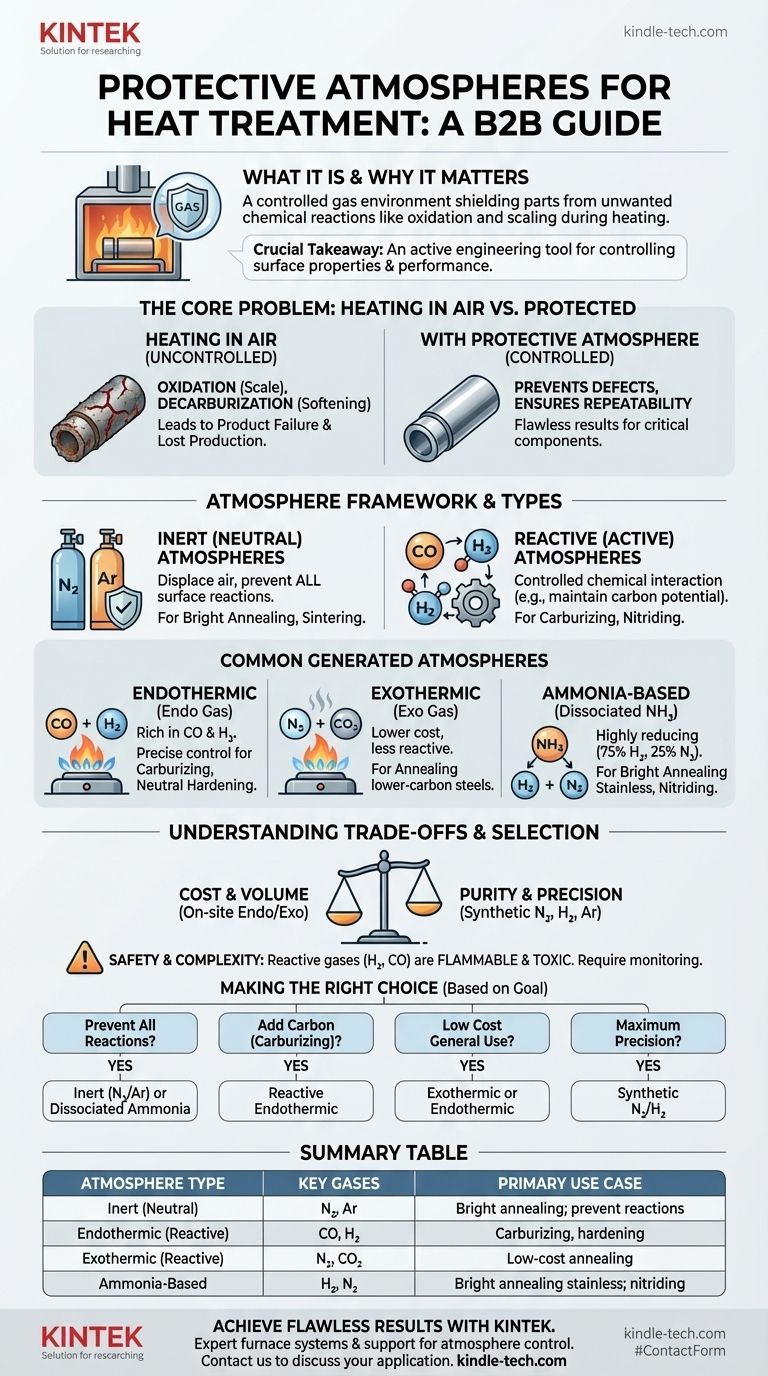
At its core, a protective atmosphere for heat treatment is a specifically controlled gas environment that surrounds a metal part inside a furnace. Its purpose is to shield the part from unwanted chemical reactions—like oxidation and scaling—that would otherwise occur when heating it in open air. These atmospheres range from simple inert gases like nitrogen to complex, reactive mixtures containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen designed to actively manage the surface chemistry of the metal.
The crucial takeaway is that a protective atmosphere is not merely a passive shield; it is an active engineering tool. Selecting the correct atmosphere is fundamental to controlling the final surface properties, microstructure, and performance of a heat-treated component, preventing defects and ensuring process repeatability.

The Core Problem: Why a Protective Atmosphere is Necessary
The Effect of Heating in Air
When you heat steel or other alloys to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen, a destructive chemical reaction occurs. This process, known as oxidation, forms a layer of scale on the surface.
This scaling can ruin the part's surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Furthermore, oxygen can react with the carbon within the steel's surface, a process called decarburization, which softens the material and compromises its strength and wear resistance.
The Cost of an Uncontrolled Environment
Failing to use a proper protective atmosphere leads directly to product failure. The consequences include rejected parts, wasted materials, and lost production time.
For mission-critical components in industries like aerospace, automotive, or medical, a surface defect caused by an improper atmosphere could have catastrophic safety implications.
A Framework for Understanding Atmospheres
Protective atmospheres can be broadly classified into two main categories based on how they interact with the workpiece.
Inert (Neutral) Atmospheres
Inert atmospheres are designed to be completely non-reactive with the metal. Their sole purpose is to displace the ambient air, primarily oxygen, to prevent any surface reactions.
Gases like pure Nitrogen (N2) and Argon (Ar) are the most common choices. They are used for processes like bright annealing and sintering, where the goal is to heat and cool the part without altering its surface in any way.
Reactive (Active) Atmospheres
Reactive atmospheres are engineered to achieve a specific, controlled chemical interaction with the surface of the metal. These are not just shields; they are part of the treatment itself.
These gas mixtures can prevent decarburization by maintaining a specific carbon potential that is in equilibrium with the carbon content of the steel. They can also be used to intentionally add elements, such as in carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen).
Common Types of Generated Atmospheres
While pure bottled gases are used, many industrial furnaces generate their own atmospheres on-site for cost-effectiveness.
Endothermic Atmospheres
Often called "endo gas," this is a common reactive atmosphere generated from the partial combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel gas. It is rich in carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2).
Endothermic gas is highly versatile and is the standard for neutral hardening, carburizing, and carbonitriding because its carbon potential can be precisely controlled.
Exothermic Atmospheres
"Exo gas" is produced from the more complete combustion of a hydrocarbon. It consists mainly of nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapor, with smaller amounts of CO and H2.
It is less expensive to produce than endo gas but is also less reactive. Its primary use is for annealing lower-carbon steels and non-ferrous metals where a high-purity environment is not required.
Ammonia-Based Atmospheres
Dissociated ammonia produces a highly reducing atmosphere of 75% hydrogen and 25% nitrogen. This clean, dry mixture is excellent for the bright annealing of stainless steels.
Ammonia is also the source of nitrogen for nitriding and carbonitriding processes, where nitrogen is intentionally diffused into the surface of the part to create a hard case.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost vs. Purity and Control
On-site generated atmospheres like endothermic and exothermic gas are generally more cost-effective for high-volume operations.
However, synthetic atmospheres made from pure, bottled gases (Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Argon) offer superior purity and more precise control, which is essential for aerospace, medical, and electronics applications.
Safety and Complexity
Reactive atmospheres containing high concentrations of hydrogen and carbon monoxide are flammable, explosive, and toxic. They require sophisticated safety interlocks, ventilation, and monitoring systems.
Controlling a reactive atmosphere is also complex. It requires constant monitoring of variables like dew point and gas composition to prevent undesirable outcomes like sooting or unintended decarburization. Inert atmospheres are far simpler and safer to manage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct atmosphere is a critical decision based entirely on the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is preventing all surface reactions (e.g., bright annealing): A pure inert atmosphere like Nitrogen or Argon, or a strongly reducing dissociated ammonia atmosphere, is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is adding carbon to the surface (carburizing): A reactive endothermic atmosphere with a precisely controlled carbon potential is required.
- If your primary focus is general hardening or annealing at a lower cost: A generated exothermic or endothermic atmosphere is often the most practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is maximum precision for critical parts: A synthetic mixture of high-purity nitrogen and hydrogen provides the ultimate level of control, cleanliness, and repeatability.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is impossible without mastering the selection and control of its protective atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Gases | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Inert (Neutral) | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Bright annealing; prevents all surface reactions |
| Endothermic (Reactive) | Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H₂) | Carburizing, neutral hardening, carbonitriding |
| Exothermic (Reactive) | Nitrogen (N₂), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Low-cost annealing of lower-carbon steels |
| Ammonia-Based | Hydrogen (H₂), Nitrogen (N₂) | Bright annealing of stainless steel; nitriding |
Achieve flawless results and protect your critical components. Selecting the right protective atmosphere is key to successful heat treatment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise furnace systems and expert support your laboratory needs to master atmosphere control. Contact us today to discuss your application and ensure process repeatability. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding



















