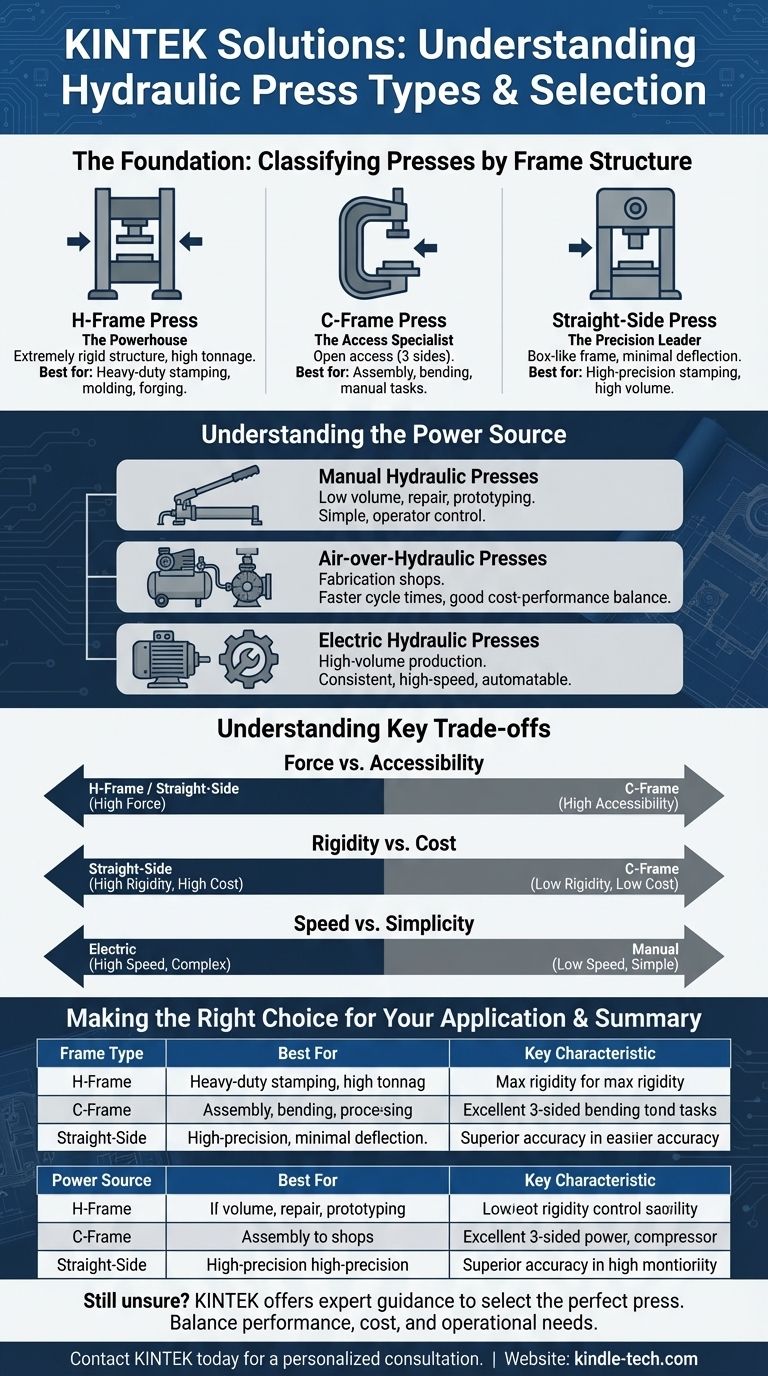
Understanding the types of hydraulic presses is essential for selecting the right tool for the job. While many variations exist, presses are primarily categorized by their physical frame design and their power source. The most common frame types are the H-Frame, C-Frame, and Four-Post press, each offering a different balance of force capacity and accessibility.
The "best" hydraulic press does not exist. The right choice is a function of your specific application, balancing the need for raw force and rigidity against the need for works-pace access and operational speed.

The Foundation: Classifying Presses by Frame Structure
The frame is the backbone of the press. It dictates the machine's rigidity, its ability to handle off-center loads, and how easily an operator can access the work area.
The H-Frame Press: The Powerhouse
H-Frame presses, often called four-column presses, are the workhorses of industrial applications. They are constructed with two vertical columns, a stationary bed, and a movable upper beam or platen.
This design creates an extremely rigid structure, allowing for very high tonnage capacities. It excels at distributing force evenly, making it ideal for heavy-duty stamping, molding, deep drawing, and forging operations.
The C-Frame Press: The Access Specialist
As its name suggests, the C-Frame press has a frame shaped like the letter "C." This provides open access to the work area from three sides (front, left, and right).
This accessibility makes the C-Frame press ideal for tasks that require manual loading and unloading of parts, frequent tooling changes, or assembly work. They are common in workshops for straightening, bending, and general fabrication.
The Straight-Side Press: The Precision Leader
Straight-Side presses offer the ultimate in rigidity and precision. They feature a solid, box-like frame structure that minimizes any lateral deflection, even under extreme force.
This superior accuracy makes them the top choice for complex, high-precision stamping and blanking operations where die life and part consistency are critical. They are typically used in high-volume production environments.
Understanding the Power Source
While all these machines use hydraulic fluid to generate force, the method used to pressurize that fluid defines the press's speed, control, and cost.
Manual Hydraulic Presses
These presses use a hand-operated pump to build pressure. They are simple, inexpensive, and offer the operator a high degree of control over the ram's movement.
Their use is primarily for low-volume applications like repair shops, garages, and small-scale prototyping where speed is not a primary concern.
Air-over-Hydraulic Presses
Also known as pneumatic-hydraulic presses, these use compressed shop air to drive a hydraulic pump. This provides much faster cycle times than a manual pump.
They represent a good balance between cost and performance, making them a popular choice for fabrication shops that need more speed than a manual press can offer.
Electric Hydraulic Presses
These are the most common type in industrial production. An electric motor drives a hydraulic pump, providing consistent, high-speed, and high-force operation.
These systems can be integrated with advanced controls (PLCs) for full automation, making them suitable for high-volume, repetitive manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a press involves navigating a clear set of engineering and economic compromises. Understanding them is key to avoiding a costly mistake.
Force vs. Accessibility
This is the primary trade-off. H-Frame and Straight-Side presses provide superior force capacity and rigidity but limit access to the workpiece. A C-Frame offers excellent access but is more prone to frame deflection ("throating") under very high or off-center loads.
Rigidity vs. Cost
The more rigid the frame, the higher the cost. A C-Frame is the most economical design, an H-Frame is the mid-range standard, and a Straight-Side press represents the highest investment due to its robust construction and precision.
Speed vs. Simplicity
A manual press is the simplest system but also the slowest. Adding an air or electric power source increases speed and the potential for automation, but it also adds complexity, cost, and maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct press requires matching its design characteristics to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum force for heavy molding or forging: An H-Frame or Straight-Side press with an electric power unit is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is accessibility for assembly or frequent tool changes: A C-Frame press provides the best operational flexibility for manual tasks.
- If your primary focus is low-volume repair or budget-conscious fabrication: A manual or air-over-hydraulic H-Frame press offers a cost-effective and versatile solution.
By aligning the press's frame and power system with your specific task, you ensure optimal performance, safety, and return on your investment.
Summary Table:
| Frame Type | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| H-Frame | Heavy-duty stamping, forging, molding | Maximum rigidity & high tonnage |
| C-Frame | Assembly, bending, straightening | Excellent 3-sided accessibility |
| Straight-Side | High-precision stamping, blanking | Superior accuracy & minimal deflection |
| Power Source | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | Low-volume repair, prototyping | Simple, low-cost, operator-controlled |
| Air-over-Hydraulic | Fabrication shops | Good balance of speed and cost |
| Electric | High-volume industrial production | High-speed, consistent, automatable |
Still unsure which hydraulic press is right for your lab or workshop? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to help you select the perfect press for your specific application—whether you need high force, precision, or accessibility. Our team can help you balance performance, cost, and operational needs to maximize your efficiency and ROI.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the ideal hydraulic press solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for LGVO synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Solid Electrolytes
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is the role of a hydraulic press with heating plates in copper welding tests? Analyze Stress & Thermal Cycles



















