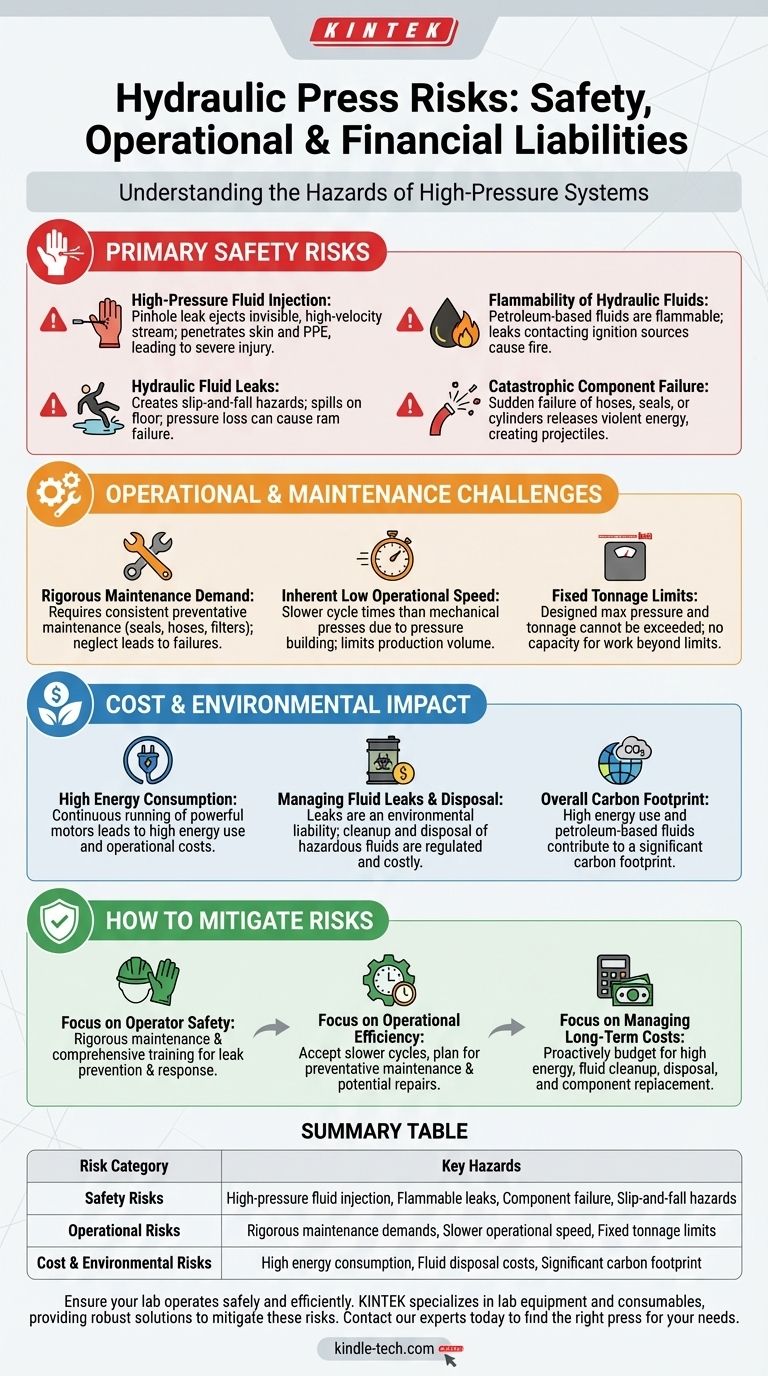
While immensely powerful, hydraulic presses introduce a distinct set of risks that demand careful management. The primary dangers stem from the high-pressure fluid system itself, including flammable fluid leaks, the need for intensive maintenance, and high energy consumption that impacts both cost and the environment.
The core risks of a hydraulic press extend far beyond the obvious crushing hazard. The most critical challenges lie in managing the high-pressure hydraulic system, where fluid leaks, component failure, and high energy consumption create significant safety, operational, and financial liabilities.
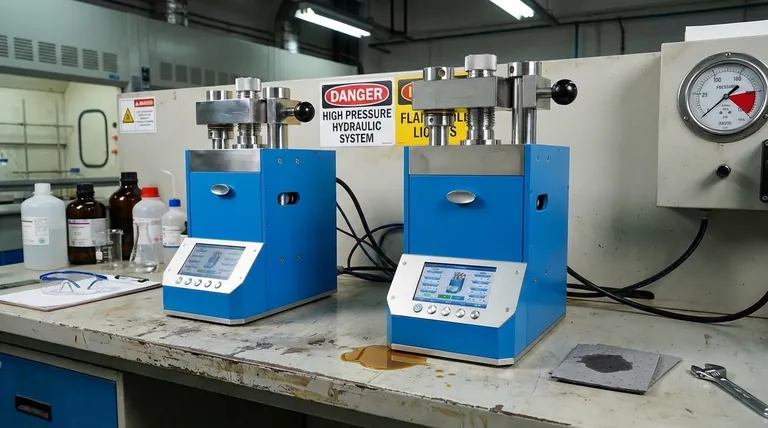

The Primary Safety Risks: Beyond Crushing Force
The most severe dangers of a hydraulic press are often hidden within the system that gives it power. Understanding these hydraulic specific-risks is the first step toward a safe operating environment.
High-Pressure Fluid Injection
A pinhole leak in a high-pressure hose can eject a nearly invisible stream of hydraulic fluid at extreme velocity.
This stream can easily penetrate skin and personal protective equipment. This type of injury is a severe medical emergency that can lead to tissue death and amputation if not treated immediately.
Hydraulic Fluid Leaks
Even without high-velocity injection, leaking fluid creates a dangerous work area.
Spills on the floor are a significant slip-and-fall hazard. Furthermore, a substantial leak can lead to a loss of system pressure, potentially causing the ram to drift or fail unexpectedly.
Flammability of Hydraulic Fluids
Many standard hydraulic fluids are petroleum-based and therefore flammable.
A leak that comes into contact with an ignition source—such as a welding arc, grinding spark, or faulty electrical component—can result in a serious fire.
Catastrophic Component Failure
The immense pressure contained within the system places constant strain on hoses, seals, and cylinders.
A sudden failure, like a bursting hose or a fractured cylinder, can violently release energy, turning components into high-speed projectiles and causing severe injury.
Operational and Maintenance Challenges
Beyond immediate safety threats, hydraulic presses present inherent operational and maintenance hurdles that can impact productivity and reliability.
The Demand for Rigorous Maintenance
Hydraulic systems are less forgiving than mechanical ones. They require consistent and preventative maintenance to function safely and reliably.
Neglecting to replace seals, hoses, and filters or failing to monitor fluid quality directly increases the risk of leaks and catastrophic failures.
Inherent Low Operational Speed
By their nature, hydraulic presses are generally slower than their mechanical counterparts. The time it takes for the hydraulic pump to build pressure and move the fluid limits the machine's cycle speed.
This lower operational speed can be a significant bottleneck in high-volume production environments.
Fixed Tonnage Limits
Every hydraulic press is designed with a maximum pressure and tonnage rating that cannot be exceeded.
While this acts as a built-in safety feature against overloads, it also means the machine has no capacity for work beyond its design limits, which can be a risk if production needs change.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost and Environmental Impact
The power of a hydraulic press comes with significant, ongoing costs related to energy use and environmental management.
High Energy Consumption
Generating thousands of PSI of hydraulic pressure requires powerful electric motors that run continuously. This results in high energy consumption, even when the press is idle between cycles.
These energy demands translate directly into higher operational costs.
Managing Fluid Leaks and Disposal
Hydraulic fluid is a hazardous material. Leaks not only pose safety risks but also create an environmental liability.
Proper cleanup of spills and the disposal of used hydraulic fluid are regulated processes that add to the machine's total cost of ownership.
The Overall Carbon Footprint
The combination of high energy consumption and the use of petroleum-based fluids gives hydraulic presses a notable carbon footprint.
This is an increasingly important consideration for companies focused on sustainability and environmental governance.
How to Mitigate These Risks
Your approach to managing a hydraulic press depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Your highest priority must be a rigorous maintenance schedule and comprehensive training to prevent and respond to high-pressure fluid leaks.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: You must accept the slower cycle times and factor in the necessary downtime for preventative maintenance and potential repairs.
- If your primary focus is managing long-term costs: You must proactively budget for high energy consumption and the expenses related to fluid cleanup, disposal, and component replacement.
Proactively managing these systemic risks is the key to harnessing the immense power of a hydraulic press safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Hazards |
|---|---|
| Safety Risks | High-pressure fluid injection, Flammable fluid leaks, Catastrophic component failure, Slip-and-fall hazards |
| Operational Risks | Rigorous maintenance demands, Slower operational speed, Fixed tonnage limits |
| Cost & Environmental Risks | High energy consumption, Fluid disposal costs, Significant carbon footprint |
Ensure your lab operates safely and efficiently. The risks of hydraulic presses—from high-pressure leaks to high energy costs—demand reliable equipment and expert support. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions and guidance to mitigate these risks for your laboratory. Don't let safety and operational challenges compromise your work. Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to find the right press for your needs and ensure a safer, more productive lab environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory manual hydraulic press facilitate the FT-IR characterization of catalysts? Master Sample Prep.
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis
- Why is a hydraulic pellet press used for FTIR? Transform Nanofillers into Clear Data
- What is the use of manual hydraulic press? A Cost-Effective Tool for Lab Sample Preparation
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in preparing solid model materials? Standardize for Precise Data.



















