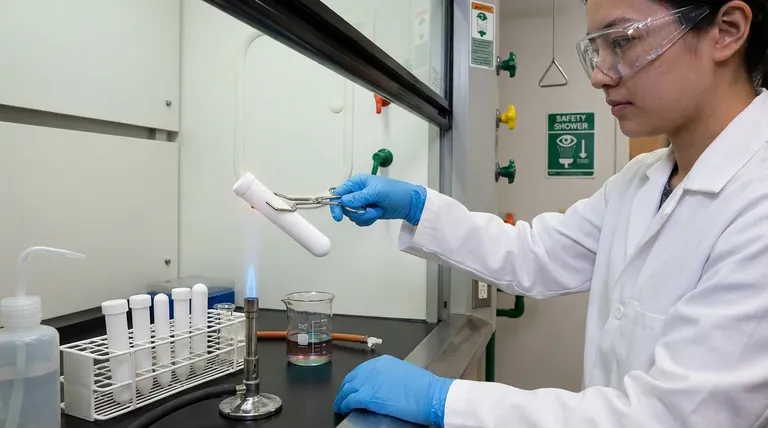
Using a test tube safely is a fundamental skill in any laboratory setting. It involves a critical combination of proper handling techniques, awareness of potential hazards like heat and chemical reactions, and the consistent use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
The core principle of test tube safety is to treat every procedure as potentially hazardous. This means always controlling the direction of the tube's opening, managing heat application with care, and using the correct equipment to prevent chemical exposure, heat burns, and injuries from broken glass.

Foundational Checks: Before You Begin
Proper preparation is the first line of defense against accidents. Rushing this stage introduces unnecessary risk into your work.
Inspect for Damage
Before use, always inspect your test tube for cracks, chips, or scratches. Even a small imperfection can create a weak point that may cause the glass to shatter under heat or pressure.
Wear Appropriate PPE
Non-negotiable personal protective equipment (PPE) includes safety goggles, a lab coat, and appropriate gloves. Goggles protect your eyes from splashes, while a lab coat and gloves shield your skin from chemical contact.
Use the Correct Tools
Never hold a test tube directly in your hand during a reaction or while heating. Always use a test tube holder or clamp to maintain a safe distance and protect yourself from heat and chemicals.
Safe Handling During Experiments
How you handle the test tube while working is the most critical factor in preventing accidents.
Point the Opening Away
This is the most important rule. Always ensure the open end of the test tube is pointing away from yourself and everyone else in the lab. Never look down into the opening of a test tube.
Avoid Using Your Thumb as a Stopper
Never use your thumb or a solid stopper to cover a test tube during a reaction, especially when mixing. This can lead to pressure buildup or direct chemical exposure to your skin.
Mix with Caution
To mix contents, gently swirl the test tube or lightly flick the bottom with your finger. This is far safer than shaking, which can cause the contents to splash out.
The Specific Dangers of Heating
Heating introduces a higher level of risk due to the potential for sudden boiling, pressure changes, and severe burns.
Apply Heat Evenly
When heating a test tube over a Bunsen burner, move it back and forth through the flame at an angle. Never heat only the bottom, as this can cause the liquid to boil violently and erupt from the tube, a phenomenon known as bumping.
Never Stopper a Heated Tube
Placing a stopper in a test tube that you are heating is extremely dangerous. The expanding gas will create immense pressure, potentially turning the test tube into a projectile or causing it to explode.
Let Glass Cool Properly
Hot glass looks identical to cold glass. After heating, place the test tube in a designated test tube rack to cool down. Never touch it to check its temperature.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even experienced lab personnel can make mistakes. Being aware of these common errors helps build a culture of safety.
Assuming "Clean" Glass is Safe
Never assume a piece of glassware is clean. It may contain invisible chemical residue from previous use. Always follow proper cleaning and rinsing protocols.
Underestimating Small Volumes
A small amount of a corrosive or toxic chemical is still dangerous. Treat every substance with respect, regardless of the quantity.
Rushing the Process
Most lab accidents occur when people are in a hurry. Moving too quickly leads to spills, breakage, and a failure to follow critical safety steps. Be methodical and deliberate in your work.
Applying These Rules to Your Goal
Your specific task determines which safety precautions are most critical in the moment.
- If your primary focus is heating a substance: Always point the tube away from everyone and apply heat gently and evenly to prevent violent bumping.
- If your primary focus is mixing chemicals: Never use your thumb as a stopper; instead, gently swirl the tube or use a proper vortex mixer.
- If your primary focus is cleaning and disposal: Handle all used glassware as if it were still contaminated and dispose of any broken glass in a designated sharps container immediately.
- If your primary focus is simple observation: Always wear your safety goggles, as even seemingly calm reactions can splash or release fumes unexpectedly.
Proper technique is not about memorizing rules; it is about building a professional habit of safety and respect for the materials you work with.
Summary Table:
| Safety Area | Key Precaution | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Inspect for damage, wear PPE (goggles, coat, gloves). | Prevents injury from broken glass and chemical exposure. |
| Handling | Always point opening away, use a test tube holder. | Controls direction of potential splashes and heat. |
| Heating | Heat evenly, never stopper, let cool on a rack. | Prevents violent "bumping" and explosions from pressure buildup. |
| Mixing | Gently swirl; never use your thumb as a stopper. | Avoids pressure buildup and direct skin contact with chemicals. |
Equip your lab for safety and precision with KINTEK.
Following these test tube safety guidelines is essential, but having the right, high-quality equipment is just as critical for a secure and efficient workspace. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including durable test tubes, secure holders, and essential PPE.
Let us help you build a safer laboratory. Our products are designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern research and testing, ensuring you can focus on your work with confidence.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a centrifuge? Achieve Rapid, High-Resolution Sample Separation
- Why are high-purity ceramic tubes used in high-temperature oxidation reaction chambers? Optimize Your Research Integrity
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What are the benefits of using nickel-based alloys for reaction tubes? Ensure Purity in Supercritical Esterification
- What is the primary function of an Alumina (Al2O3) tube in LLZTO sintering? Optimize Your Thermal Processing



















