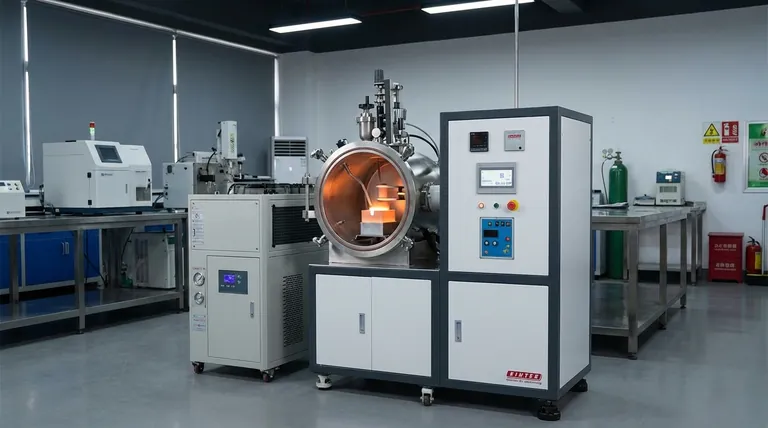
At its core, an induction furnace is a powerful tool for melting metals with exceptional speed and purity. It is widely used in foundries and metallurgical operations to melt everything from iron and steel to copper, aluminum, and precious metals. The process is valued for being significantly cleaner than traditional gas furnaces, as the heat is generated directly within the metal itself, minimizing contamination.
The fundamental advantage of an induction furnace is its method of contactless heating. By using a magnetic field to generate heat directly inside the target material, it offers unparalleled control, efficiency, and purity for melting and high-temperature material processing.

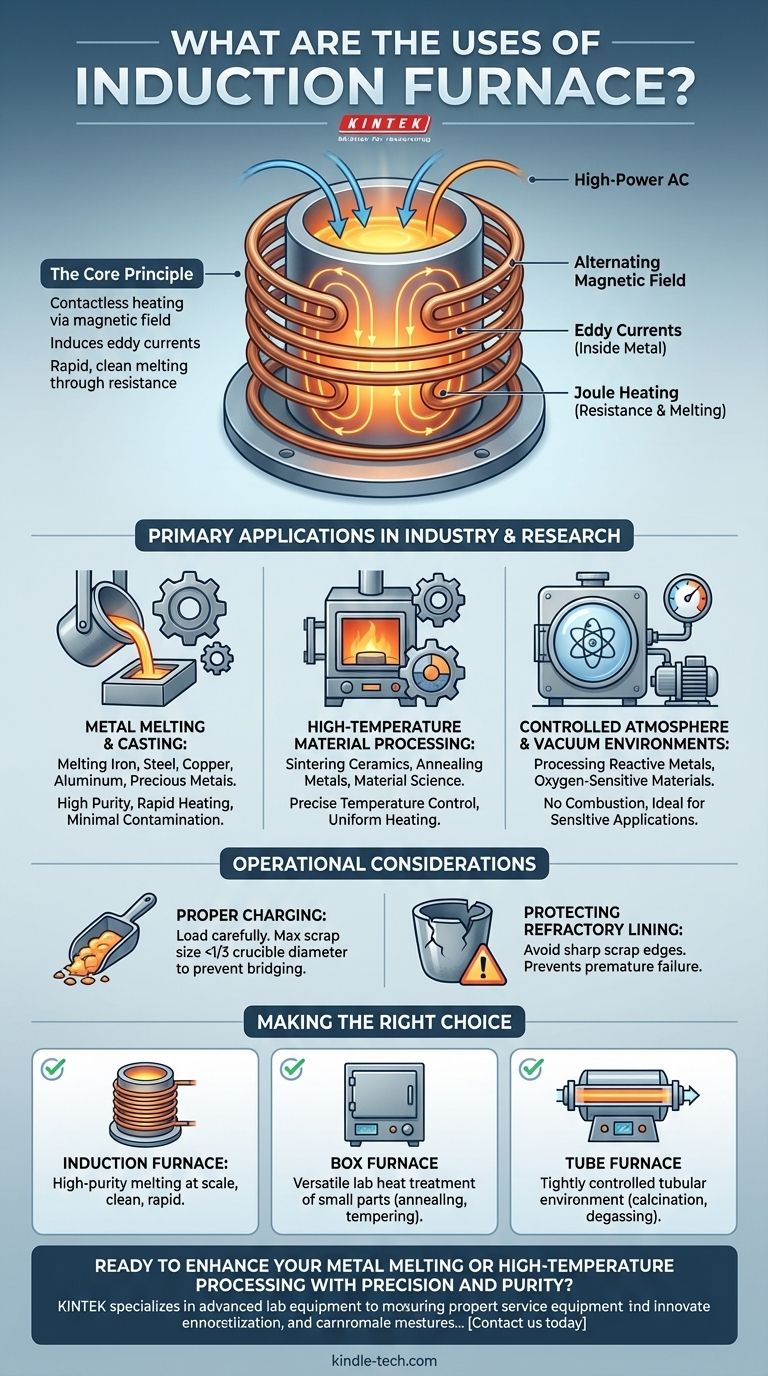
The Core Principle: How Induction Heating Works
To understand the applications of an induction furnace, you must first understand its unique heating mechanism. Unlike conventional furnaces that rely on burning fuel or external heating elements, an induction furnace heats the material from the inside out.
The Alternating Magnetic Field
The process begins with a high-power alternating current passing through a copper coil. This coil, which surrounds the crucible holding the material, generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This magnetic field penetrates the electrically conductive material placed inside the crucible. According to Faraday's law of induction, the fluctuating magnetic field induces circular electric currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Heating Through Resistance (Joule Heating)
As these strong eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This resistance causes intense heat to be generated—a phenomenon known as Joule heating—which rapidly melts the material.
Primary Applications in Industry and Research
The unique heating method of an induction furnace makes it suitable for a range of demanding applications where precision, speed, and purity are critical.
Metal Melting and Casting
This is the most common use for induction furnaces. Foundries rely on them to produce high-quality liquid metal for casting into molds. The clean melting process ensures the final cast product has fewer impurities.
High-Temperature Material Processing
Beyond simple melting, induction furnaces are essential tools across numerous fields for specialized thermal processes. This includes sintering ceramics, annealing metals to alter their properties, and conducting high-temperature experiments for material science.
Controlled Atmosphere and Vacuum Environments
Because no combustion is involved, an induction furnace can easily be enclosed in a vacuum chamber or a controlled atmosphere. This is critical for processing reactive metals or creating materials that cannot be exposed to oxygen at high temperatures.
Understanding the Operational Considerations
While powerful, an induction furnace requires specific operating procedures to ensure safety, efficiency, and longevity of the equipment.
Proper Charging Technique
The material, or charge, must be loaded carefully. The maximum size of any single piece of scrap should not exceed one-third of the crucible's diameter to prevent a "bridging" event where material gets stuck.
Protecting the Refractory Lining
The refractory lining of the crucible is a critical and sensitive component. Scrap with sharp edges must be avoided as it can gouge or damage the lining during charging, leading to premature failure.
A Note on Other Furnace Types
It's helpful to distinguish induction furnaces from other common types. Tube furnaces are often used for lab-scale processes like analysis or annealing in a controlled tube environment. Box furnaces are general-purpose lab units used for heat-treating small parts, element analysis, and other smaller-scale heating tasks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on the material you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metal melting at scale: An induction furnace is the definitive choice for its clean, rapid, and efficient heating.
- If your primary focus is versatile laboratory heat treatment of small parts: A box furnace offers flexibility for a wide range of tasks like annealing, tempering, and sintering small samples.
- If your primary focus is processing materials in a tightly controlled tubular environment: A tube furnace is specifically designed for applications like calcinations, degassing, or coating in a lab setting.
Ultimately, understanding the principle behind each furnace type is the key to leveraging its unique power for your specific material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Application | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Melting & Casting | Melting iron, steel, copper, aluminum, precious metals | High purity, rapid heating, minimal contamination |
| High-Temperature Processing | Sintering, annealing, material science experiments | Precise temperature control, uniform heating |
| Controlled Atmosphere/Vacuum | Processing reactive metals, oxygen-sensitive materials | No combustion, ideal for sensitive applications |
Ready to enhance your metal melting or high-temperature processing with precision and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction furnaces, designed for foundries and research laboratories seeking efficient, contamination-free heating solutions. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for melting, sintering, or annealing metals and ceramics. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can power your productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















