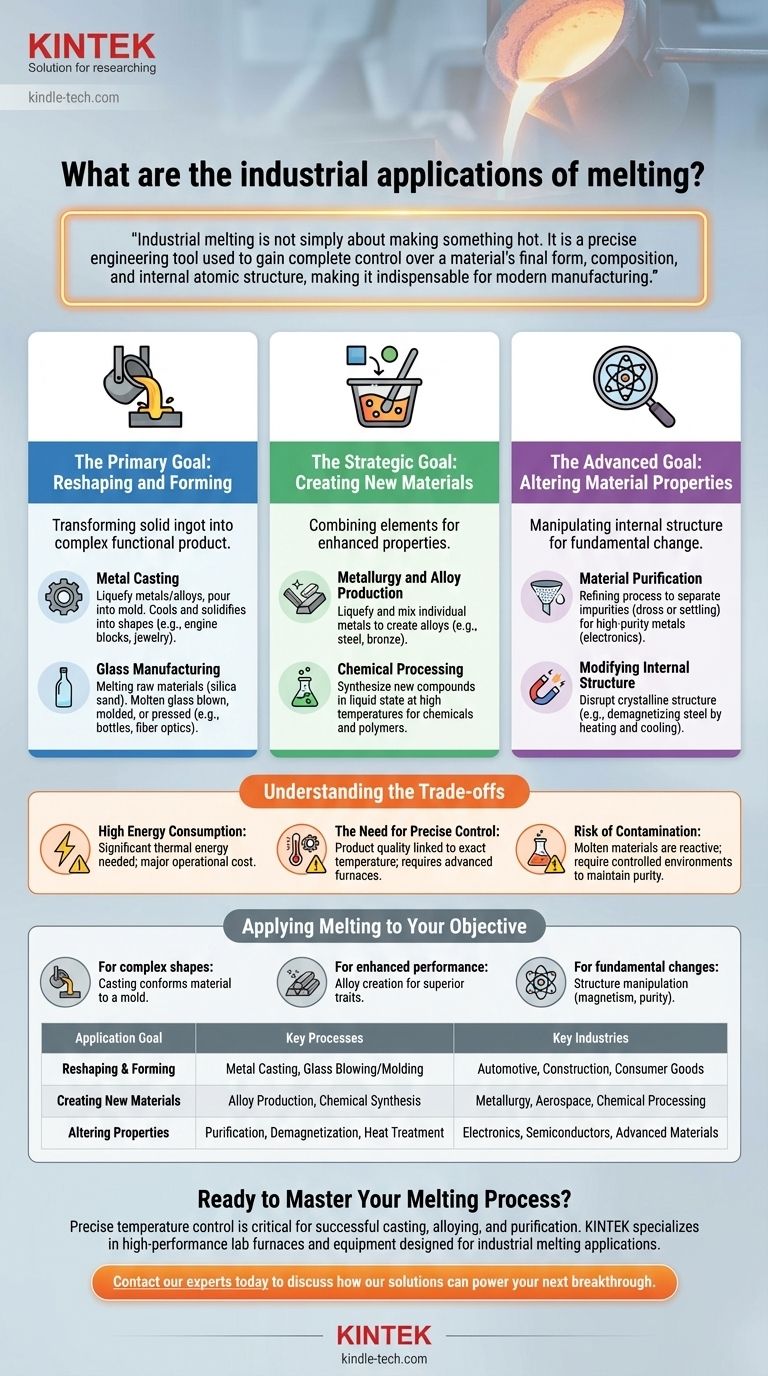
At its core, industrial melting is a foundational process in metallurgy, glass manufacturing, ceramics, and chemical processing. This technique involves liquefying a solid material, not merely to change its state, but to fundamentally reshape it, combine it with other elements, or alter its intrinsic physical properties for a specific, high-value application.
Industrial melting is not simply about making something hot. It is a precise engineering tool used to gain complete control over a material's final form, composition, and internal atomic structure, making it indispensable for modern manufacturing.

The Primary Goal: Reshaping and Forming
The most direct application of melting is to transform a solid, often with a simple shape like an ingot, into a complex and functional product. This is achieved by making the material flow into a predetermined form.
Metal Casting
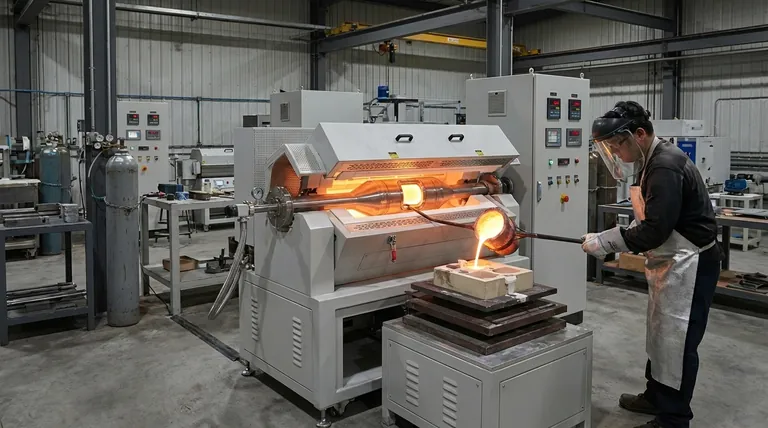
Melting is the first and most critical step in metal casting. Metals or alloys are heated in a furnace until they become fully liquid.
This molten metal is then poured into a mold or die. As it cools and solidifies, it takes the shape of the mold, creating everything from engine blocks to intricate jewelry.
Glass Manufacturing
The production of nearly all glass products begins with melting. Raw materials, primarily silica sand, are heated to extreme temperatures in a furnace.
This creates molten glass, a viscous fluid that can be poured, blown, molded, or pressed into forms like bottles, windows, and fiber optics. The process requires precise temperature control to ensure clarity and strength.
The Strategic Goal: Creating New Materials
Beyond simple reshaping, melting is essential for combining different elements to create entirely new materials with enhanced properties.
Metallurgy and Alloy Production
Alloys are mixtures of metals, or metals combined with other elements, and they are almost always created through melting.
Individual metals are liquefied in a furnace, allowing them to be thoroughly mixed. This process is how we produce essential materials like steel (iron and carbon), bronze (copper and tin), and countless other high-performance alloys.
Chemical Processing
In the chemical industry, melting is often a key step in synthesizing new compounds. Certain reactions only occur when reactants are in a liquid state at high temperatures.
This allows for the controlled combination of elements to produce specialized chemicals, polymers, or other precursor materials for various industries.
The Advanced Goal: Altering Material Properties
The most sophisticated use of melting is to manipulate the internal structure of a material to change its fundamental characteristics. This goes far beyond shape and composition.
Material Purification
Melting can be used as a refining process. As a material melts, impurities can be separated out, either by rising to the surface as dross or by settling at the bottom due to differences in density.
This is a common step in producing high-purity metals required for electronics and aerospace applications.
Modifying Internal Structure
Heating a metal to its melting point disrupts its crystalline atomic structure. A prime example is demagnetizing steel.
When magnetized steel is heated, the orderly alignment of its magnetic domains is randomized. Upon cooling, the magnetism is gone because the structure did not reform in its previously aligned state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, industrial melting is a demanding process with significant operational challenges that must be carefully managed.
High Energy Consumption
Bringing materials to their melting point requires an enormous amount of thermal energy. This makes melting one of the most energy-intensive processes in manufacturing, representing a major operational cost.
The Need for Precise Control
Product quality is directly tied to temperature. If the material is too hot or not hot enough, it can lead to defects, impurities, or a failed batch. Modern electric furnaces are used to achieve the precise temperature control needed for consistent results.
Risk of Contamination
In their molten state, many materials are highly reactive and can easily absorb impurities from the surrounding atmosphere or the crucible containing them. This requires controlled environments to maintain the purity of the final product.
Applying Melting to Your Objective
The specific use of melting is determined entirely by the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex shape: Casting is the most direct application, where melting allows a liquid material to perfectly conform to a mold.
- If your primary focus is enhancing material performance: Melting is the essential first step for creating alloys, combining elements to achieve superior strength, corrosion resistance, or other desired traits.
- If your primary focus is changing a fundamental characteristic: Controlled melting and cooling cycles can be used to manipulate a material's internal atomic structure, such as removing magnetism or refining its purity.
Ultimately, viewing melting as a tool for precise material control is key to leveraging its full potential in any industrial setting.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Key Processes | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Reshaping & Forming | Metal Casting, Glass Blowing/Molding | Automotive, Construction, Consumer Goods |
| Creating New Materials | Alloy Production, Chemical Synthesis | Metallurgy, Aerospace, Chemical Processing |
| Altering Properties | Purification, Demagnetization, Heat Treatment | Electronics, Semiconductors, Advanced Materials |
Ready to Master Your Melting Process?
Precise temperature control is critical for successful casting, alloying, and purification. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for the exacting demands of industrial melting applications.
We provide the reliable tools you need to achieve superior material outcomes, improve batch consistency, and enhance your manufacturing efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can power your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















