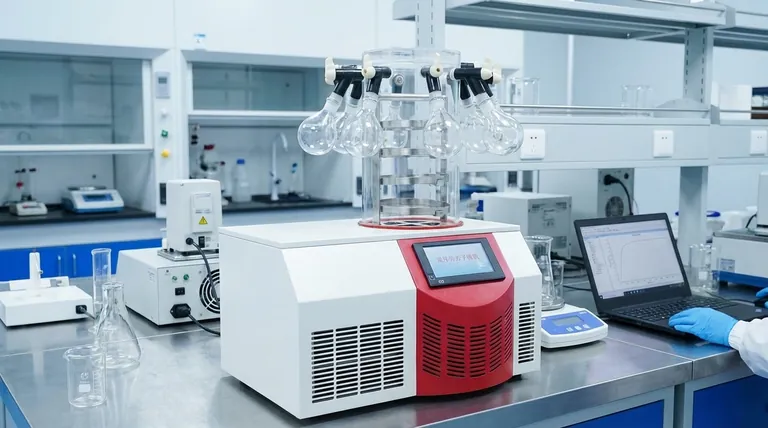
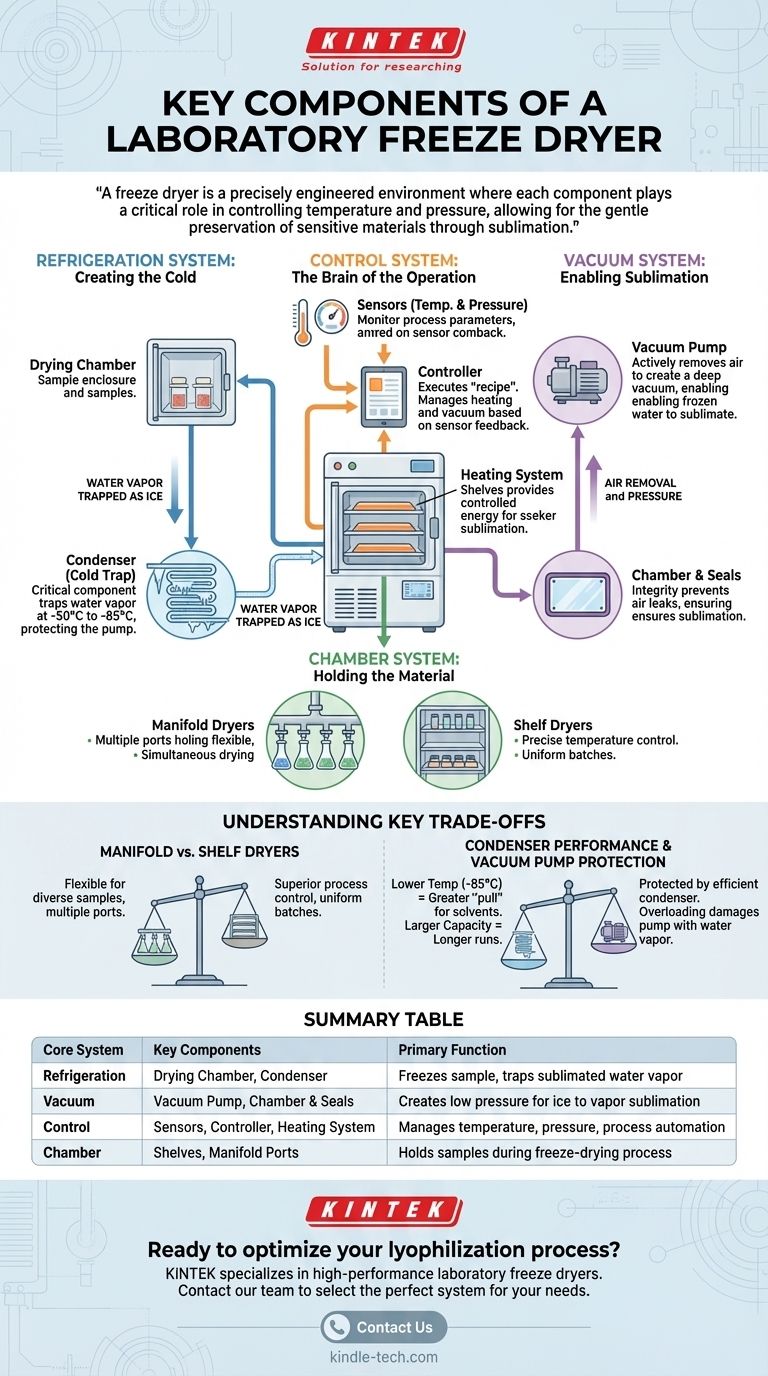
At its core, a laboratory freeze dryer is built around four primary systems. These are a refrigeration system to freeze the sample and trap moisture, a vacuum system to lower the pressure for sublimation, a control system to manage the process, and a chamber to hold the material. Each system contains specific components designed to work in concert to gently remove water from a frozen state directly into a gas.
A freeze dryer, or lyophilizer, isn't just a freezer connected to a vacuum pump. It is a precisely engineered environment where each component plays a critical role in controlling temperature and pressure, allowing for the gentle preservation of sensitive materials through sublimation.

The Core Systems of Lyophilization
Understanding a freeze dryer means understanding its integrated systems. The device is more than a list of parts; it's a sequence of functions performed by specialized components.
The Refrigeration System: Creating the Cold
The entire process begins and ends with cold. This system is responsible for freezing the sample and, critically, for trapping the water vapor removed during drying.
- The Drying Chamber: This is the stainless steel enclosure where your samples are placed. It can be configured with heated shelves for drying materials in vials or with a manifold of ports for attaching flasks.
- The Condenser (or Cold Trap): This is the most critical part of the system for protecting the equipment. The condenser is a refrigerated surface, often a coil, that is held at a much lower temperature than the sample (e.g., -50°C to -85°C).
- The Function of the Condenser: As water molecules leave the sample as a gas, they travel through the vacuum and are immediately frozen onto the extremely cold condenser surface. This "traps" the water, preventing it from reaching and damaging the vacuum pump.
The Vacuum System: Enabling Sublimation
Removing pressure is what makes freeze-drying possible. This system creates the low-pressure environment where frozen water can turn directly into a gas without melting.
- The Vacuum Pump: This is the heart of the vacuum system. It actively removes air and other gases from the chamber and condenser, reducing the pressure to a deep vacuum (measured in Pascals or mTorr).
- The Chamber and Seals: The integrity of the vacuum depends on the chamber and its seals. The drying chamber must be robust and perfectly sealed with gaskets to prevent air from leaking in, which would disrupt the sublimation process.
The Control System: The Brain of the Operation
A freeze dryer's success hinges on precise management of the process over many hours or even days.
- Sensors (Temperature and Pressure): These are the system's eyes and ears. Temperature sensors monitor the sample shelves and the condenser, while pressure sensors (like a Pirani gauge) monitor the vacuum level. This data is essential for process control.
- The Controller: This is the user interface and central processor. It executes the drying "recipe," adjusting heating and maintaining vacuum levels based on feedback from the sensors to ensure the sample dries without melting.
- The Heating System: While it seems counterintuitive, a small amount of heat is required during the drying phase. This system, often embedded in the shelves, provides the controlled energy needed to encourage the frozen water molecules to sublimate.
Understanding Key Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a freeze dryer involves balancing performance, flexibility, and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for successful outcomes.
Manifold vs. Shelf Dryers
A primary decision is the type of drying chamber.
- Manifold Dryers: These have multiple ports where you can attach individual flasks. They are highly flexible for drying different samples simultaneously but offer less precise temperature control for each sample.
- Shelf Dryers: These have temperature-controlled shelves inside the chamber for holding vials or trays. They provide superior process control and consistency, making them essential for pharmaceutical development and producing uniform batches.
Condenser Performance
The condenser's specifications directly impact drying efficiency and equipment longevity.
- Condenser Temperature: A lower condenser temperature (-85°C vs. -50°C) provides a greater "pull" for water vapor and is necessary for samples with low freezing points (e.g., those containing solvents).
- Condenser Capacity: This refers to how much ice the condenser can hold before it must be defrosted. A larger capacity allows for longer runs or drying samples with higher water content without interruption.
Vacuum Pump Protection
The vacuum pump is a sensitive and expensive component. Its primary enemy is water vapor. If the condenser is overloaded or not cold enough, water vapor will pass through to the pump, contaminating its oil and causing severe damage. This is why condenser performance is not a feature to compromise on.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application determines which components and features are most critical for your work.
- If your primary focus is routine research with diverse samples: A flexible manifold dryer with a reliable -50°C condenser is often sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is process development or producing cGMP batches: A tray-style shelf dryer with advanced temperature controls and data logging is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is drying samples containing solvents or acids: You must select a unit with a very low condenser temperature (-85°C or lower) and potentially a specialized, corrosion-resistant vacuum pump.
By understanding how these core components function as an integrated system, you can ensure the successful preservation and long-term stability of your valuable samples.
Summary Table:
| Core System | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigeration System | Drying Chamber, Condenser (Cold Trap) | Freezes the sample and traps sublimated water vapor |
| Vacuum System | Vacuum Pump, Chamber & Seals | Creates low pressure for sublimation of ice to vapor |
| Control System | Sensors, Controller, Heating System | Manages temperature, pressure, and process automation |
| Chamber System | Shelves, Manifold Ports | Holds samples during the freeze-drying process |
Ready to optimize your lyophilization process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory freeze dryers and consumables, designed to meet the precise needs of research and pharmaceutical labs. Whether you require a flexible manifold dryer for diverse samples or a sophisticated shelf dryer for cGMP batches, our experts can help you select the perfect system for your application. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your sample preservation and laboratory efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling



















