While a powerful technique for low-temperature deposition, Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) introduces significant disadvantages related to potential material damage, film contamination, and increased process complexity. Unlike purely thermal methods, the use of an energetic plasma, while beneficial, is also the source of its primary drawbacks.
The core challenge of PECVD is a direct trade-off: the plasma that enables lower processing temperatures can also bombard the growing film, introduce impurities, and create non-ideal material structures that are less common in higher-temperature thermal CVD.

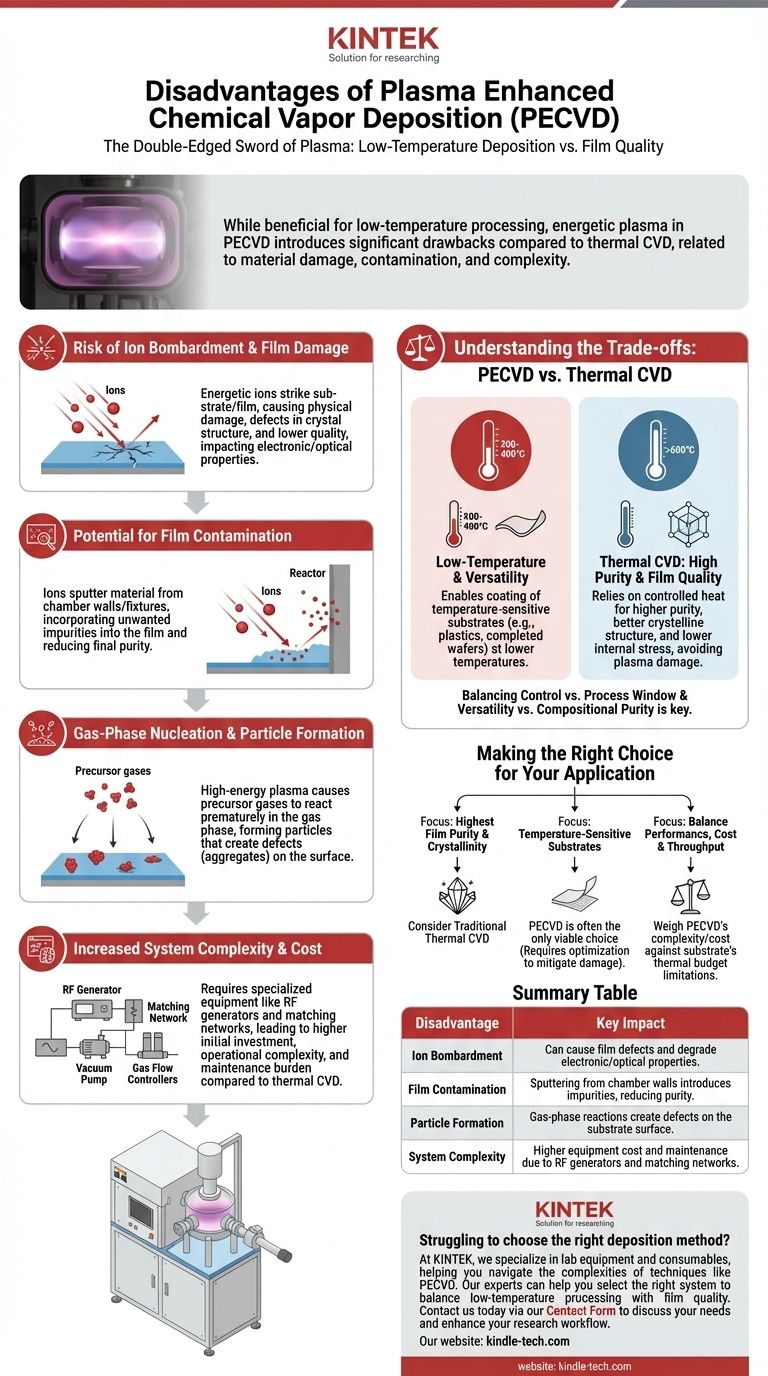
The Core Challenge: The Double-Edged Sword of Plasma
The fundamental difference between PECVD and conventional thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the energy source. Where thermal CVD uses heat to drive chemical reactions, PECVD uses an energized gas, or plasma. This plasma is both the primary advantage and the source of its main disadvantages.
Risk of Ion Bombardment and Film Damage
In a plasma environment, charged ions are accelerated and can strike the surface of the substrate and the growing film with significant energy.
This physical bombardment can create defects in the film's crystal structure, leading to lower-quality material. In sensitive applications, this can negatively impact the electronic or optical properties of the deposited layer.
Potential for Film Contamination
The same energetic ions that can damage the film can also sputter material off the reactor chamber walls or the electrode fixtures.
This sputtered material can then be incorporated into the growing film as an unwanted impurity. This reduces the purity of the final material, a key advantage often sought with CVD processes.
Gas-Phase Nucleation and Particle Formation
The high-energy environment of the plasma can sometimes cause precursor gases to react and form particles in the gas phase before they even reach the substrate.
These particles can fall onto the surface, creating defects known as aggregates or inclusions. This is a common challenge in many CVD processes but can be particularly pronounced in a reactive plasma environment, compromising the integrity of bulk materials.
Increased System Complexity
A PECVD system is inherently more complex than a thermal CVD furnace. It requires specialized equipment to generate and sustain the plasma.
This includes RF or microwave power generators, impedance-matching networks, and more sophisticated vacuum chamber designs. This added complexity increases both the initial equipment cost and the ongoing maintenance burden.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PECVD vs. Thermal CVD
Choosing PECVD is rarely about it being universally "better" or "worse" than other methods. The decision hinges on understanding its specific trade-offs, especially when compared to its thermal counterpart.
Temperature vs. Film Quality
The main reason to use PECVD is its ability to deposit films at much lower temperatures (e.g., 200-400°C) than thermal CVD (often >600°C). This makes it possible to coat temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics or fully fabricated semiconductor wafers.
However, this advantage comes at a cost. Thermal CVD, relying on controlled heat, often produces films with higher purity, better crystalline structure, and lower internal stress because it avoids the damaging effects of ion bombardment.
Control vs. Process Window
While all CVD processes offer a high degree of control, the process window for achieving a high-quality film in PECVD can be narrower and more complex.
Engineers must carefully balance gas flow, pressure, plasma power, frequency, and temperature. A small deviation in one parameter can significantly impact the final film properties, making process optimization more challenging than in a purely thermal system.
Versatility vs. Compositional Purity
PECVD's low-temperature nature makes it versatile for a wide range of substrates. However, synthesizing multi-component materials can be challenging.
Variations in how different precursor gases react within the plasma can lead to a heterogeneous or non-stoichiometric film composition, a problem that is often easier to manage with the more predictable kinetics of thermal reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice between PECVD and another deposition method must be driven by the non-negotiable requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible film purity and crystallinity: Consider traditional thermal CVD, as the absence of plasma bombardment minimizes defects and impurities.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is often the only viable choice, and your effort should be on optimizing plasma parameters to mitigate potential film damage.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance with manufacturing cost and throughput: You must weigh the higher complexity and cost of PECVD equipment against the thermal budget limitations of your substrate.
Understanding these inherent trade-offs is the key to leveraging PECVD's low-temperature capabilities while controlling for its unique challenges.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Ion Bombardment | Can cause film defects and degrade electronic/optical properties. |
| Film Contamination | Sputtering from chamber walls introduces impurities, reducing purity. |
| Particle Formation | Gas-phase reactions create defects on the substrate surface. |
| System Complexity | Higher equipment cost and maintenance due to RF generators and matching networks. |
Struggling to choose the right deposition method for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, helping you navigate the complexities of techniques like PECVD. Our experts can help you select the right system to balance low-temperature processing with film quality, ensuring your laboratory achieves optimal results.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and development workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















