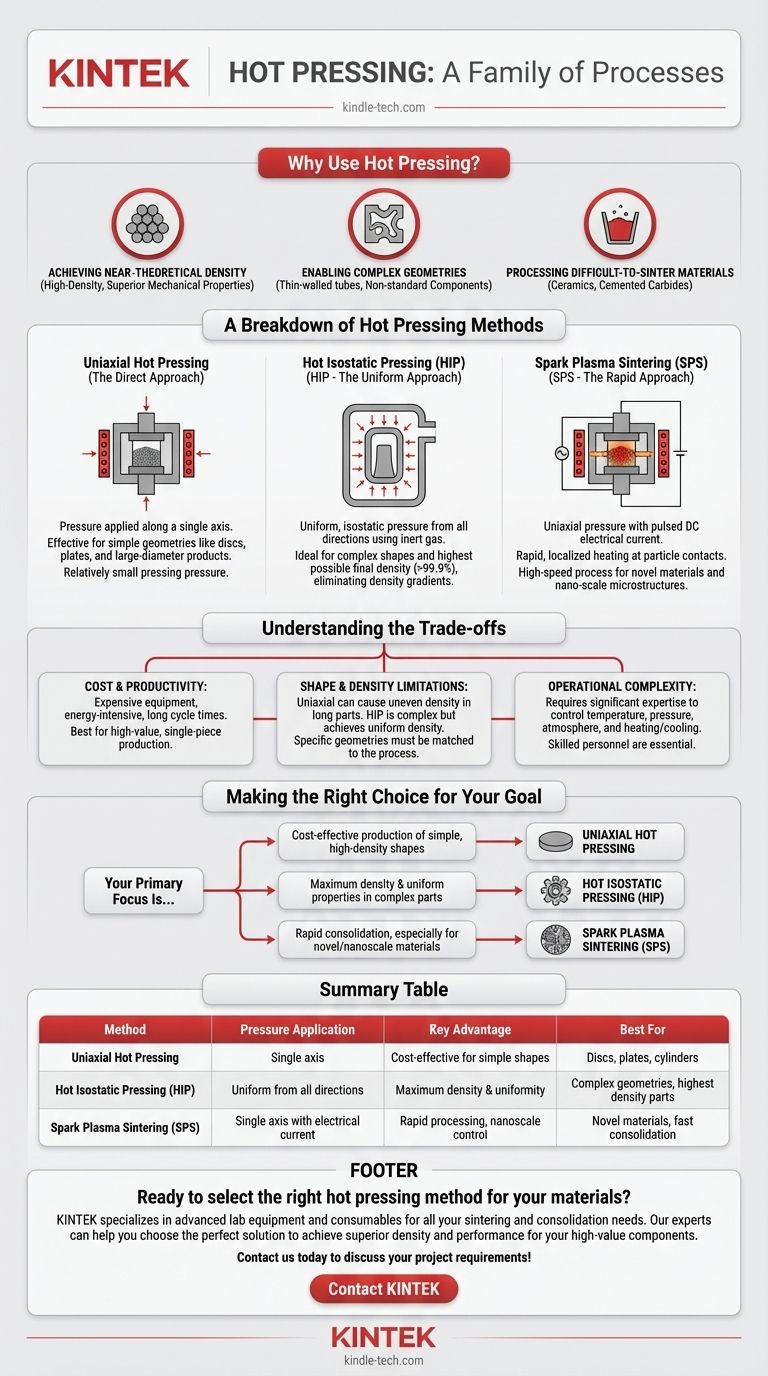
Fundamentally, hot pressing is a family of processes, not a single technique. These methods are primarily categorized by how pressure and heat are simultaneously applied to a powder material, with the main types being Uniaxial Hot Pressing, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), and the advanced field-assisted method, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Each variant is designed to consolidate powders into a dense solid part, overcoming the limitations of traditional sintering.
The core purpose of any hot pressing method is to create highly dense, high-performance components from powders. The critical difference between the types lies in how pressure is applied—from one direction, all directions, or with electrical assistance—which directly dictates the final part's geometry, uniformity, and cost.
The Core Principle: Why Use Hot Pressing?
Hot pressing is employed when other consolidation methods fail to meet density, performance, or material requirements. The combination of heat and pressure provides distinct advantages.
Achieving Near-Theoretical Density
By applying external pressure during heating, the process physically forces powder particles together. This action closes internal porosity far more effectively than pressureless sintering, resulting in high-density products with superior mechanical properties.
Enabling Complex Geometries
The heat makes the powder material behave with thermoplasticity, allowing it to flow and fill intricate mold details. This enables the production of parts with complex shapes, such as thin-walled tubes or other non-standard components, that would be difficult to form otherwise.
Processing Difficult-to-Sinter Materials
Many advanced materials, like certain ceramics and cemented carbides, have very high melting points and are resistant to densification. Hot pressing provides the necessary energy and force to consolidate these materials effectively.
A Breakdown of Hot Pressing Methods
While all types share the same goal, their mechanics are distinct, leading to different applications.
Uniaxial Hot Pressing (The Direct Approach)
This is the most conventional form of hot pressing. Powder is placed in a die, and pressure is applied along a single axis by one or two moving punches while the entire assembly is heated.
It is highly effective for producing simple geometries like discs, plates, and cylinders. The pressing pressure is relatively small, allowing for the creation of large-diameter products.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP - The Uniform Approach)
In HIP, a part (often pre-formed or encapsulated) is placed in a high-pressure vessel. An inert gas, typically Argon, is heated and pressurized, exerting uniform, or isostatic, pressure on the component from all directions.
This method eliminates the density gradients seen in uniaxial pressing, making it ideal for parts with highly complex shapes or for achieving the highest possible final density (often >99.9%).
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS - The Rapid Approach)
Often considered a modern evolution of hot pressing, SPS (also known as Field Assisted Sintering Technology or FAST) uses a similar uniaxial press setup. However, it also passes a pulsed DC electrical current directly through the powder and die.
This current generates extremely rapid, localized heating at the particle contact points, drastically reducing the required time and temperature. It is a high-speed process excellent for novel materials and preserving nano-scale microstructures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The power of hot pressing comes with inherent complexities and costs that must be considered.
Cost and Productivity
Hot pressing equipment is expensive, and the processes are energy-intensive. Cycle times, especially for conventional uniaxial and HIP processes, are long.
Consequently, these methods are characterized by low productivity and high costs, making them most suitable for high-value components, prototypes, or single-piece production rather than mass manufacturing.
Shape and Density Limitations
While excellent for complex shapes, uniaxial pressing can result in uneven density in long or high-aspect-ratio parts due to friction with the die walls. HIP overcomes this but requires a more complex setup.
The ability to make large size, non-deformed products is a key advantage, but the specific geometry must be matched to the correct process type to ensure uniformity.
Operational Complexity
Successfully running a hot press cycle demands significant expertise. Operators must precisely control temperature, pressure, heating/cooling rates, and vacuum or inert atmospheres.
These high operational technology requirements mean that skilled personnel are essential to achieving consistent and successful outcomes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct hot pressing technique depends entirely on your project's specific material, geometry, and performance targets.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of simple, high-density shapes: Uniaxial Hot Pressing is your most direct and established solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and uniform properties in complex parts: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the superior choice, despite its higher operational cost.
- If your primary focus is rapid consolidation, especially for novel or nanoscale materials: Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) offers unmatched speed and unique microstructural control.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the precise manufacturing process that aligns with your material, geometric, and performance requirements.

Summary Table:
| Method | Pressure Application | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uniaxial Hot Pressing | Single axis | Cost-effective for simple shapes | Discs, plates, cylinders |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Uniform from all directions | Maximum density & uniformity | Complex geometries, highest density parts |
| Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Single axis with electrical current | Rapid processing, nanoscale control | Novel materials, fast consolidation |
Ready to select the right hot pressing method for your materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for all your sintering and consolidation needs. Our experts can help you choose the perfect solution to achieve superior density and performance for your high-value components. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does the vacuum environment serve during the densification of Ag-SnO2-Y2O3? Optimize Material Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press furnace for sintering CNT/Cu composites? Superior Density & Bonding
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot-pressing furnace in the preparation of Cu-2Ni-7Sn/45 steel composites?



















