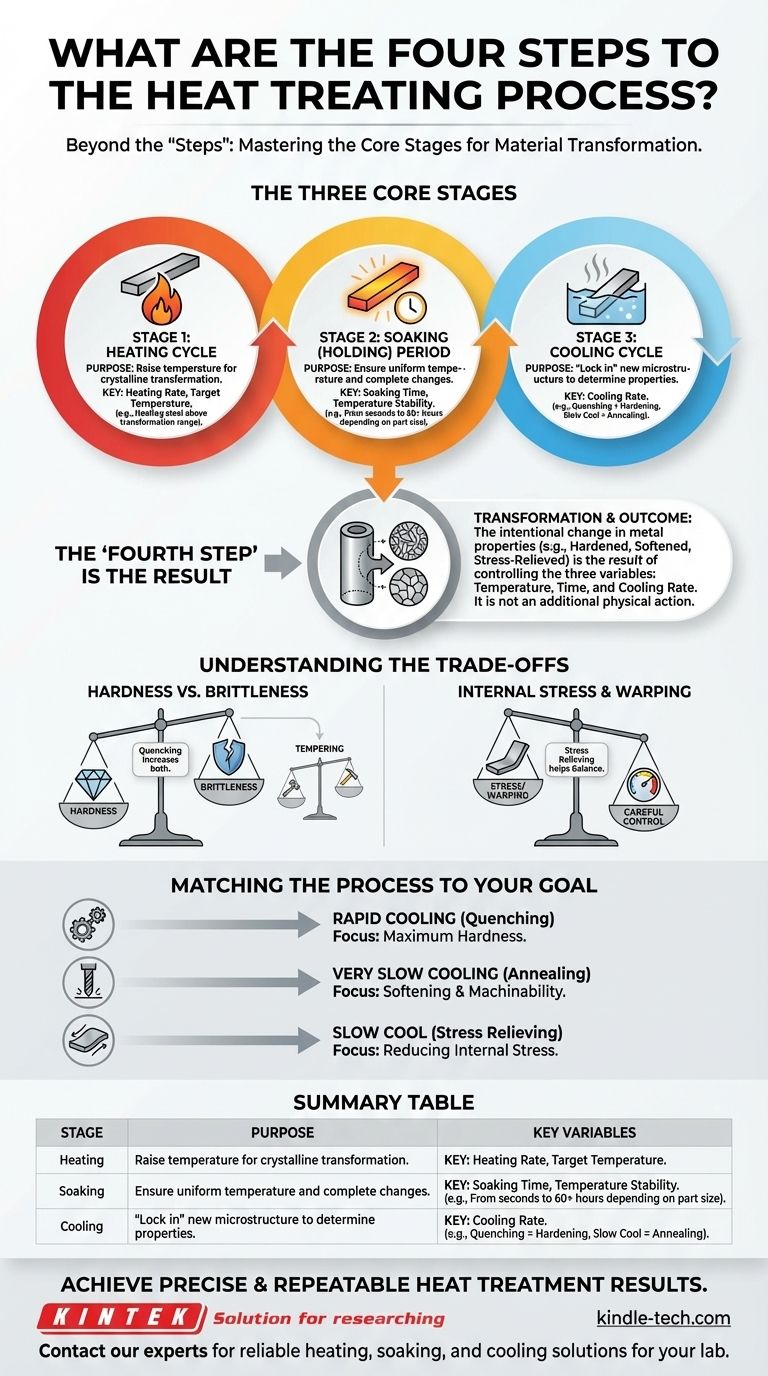
While the process is sometimes described in different ways, industrial heat treatment fundamentally consists of three critical stages: heating the material to a specific temperature, holding it there for a precise duration, and cooling it at a controlled rate. The "fourth step" is not a physical action but the resulting transformation—the intentional change in the metal's properties, which is the entire purpose of the process.
The success of any heat treatment is not determined by a rigid number of steps, but by the precise control of three interdependent variables: temperature, time, and cooling rate. Mastering the interplay between these three factors is what allows for the intentional modification of a metal's mechanical properties.

The Three Core Stages of Heat Treatment
To truly understand how heat treatment works, you must think of it as a unified process with three distinct, controllable phases. Each phase plays a crucial role in altering the microscopic structure of the metal to achieve a desired outcome.
Stage 1: The Heating Cycle
The goal of this first stage is to raise the temperature of the material in a controlled manner. This is done to bring its internal crystalline structure to a point where transformation is possible.
For many common steels, this means heating above a critical "transformation range." This allows the microstructure to change into a form, known as austenite, which is necessary for subsequent hardening or softening.
The rate of heating is also important. Heating a part too quickly can cause thermal shock and internal stress, especially in complex geometries.
Stage 2: The Soaking (Holding) Period
Once the material reaches the target temperature, it is held there for a specific amount of time. This stage is known as soaking.
The purpose of soaking is twofold: to ensure the temperature is uniform throughout the entire volume of the part and to allow the necessary metallurgical changes to fully take place.
The required soaking time can vary dramatically, from a few seconds for surface treatments to over 60 hours for very large components, depending on the material and the desired outcome.
Stage 3: The Cooling Cycle
The cooling stage is often the most critical phase, as it "locks in" the new microscopic structure and determines the final properties of the metal.
The rate of cooling dictates the result. A very rapid cooling process, called quenching (often using oil or water), is used for hardening. It traps the atoms in a hard, brittle structure.
Conversely, a very slow cooling rate, such as letting a part cool in the furnace, is used for annealing. This results in a much softer, more ductile material that is easier to machine.
Why "Four Steps" Can Be Misleading
The common confusion about a "fourth step" often stems from mixing up the core process with specific methods or outcomes.
Confusing Methods with Steps
Terms like annealing, hardening, and stress relieving are not sequential steps in one process. They are distinct types of heat treatment, each utilizing the three core stages (heating, holding, cooling) with different parameters.
For example, quenching is not a separate step from cooling; it is simply one method of executing the cooling stage.
Confusing Process with Outcome
The final state of the material—be it hardened, softened, or stress-relieved—is the result of the three-stage process. It is the outcome you engineer by manipulating the variables, not an additional action you perform.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Altering a metal's properties is always an exercise in balancing competing characteristics. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for selecting the correct heat treatment.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and brittleness. A process like quenching creates extreme hardness and wear resistance, but it also makes the metal brittle and prone to fracture.
This is why a secondary treatment called tempering is often required after hardening. Tempering slightly reduces hardness but significantly improves toughness, making the part more durable.
Internal Stress and Warping
Anytime a material is heated and cooled, internal stresses are introduced. If the heating or cooling rates are not carefully controlled, these stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack.
Stress relieving is a specific heat treatment designed to reduce these internal stresses without significantly altering the hardness or other mechanical properties.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right approach depends entirely on what you need the final component to do.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Hardness: Prioritize a very rapid cooling rate (quenching) after reaching the correct transformation temperature.
- If your primary focus is Softening and Improving Machinability: Use a very slow cooling rate (as in annealing) to produce a soft, ductile microstructure.
- If your primary focus is Reducing Internal Stress: Employ a stress-relieving process, which involves heating to a lower temperature and cooling slowly to relax stresses without significantly changing hardness.
Ultimately, understanding heat treatment is not about counting steps, but about controlling the fundamental variables of temperature, time, and cooling to achieve a predictable and desired material outcome.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Purpose | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Heating | Raise the material to a specific temperature for transformation. | Target temperature, heating rate |
| 2. Soaking | Hold the temperature to ensure uniformity and complete the metallurgical change. | Soaking time, temperature stability |
| 3. Cooling | Lock in the new microstructure at a controlled rate to determine final properties. | Cooling rate (e.g., quenching, annealing) |
Achieve precise and repeatable heat treatment results in your lab. The success of your process hinges on precise control of temperature, time, and cooling. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for reliable heating, soaking, and cooling cycles. Whether you are hardening, annealing, or stress-relieving, our solutions help you achieve the material properties you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heat treatment requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy
- What is the temperature and time for ashing? Achieve Accurate Results with the Right Parameters
- What is the method of determining ash? Choose the Right Ashing Method for Your Lab
- How do you determine the ash content of a plant sample? A Step-by-Step Guide to Mineral Analysis
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results



















