At its core, the primary advantage of laboratory freeze drying, or lyophilization, is its unparalleled ability to preserve sensitive and unstable materials without damaging their essential properties. This low-temperature dehydration process removes water while maintaining the material's physical structure, biological activity, and chemical integrity.
Freeze drying excels where other preservation methods fail because it avoids the damaging effects of heat. By transforming frozen water directly into vapor (sublimation), it creates a stable, lightweight, and easily reconstituted product, making it the gold standard for delicate biological and pharmaceutical samples.

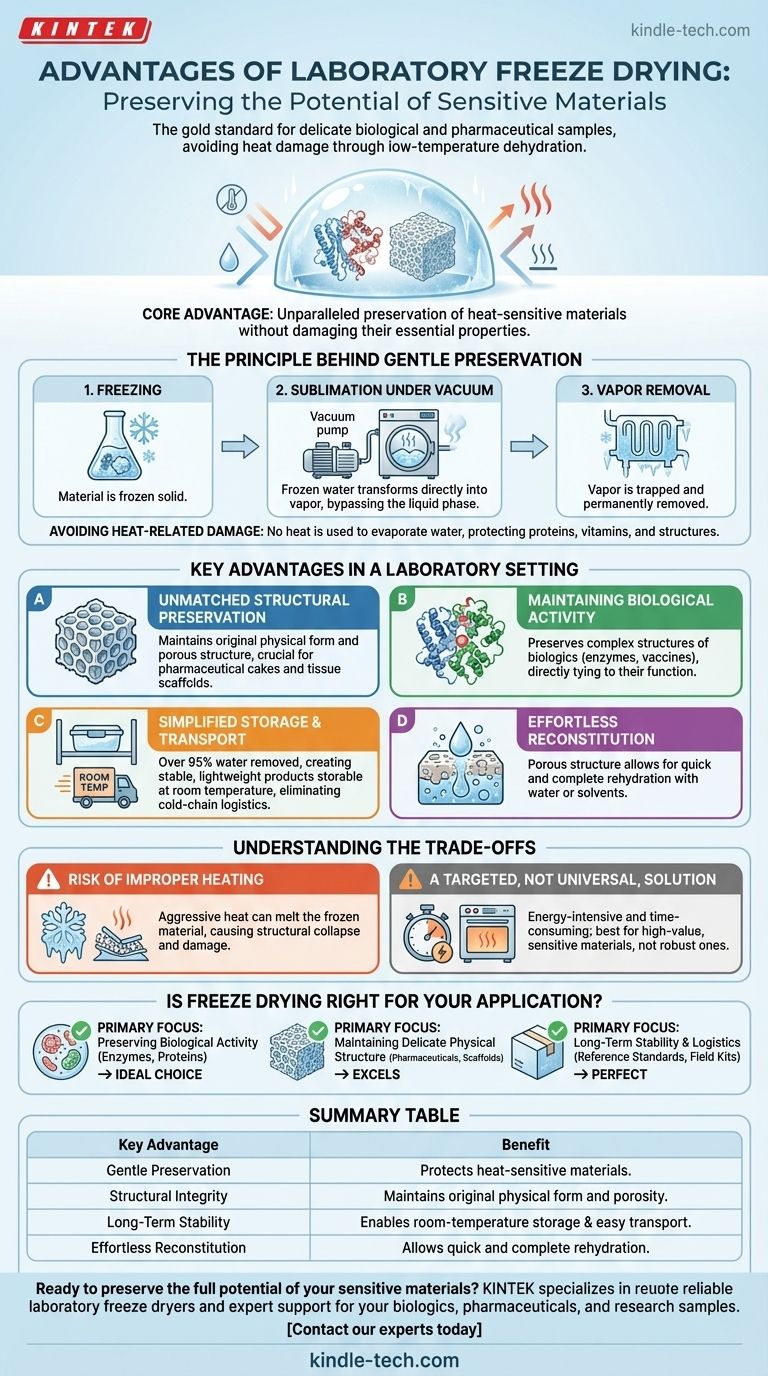
The Principle Behind Gentle Preservation
To understand the advantages of freeze drying, we must first understand how it works. The entire process is engineered to be exceptionally gentle on the sample material.
Sublimation Under Vacuum
Freeze drying involves first freezing the material and then placing it under a deep vacuum. Heat is carefully applied, not to melt the water, but to give the frozen water molecules enough energy to turn directly into a gas.
This process is called sublimation. The vacuum significantly speeds up this phase, and a cold condenser surface in the freeze dryer traps the resulting water vapor, permanently removing it from the sample.
Avoiding Heat-Related Damage
Conventional drying methods use heat to evaporate water, which can denature proteins, destroy vitamins, and fundamentally alter a material's structure and activity.
Freeze drying bypasses this entirely. By keeping the temperature low throughout the process, it protects heat-sensitive materials that would otherwise be destroyed.
Key Advantages in a Laboratory Setting
The unique principle of sublimation provides several critical benefits for research, development, and diagnostic applications.
Unmatched Structural Preservation
Because the water is removed from a solid, frozen state, the material's underlying physical structure is left intact. The final product is often porous and occupies the same volume as the original frozen material.
This is crucial for applications where the physical form, such as in a pharmaceutical cake or a tissue scaffold, is essential.
Maintaining Biological Activity
For biologics like proteins, enzymes, vaccines, and microorganisms, maintaining activity is the primary goal. Freeze drying is the preferred method because it preserves their complex three-dimensional structures, which are directly tied to their function.
The quality of a freeze-dried biological sample is often considered second only to a fresh one.
Simplified Storage and Transport
Removing water—typically over 95% of it—results in a lightweight, stable product that is easy to handle.
This material can be stored at room temperature for long periods and transported without the need for expensive and complex cold-chain logistics like refrigeration or dry ice.
Effortless Reconstitution
A key advantage is the ease with which the final product can be restored. Due to the porous structure left behind by the sublimated ice crystals, water or other solvents can quickly and completely rehydrate the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, freeze drying is a sophisticated process that requires careful control to be successful. It is not a universally perfect solution for all materials.
The Risk of Improper Heating
The most critical phase is primary drying, where the bulk of the water is removed. While it is a low-temperature process, some heat must be added to drive sublimation.
Applying this heat too aggressively can overwhelm the system, causing the frozen material to melt. This collapses the structure and can lead to the same damage that the process is meant to avoid.
A Targeted, Not Universal, Solution
Freeze drying is an energy-intensive and time-consuming process compared to simple oven drying.
Its use is justified for high-value or highly sensitive materials where other methods would result in an unacceptable loss of quality or function. It is overkill for robust materials that can tolerate heat.
Is Freeze Drying Right for Your Application?
Choosing a preservation method depends entirely on the nature of your sample and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Freeze drying is the ideal choice for enzymes, proteins, antibodies, and microbial cultures.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a delicate physical structure: This method excels at creating stable pharmaceutical formulations and preserving porous scaffolds.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability and logistics: Freeze drying creates samples that are easy to store and transport without refrigeration, perfect for reference standards or field kits.
Ultimately, freeze drying provides a powerful solution for preserving the full potential of your most sensitive materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Gentle Preservation | Protects heat-sensitive materials like proteins and enzymes from damage. |
| Structural Integrity | Maintains the original physical form and porous structure of the sample. |
| Long-Term Stability | Enables room-temperature storage and easy transport without refrigeration. |
| Effortless Reconstitution | Porous structure allows for quick and complete rehydration. |
Ready to preserve the full potential of your sensitive materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory freeze dryers and expert support to help you achieve superior preservation for your biologics, pharmaceuticals, and research samples.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect lyophilization solution for your lab's needs and ensure the integrity of your most valuable samples.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling



















