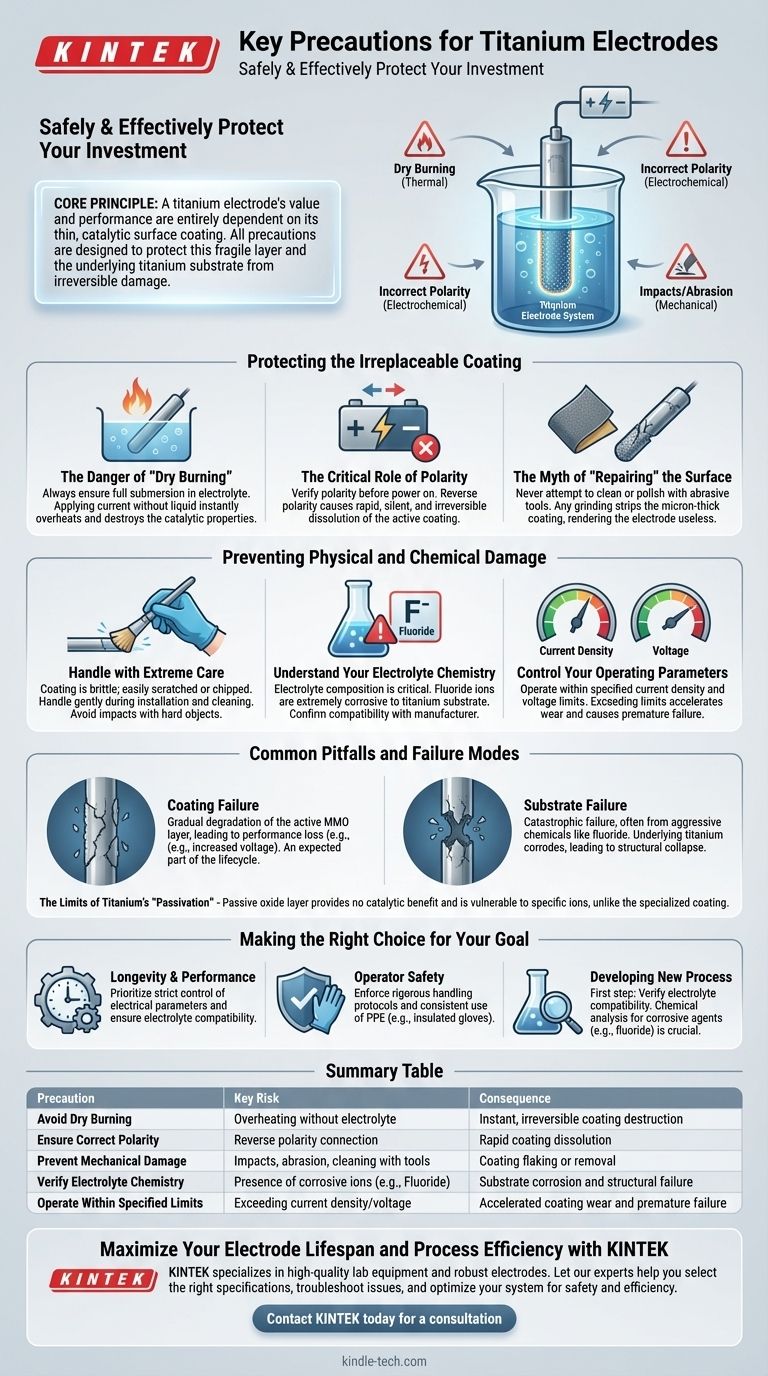
To safely and effectively use titanium electrodes, you must prioritize protecting their delicate surface coating from three primary threats: thermal damage from operating without an electrolyte ("dry burning"), electrochemical damage from incorrect polarity, and mechanical damage from impacts or abrasion. These precautions are critical because the specialized coating is irreparable and essential for the electrode's function.
The core principle is this: a titanium electrode's value and performance are entirely dependent on its thin, catalytic surface coating. All precautions—electrical, chemical, and physical—are designed to protect this fragile layer and the underlying titanium substrate from irreversible damage.

Protecting the Irreplaceable Coating
The active coating on a titanium electrode is a sophisticated, engineered layer of mixed metal oxides (MMO), not a simple piece of metal. Its integrity is paramount.
The Danger of "Dry Burning"
When an electrical current is applied, the electrode must be fully submerged in the electrolyte. The liquid is essential for dissipating heat and enabling the electrochemical reaction.
Applying current without this medium causes the coating to overheat and burn out almost instantly, permanently destroying its catalytic properties.
The Critical Role of Polarity
Always verify the correct electrical polarity before turning on the power supply. Titanium electrodes are designed to function as either an anode or a cathode, but not both interchangeably.
Connecting the electrode with reverse polarity will cause the active coating to rapidly dissolve into the electrolyte. This damage is swift, silent, and irreversible.
The Myth of "Repairing" the Surface
Never attempt to clean, polish, or "reactivate" a worn electrode surface with sandpaper or other abrasive tools.
The coating is a deposited layer only a few microns thick. Any form of grinding or mechanical abrasion will strip this layer off completely, exposing the less-reactive titanium substrate and rendering the electrode useless.
Preventing Physical and Chemical Damage
Beyond operational errors, the electrode's environment and handling are equally important for ensuring a long service life.
Handle with Extreme Care
The coating is often brittle and can be easily scratched, chipped, or flaked off.
Always handle the electrode gently during installation, removal, and cleaning. Avoid any impact with hard objects, as even minor physical damage can create a point of failure.
Understand Your Electrolyte Chemistry
The electrolyte composition is a critical factor. While the coating may be resilient, the titanium substrate is vulnerable to certain ions.
Fluoride ions (F⁻) are extremely corrosive to titanium metal. If your electrolyte contains fluoride, you must confirm with the manufacturer that your specific electrode coating is designed to resist it and protect the substrate.
Control Your Operating Parameters
Operate the electrode within its specified limits for current density and voltage.
Exceeding these parameters can accelerate coating wear, cause premature failure, and potentially generate unwanted byproducts in your process.
Common Pitfalls and Failure Modes
Understanding how these electrodes fail is key to preventing it. Mistaking a symptom for a problem can lead to incorrect and damaging actions.
Coating Failure vs. Substrate Failure
Coating failure is the gradual degradation of the active MMO layer. This leads to a loss of performance, such as increased voltage requirements. It is an expected part of the electrode's lifecycle.
Substrate failure, often caused by aggressive chemicals like fluoride, is a catastrophic failure. The underlying titanium itself corrodes, leading to the complete structural collapse of the electrode.
The Limits of Titanium's "Passivation"
Bare titanium naturally forms a passive, non-conductive oxide layer that protects it from general corrosion.
However, this passive layer is not the same as the electrode's active catalytic coating. It offers no catalytic benefit and can be compromised by specific ions, which is why protecting the specialized coating is so critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational focus will determine which precautions are most critical to emphasize in your procedures.
- If your primary focus is longevity and performance: Prioritize strict control over electrical parameters (no dry burning, correct polarity) and ensure your electrolyte is chemically compatible with both the coating and the substrate.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Enforce rigorous handling protocols and the consistent use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves, and ensure all equipment stands are properly insulated.
- If you are developing a new process: Your first step must be to verify electrolyte compatibility. A simple chemical analysis to check for destructive agents like fluoride can prevent catastrophic and expensive failures.
Ultimately, disciplined handling and a thorough understanding of your operating environment are the keys to maximizing the life and effectiveness of your titanium electrodes.
Summary Table:
| Precaution | Key Risk | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Avoid Dry Burning | Overheating without electrolyte | Instant, irreversible coating destruction |
| Ensure Correct Polarity | Reverse polarity connection | Rapid coating dissolution |
| Prevent Mechanical Damage | Impacts, abrasion, or cleaning with tools | Coating flaking or removal |
| Verify Electrolyte Chemistry | Presence of corrosive ions (e.g., Fluoride) | Substrate corrosion and structural failure |
| Operate Within Specified Limits | Exceeding current density/voltage | Accelerated coating wear and premature failure |
Maximize Your Electrode Lifespan and Process Efficiency with KINTEK
Properly maintaining your titanium electrodes is critical for consistent results and cost-effective operations. The specialized coatings are engineered for peak performance, but they require expert handling and compatible systems to avoid irreversible damage.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including robust electrodes designed for demanding applications. We understand the precise operational parameters and chemical compatibilities needed to protect your investment.
Let our experts help you:
- Select the right electrode specification for your specific electrolyte and process goals.
- Troubleshoot performance issues and identify the root cause of premature failure.
- Ensure your entire system is optimized for safety, longevity, and efficiency.
Don't risk costly downtime or damaged equipment. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and ensure your electrodes deliver the reliable performance you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- How should a platinum wire/rod electrode be cleaned before use? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What is a common application for the platinum wire/rod electrode? The Essential Guide to Counter Electrodes
- What are the performance characteristics of platinum wire/rod electrodes? Unmatched Stability for Your Lab
- What is the difference between ring disk electrode and rotating disk electrode? Unlock Deeper Electrochemical Insights



















