Geometries
CVD's use of gases allows it to coat complex, non-line-of-sight surfaces with high uniformity, as the gas can flow into and react within intricate shapes.
PVD is a directional, line-of-sight process. While parts can be rotated on complex fixtures to ensure coverage, uniformly coating deep recesses or internal channels can be challenging.
Acknowledging the Trade-offs
No technology is without limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging the trade-offs inherent in choosing PVD.
The Vacuum Requirement
The need for a high-vacuum environment means PVD equipment is a significant capital investment. The process cycle includes time to pump down the chamber to the required vacuum level, which can make it more time-consuming for batch processing compared to non-vacuum methods.
While the deposition rate itself can be high once the process starts, the overall cycle time (load, pump, coat, vent, unload) must be considered.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
As mentioned, PVD is fundamentally directional. Surfaces must be "visible" to the source material target to be coated effectively. This requires careful part fixturing and rotation, adding complexity for parts with highly intricate or internal geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct coating technology depends entirely on your project's specific constraints and desired outcomes.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials or achieving the highest film purity: PVD is the superior choice due to its low-temperature process and vacuum environment.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating the inside of complex, non-line-of-sight geometries: CVD is often more effective because the reactive gases can conform to intricate shapes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material options for alloys and composite films: PVD offers an unparalleled library of materials to deposit.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact and operational safety: PVD's dry, non-toxic process presents a distinct advantage over chemical-based alternatives.
Understanding these fundamental principles empowers you to select the technology that will best achieve your material engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Versatility | Deposit almost any inorganic material (metals, alloys, ceramics) |
| High Purity & Control | Vacuum environment ensures pure, dense, adherent films with atomic-level precision |
| Low-Temperature Processing | Ideal for heat-sensitive substrates (50-500°C range) |
| Environmental Responsibility | Dry process with no hazardous waste or toxic gases |
| Strong Adhesion | High kinetic energy creates exceptional coating adhesion |
Ready to enhance your materials with high-performance PVD coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin film deposition. Our PVD solutions deliver the material versatility, purity, and low-temperature processing your R&D or production needs.
Whether you're working with heat-sensitive polymers, metals, or complex alloys, our expertise ensures you get the right coating solution for superior surface properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's PVD technology can solve your specific coating challenges and drive your innovation forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















