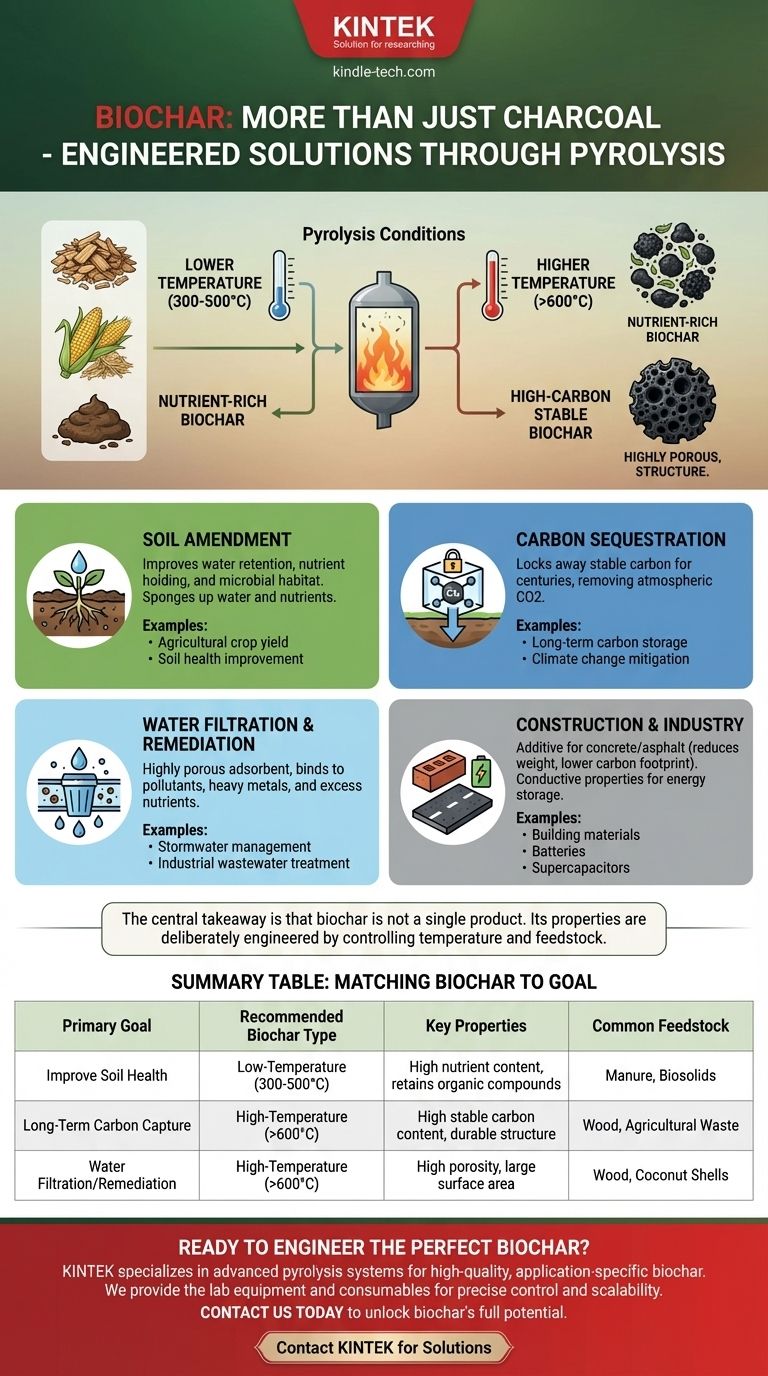
Biochar is far more than just charcoal. Produced through pyrolysis—the heating of biomass in a low-oxygen environment—its uses are diverse and significant, ranging from agricultural soil amendment and long-term carbon sequestration to environmental remediation and advanced material science. The specific application of biochar is a direct result of how it is produced.
The central takeaway is that biochar is not a single product. Its properties, and therefore its uses, are deliberately engineered during the pyrolysis process, primarily by controlling the temperature and the type of biomass used as feedstock.

How Production Defines Biochar's Purpose
The value of biochar comes from its specific physical and chemical properties. These are not accidental; they are the direct outcome of decisions made during its creation. Understanding this link is key to using it effectively.
The Critical Role of Pyrolysis Temperature
The single most influential factor in determining biochar's characteristics is the highest temperature it reaches during pyrolysis.
Lower temperatures (around 300-500°C) produce a biochar that retains more volatile organic compounds and has a different surface chemistry. This version is often richer in nutrients and better suited for agricultural uses where stimulating soil biology is the goal.
Higher temperatures (above 600°C) create a biochar with a higher percentage of stable carbon, greater porosity, and a larger surface area. This makes it ideal for applications like carbon sequestration and filtration, where stability and adsorption are paramount.
The Impact of Feedstock
The type of biomass used as the starting material, or feedstock, also defines the final product.
Biochar made from wood is typically high in carbon and has a durable structure. In contrast, biochar produced from manure or biosolids will have a higher nutrient content, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, making it a powerful soil conditioner.
Key Applications of Biochar
With an understanding of how production influences properties, we can explore the primary uses for this versatile material.
As a Soil Amendment
This is the most well-known application. Adding the right biochar to soil can dramatically improve water retention, reduce nutrient leaching, and provide a stable habitat for beneficial microorganisms. Its porous structure acts like a sponge, holding water and nutrients for plant roots.
For Carbon Sequestration
The carbon in biochar is highly stable and resistant to decomposition. When incorporated into soil, it effectively locks that carbon away for hundreds or even thousands of years. This makes biochar a powerful tool for carbon dioxide removal, converting atmospheric carbon captured by plants into a solid, stable form.
In Water Filtration and Remediation
The vast internal surface area of high-temperature biochar makes it an excellent adsorbent. It can bind to pollutants, heavy metals, and excess nutrients in water, effectively filtering and cleaning it. It is used in everything from stormwater management to industrial wastewater treatment.
In Construction and Industry
Biochar is increasingly being explored as an additive to construction materials. Adding it to concrete or asphalt can reduce weight, improve insulation, and lower the overall carbon footprint of the material. Its conductive properties also make it a candidate for use in batteries and supercapacitors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, biochar is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is contingent on proper production and application.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
Using a high-temperature, high-carbon biochar in a field where you need nutrient availability will be far less effective than using a lower-temperature, nutrient-rich version. The specific goal must dictate the type of biochar used.
Potential for Contaminants
If the initial feedstock is contaminated with heavy metals or other pollutants, those contaminants can become concentrated in the final biochar. Using such a product in agriculture could harm soil health and food safety, making feedstock sourcing a critical step.
Production Energy and Cost
The pyrolysis process itself requires an energy input. For biochar to be a net positive for the environment and economically viable, the energy source must be sustainable and the production process must be efficient.
Matching Biochar to Your Goal
To select the right biochar, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is improving soil health: Seek a nutrient-rich biochar produced at lower temperatures to preserve organic compounds and maximize water-holding capacity.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon capture: You need a highly stable, high-carbon biochar produced at high temperatures to ensure the carbon remains locked away for centuries.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation: Choose a highly porous biochar, typically from high-temperature pyrolysis, to maximize the surface area available for adsorbing pollutants.
Ultimately, the true value of biochar lies in precisely engineering its properties to solve a specific problem.
Summary Table:
| Primary Goal | Recommended Biochar Type | Key Properties | Common Feedstock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improve Soil Health | Low-Temperature (300-500°C) | High nutrient content, retains organic compounds | Manure, Biosolids |
| Long-Term Carbon Capture | High-Temperature (>600°C) | High stable carbon content, durable structure | Wood, Agricultural Waste |
| Water Filtration/Remediation | High-Temperature (>600°C) | High porosity, large surface area | Wood, Coconut Shells |
Ready to Engineer the Perfect Biochar for Your Application?
Understanding the link between pyrolysis conditions and biochar properties is the first step. The next is having the right equipment to achieve precise control. KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis systems for researchers and producers focused on creating high-quality, application-specific biochar.
We provide the lab equipment and consumables you need to:
- Precisely control temperature for targeted biochar characteristics.
- Process diverse feedstocks safely and efficiently.
- Scale your operations from R&D to production.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can help you unlock the full potential of biochar for your specific needs in agriculture, carbon sequestration, or environmental remediation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















