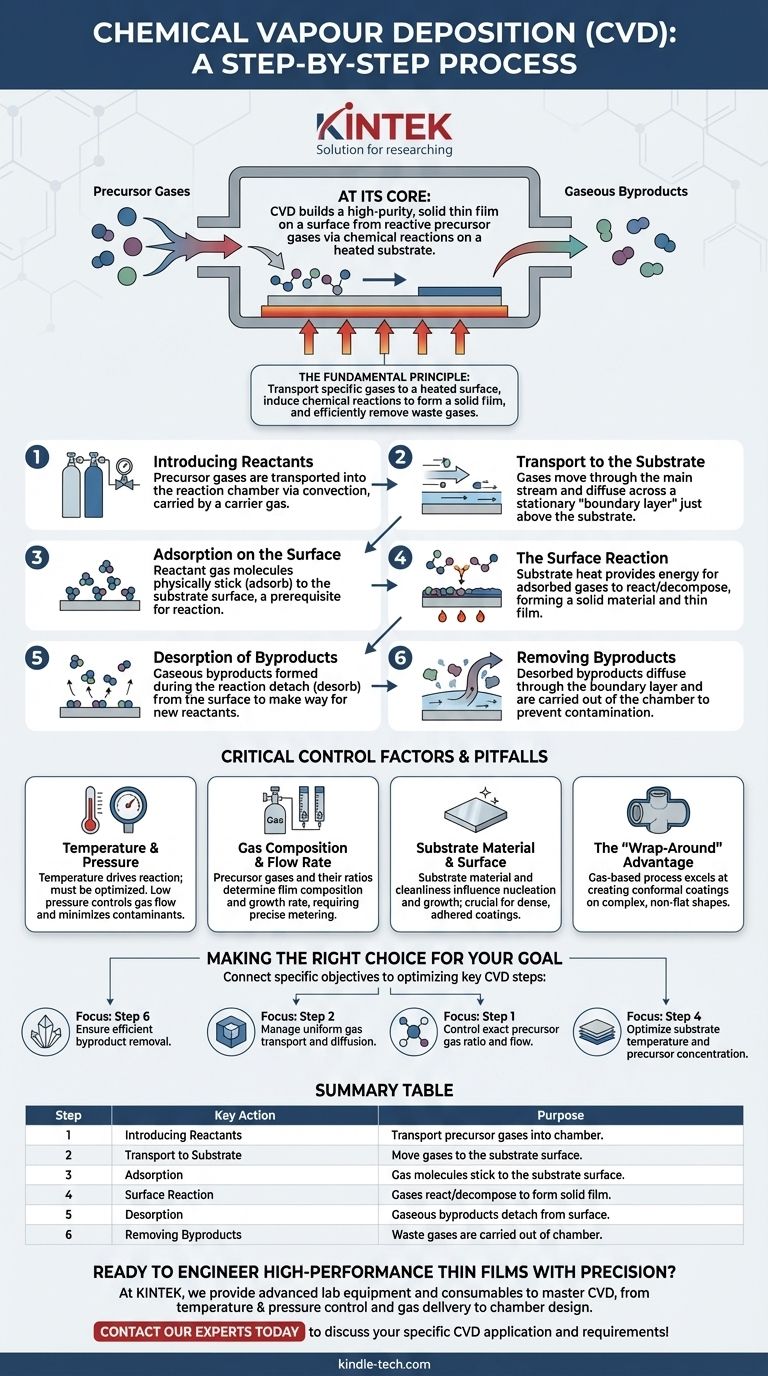
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a multi-step process that builds a high-purity, solid thin film on a surface from a gas. It begins with introducing reactive precursor gases into a chamber, which then travel to a heated substrate. On this hot surface, chemical reactions occur that deposit the desired solid material, while gaseous byproducts are formed and then transported away, leaving a pristine coating.
The fundamental principle of CVD is a transformation: specific gases are transported to a heated surface where they chemically react to form a solid film, and the resulting waste gases are then efficiently removed. Mastering this sequence of transport, reaction, and removal is the key to creating high-performance materials.
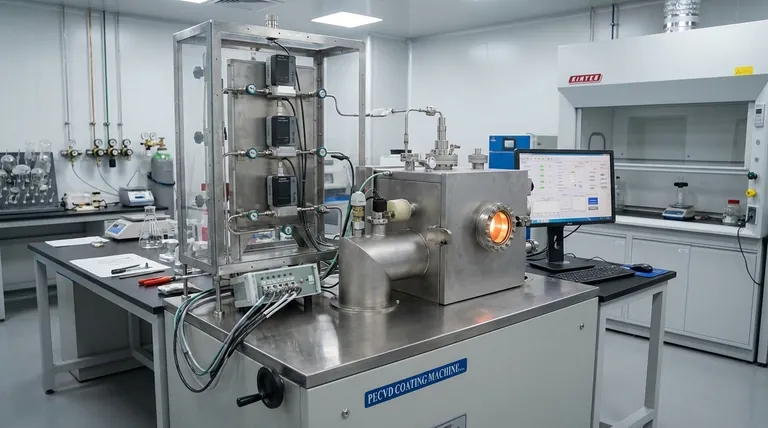

The CVD Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To fully grasp how CVD works, it's best to view it as a sequence of distinct physical and chemical events. Each step builds upon the last and must be precisely controlled to achieve the desired result.
Step 1: Introducing Reactants
The process begins by transporting the precursor gases into the reaction chamber. This is typically managed by convection, where a carrier gas flows through the system, bringing the reactive species with it.
Step 2: Transport to the Substrate
Once inside the chamber, the gases must travel to the substrate's surface. This involves moving through the main gas stream and then diffusing through a stationary "boundary layer" of gas that exists just above the substrate.
Step 3: Adsorption on the Surface
When the reactant gas molecules reach the substrate, they physically stick to the surface in a process called adsorption. This is a prerequisite for any chemical reaction to occur on the surface itself.
Step 4: The Surface Reaction
This is the heart of the CVD process. The heat of the substrate provides the energy needed for the adsorbed gases to react or decompose. This heterogeneous reaction forms a solid material that nucleates and grows into the desired thin film on the substrate.
Step 5: Desorption of Byproducts
The chemical reactions that form the solid film also create unwanted gaseous byproducts. These byproduct molecules must detach, or desorb, from the surface to make way for new reactants to arrive and continue the film growth.
Step 6: Removing Byproducts
Finally, these desorbed gaseous byproducts diffuse away from the substrate, back through the boundary layer, and are carried out of the chamber by the gas flow. This continuous removal is crucial to prevent contamination of the film.
Critical Control Factors (And Potential Pitfalls)
The quality, composition, and structure of the final film are not accidental; they are a direct result of carefully managing the process parameters. Failure to control these variables is the most common source of error.
The Role of Temperature and Pressure
Temperature is the primary driver of the surface reaction. Too low, and the reaction won't occur; too high, and unwanted gas-phase reactions can occur, leading to impurities. The chamber is typically kept under a vacuum or low pressure to control the gas flow and minimize contaminants.
Gas Composition and Flow Rate
The chemical composition of the final film is determined entirely by the precursor gases used. The ratio and flow rate of these gases must be precisely metered to control the film's stoichiometry and growth rate.
Substrate Material and Surface
The substrate is not merely a passive holder. Its material and surface condition can influence how the film nucleates and grows. A clean, well-prepared surface is essential for achieving a dense, well-adhered coating.
The "Wrap-Around" Advantage
Because the process relies on a gas reaching all surfaces, CVD excels at producing a conformal coating on complex, non-flat shapes. This "wrap-around" property is a key advantage over line-of-sight deposition methods like sputtering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the steps of CVD allows you to tailor the process to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is material purity: You must perfect Step 6, ensuring the efficient and complete removal of all gaseous byproducts.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex shape: Your main concern is managing Step 2, ensuring that gas transport and diffusion are uniform across all surfaces.
- If your primary focus is a specific chemical composition: You need absolute precision in Step 1, controlling the exact ratio and flow of your precursor gases.
- If your primary focus is growth rate and thickness: You will need to optimize Step 4 by carefully tuning the substrate temperature and precursor concentration.
By controlling each stage of this gas-to-solid transformation, you gain the ability to engineer materials with remarkable precision and performance.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Introducing Reactants | Transport precursor gases into the chamber. |
| 2 | Transport to Substrate | Move gases to the substrate surface. |
| 3 | Adsorption | Gas molecules stick to the substrate surface. |
| 4 | Surface Reaction | Gases react/decompose to form the solid film. |
| 5 | Desorption | Gaseous byproducts detach from the surface. |
| 6 | Removing Byproducts | Waste gases are carried out of the chamber. |
Ready to engineer high-performance thin films with precision?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to master the CVD process. Whether your goal is extreme material purity, coating complex 3D shapes, or achieving a specific chemical composition, our solutions are designed to give you precise control over every critical parameter.
We help you optimize:
- Temperature & Pressure Control for consistent surface reactions.
- Gas Delivery Systems for exact precursor flow and composition.
- Chamber Design for efficient byproduct removal and uniform coatings.
Let our expertise in laboratory equipment support your material science breakthroughs. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific CVD application and requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















